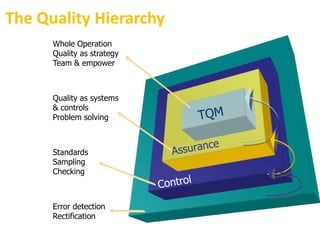
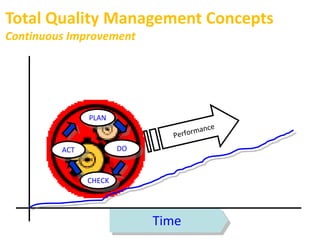
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a company-wide approach to quality that focuses on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee empowerment. Key aspects of TQM include establishing a commitment to quality at all levels of management, building quality into processes rather than inspecting outputs, and empowering employees. TQM aims to move organizations beyond traditional quality inspection and control methods toward more strategic, system-wide approaches to quality.