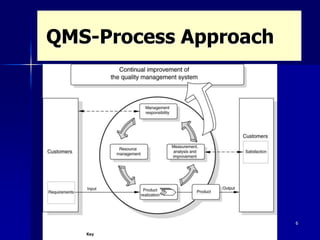
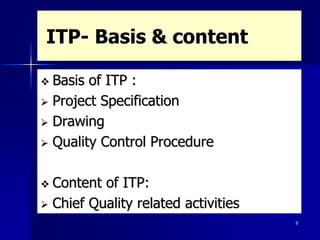
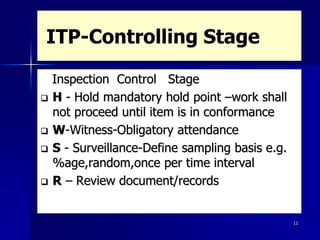
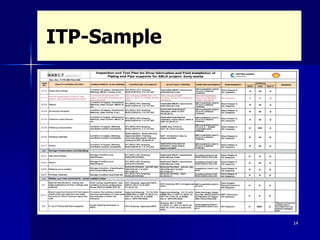
This document discusses key aspects of a quality management system used by Black Cat Engineering & Construction Company. It defines key terms like quality, quality control, quality assurance, and a quality management system. It describes the quality policy, various quality documentation like procedures, inspection and test plans, and records. It also discusses quality principles, importance of quality records, non-conformities, corrective and preventive actions, cost of poor quality, satisfying customers, and communicating quality requirements. The document emphasizes the importance of training, calibration of measuring equipment, and involvement of people in the quality system.