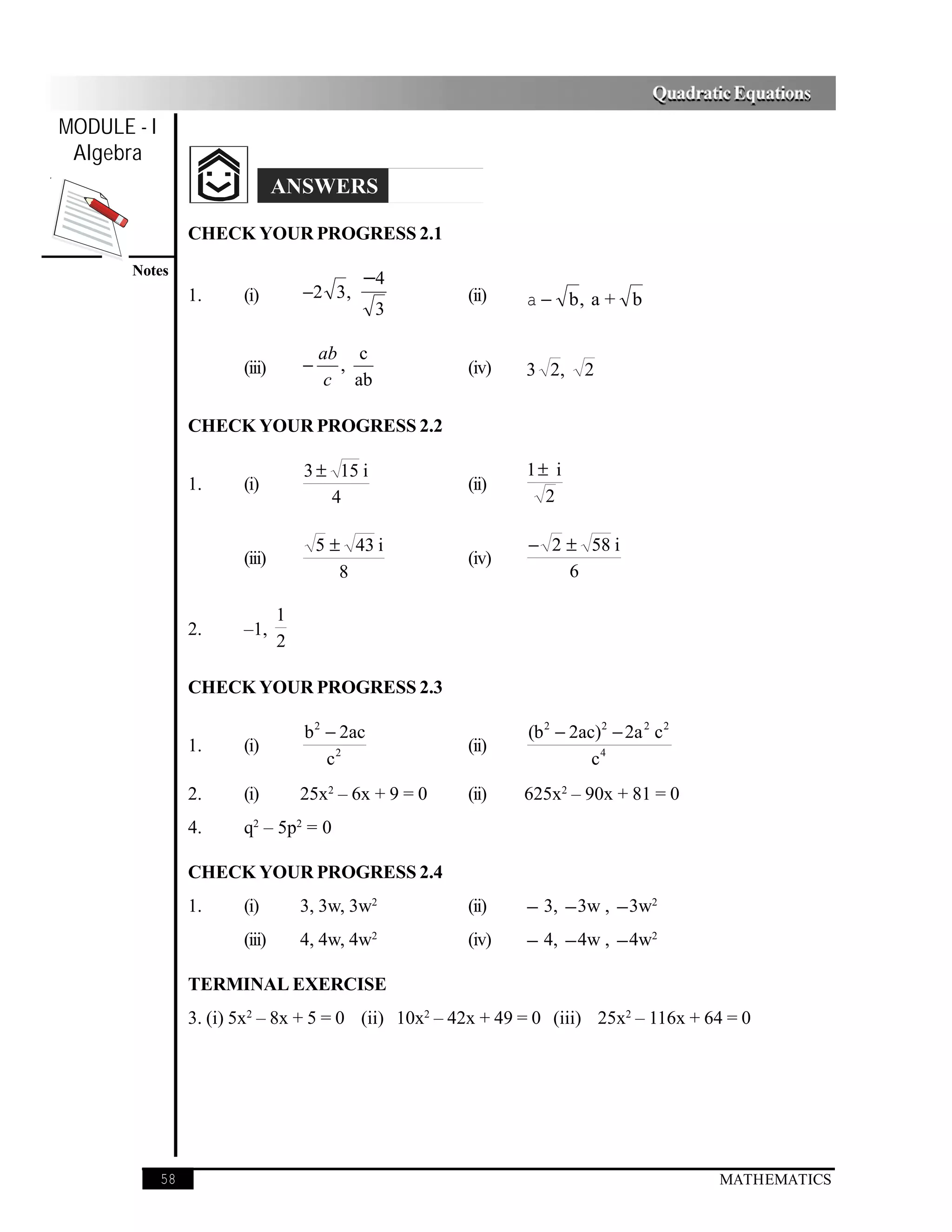
This document discusses solving quadratic equations. It begins by defining quadratic equations as equations of the second degree in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. It then discusses:
- The roots or solutions of a quadratic equation are the values that make the equation equal to 0 when substituted for the variable.
- Quadratic equations can be solved by factorization, splitting the middle term into two factors and setting each factor equal to 0 to find the roots.
- Examples are provided to demonstrate solving quadratic equations by factorization, finding the two roots.
- A more general quadratic equation with parameters a, b is also factorized to find its two equal roots.







![Quadratic Equations
Quadratic Equations
MODULE - I
∴
constant term c
Product of the roots = coefficient of x 2 = a ...(iv) Algebra
(iii) and (iv) are the required relationships between roots and coefficients of a given quadratic
equation. These relationships helps to find out a quadratic equation when two roots are
given.
Notes
Example 2.8 If, , are the roots of the equation 3x2 – 5x + 9 = 0 find the value of:
1 1
(a) 2 + 2 (b) + 2
2
Solution: (a) It is given that , are the roots of the quadratic equation 3x2 – 5x +9 = 0.
