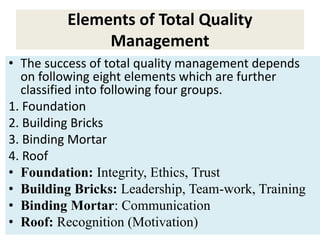
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management philosophy focused on meeting customer needs and organizational objectives through integrating all organizational functions. TQM involves everyone in the organization and focuses on continuously improving service quality. Key elements of TQM include management commitment, employee empowerment, fact-based decision making, and continuous improvement with a focus on customer satisfaction. Quality management tools like checklists, Pareto charts, histograms, and control charts are used to identify problems, prioritize issues, and track quality improvements.