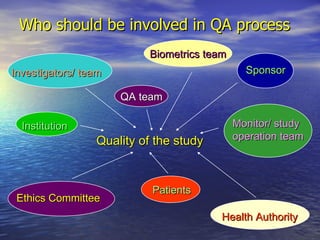
Quality assurance is the responsibility of the sponsor to ensure clinical trials are conducted properly according to regulations. It involves implementing quality control systems and allowing audits and inspections. Audits independently check that the study, data, patient safety, and regulatory compliance are accurate. Inspections allow regulatory authorities to review documents, facilities, and records. Proper preparation is key, such as having all required documents organized and understanding the protocol. Mistakes are common but can be prevented by understanding good clinical practice principles and having open communication.