5
∴ + = ... (i)
3
9
and = =3 ... (ii)
3
2 + 2 = ( + ) − 2
2
Now,
2
5
= − 2.3 [By (i) and (ii)]
3
29
=−
9
29
∴ The required value is −
9
1 1 2 +2
(b) Now, + 2 =
2 2 2
− 29
= 9 [By (i) and (ii)]
9
29
=−
81
MATHEMATICS 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quadraticequations-110625043937-phpapp01/75/Quadratic-equations-9-2048.jpg)
![Quadratic Equations
MODULE - I Example 2.9 If , are the roots of the equation 3y2 + 4y + 1 = 0, form a quadratic
Algebra
equation whose roots are 2, 2
Solution: It is given that , are two roots of the quadratic equation 3y2 + 4y + 1 = 0.
∴ Sum of the roots
Notes
coefficient of y
i.e., + = − coefficient of y 2
4
=− ... (i)
3
cons tan t term
Product of the roots i.e., = coefficient of y 2
1
= ... (ii)
3
Now, 2 + 2 = ( + )2 – 2
2
4 1
= − − 2. [ By (i) and (ii)]
3 3
16 2
= −
9 3
10
=
9
1
and 2 2 = ( )2 = [By (i) ]
9
∴ The required quadratic equation is y2 – ( 2 + 2)y + 2 2 = 0
10 1
or, y2 − y+ =0
9 9
or, 9y2 – 10y + 1 = 0
Example 2.10 If one root of the equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 be the square of
the other, prove that b3 + ac2 + a2c = 3abc
Solution: Let , 2 be two roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0.
b
∴ + 2= − ... (i)
a
48 MATHEMATICS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quadraticequations-110625043937-phpapp01/75/Quadratic-equations-10-2048.jpg)
![Quadratic Equations
Quadratic Equations
MODULE - I
and . 2 =
c Algebra
a
c
i.e., 3= . ... (ii)
a
Notes
From (i) we have
b
( + 1) = −
a
3
b b3
or, { ( + 1)} 3
= − = − 3
a a
b3
or, 3 ( 3 + 3 2 + 3 +1) = −
a3
c c b 3
or, + 3 − +1 = − b3 ... [ By (i) and (ii)]
a a a a
c2 3 bc c b3
or, – + =– 3
a2 a2 a a
or, ac2 – 3abc + a2c = − b3
or, b3 + ac2 + a2c = 3abc
which is the required result.
Example 2.11 Find the condition that the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are in the
ratio m : n
Solution: Let m and n be the roots of the equation ax2 +bx + c = 0
b
Now, m + n = – ... (i)
a
c
and mn 2 = ... (ii)
a
b
From (i) we have, (m + n ) = –
a
b2
or, (m + n)2 =
2
a2
MATHEMATICS 49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quadraticequations-110625043937-phpapp01/75/Quadratic-equations-11-2048.jpg)
![Quadratic Equations
MODULE - I c b2
Algebra or,
a
(m + n)2 = mn 2
a
[ By (ii)]
or, ac (m+n)2 = mn b2
which is the required condition
Notes
CHECK YOUR PROGRESS 2.3
1. If , are the roots of the equation ay2 + by + c = 0 then find the value of :
1 1 1 1
(i) + 2 (ii) + 4
2
4
2. If , are the roots of the equation 5x2 – 6x + 3 = 0, form a quadratic equation
whose roots are:
(i) 2, 2 (ii) 3 , 3
3. If the roots of the equation ay2 + by + c = 0 be in the ratio 3:4, prove that
12b2 = 49 ac
4. Find the condition that one root of the quadratic equation px2 – qx + p = 0
may be 1 more than the other.
