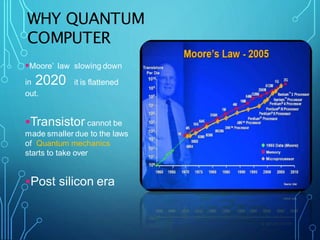
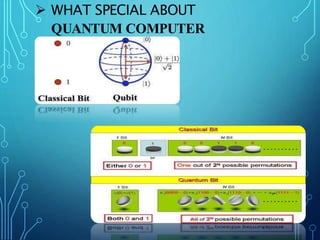
The document discusses quantum computing, detailing its history, fundamental principles, and unique features such as superposition, entanglement, and decoherence. It outlines the advantages of quantum computers, including faster computations and their effectiveness for simulations and medical applications, while also noting challenges like the need for very low operating temperatures and high error rates. Conclusion emphasizes the transformative potential of quantum computing and the ongoing efforts by companies like Google, IBM, and Microsoft to develop this technology further.