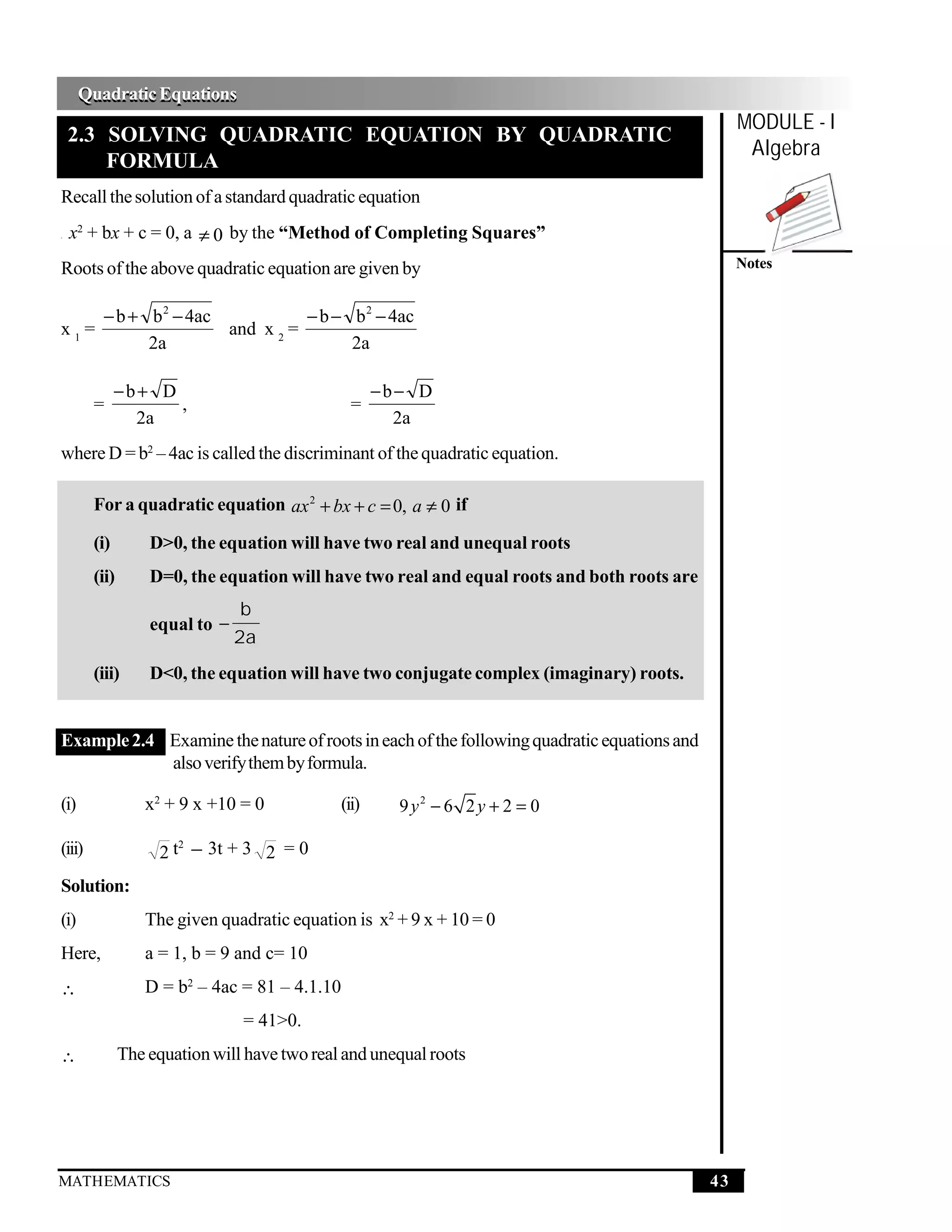
2.5 SOLUTION OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION WHEN D < 0
Let us consider the following quadratic equation:
(a) Solve for t :
t2 + 3t + 4 = 0
− 3 ± 9 −16 −3 ± −7
∴ t= =
2 2
Here, D= –7 < 0
−3 + −7 −3− − 7
∴ The roots are and
2 2
− 3 + 7 i −3 − 7 i
or, ,
2 2
Thus, the roots are complex and conjugate.
50 MATHEMATICS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quadraticequations-110625043937-phpapp01/75/Quadratic-equations-12-2048.jpg)



![Quadratic Equations
MODULE - I
Algebra ∴ Roots are − 1,
1
−
3i 1
and +
3i
which can also be written as − 1 , − w and − w2
2 2 2 2
Therefore, cube roots of − 1 are − 1 , − w and − w2
In general, roots of any cubic equation of the form x 3 = ± a3 would be
Notes
± a , ± aw and ± aw2
Example 2.12 If 1, w and w² are cube roots of unity, prove that
(a) 1 + w2 + w7 = 0
(b) (1 − w + w2) (1 + w – w2) = 4
(c) (1 + w)3 − (1 + w2)3 = 0
(d) (1 − w + w2)3 = − 8 and (1 + w − w2)3 = − 8
Solution:
(a) 1 + w2 + w7 = 0
L.H.S = 1 + w2 + (w3)2. w
= 1 + w2 + w [ since w3 =1]
=0 [ since 1+ w + w2 = 0]
= R.H.S
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
(b) (1 − w + w2) (1 + w – w2) = 4
L.H.S = (1 − w + w2) (1 + w – w2)
= (1 + w2 − w) (1 + w – w2)
(since 1 + w2 = − w and 1 + w = − w2)
= ( − w − w) ( − w2 –w2)
= ( − 2w) ( − 2w2)
= 4w3
= 4.1 = 4 =R.H.S
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
54 MATHEMATICS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quadraticequations-110625043937-phpapp01/75/Quadratic-equations-16-2048.jpg)