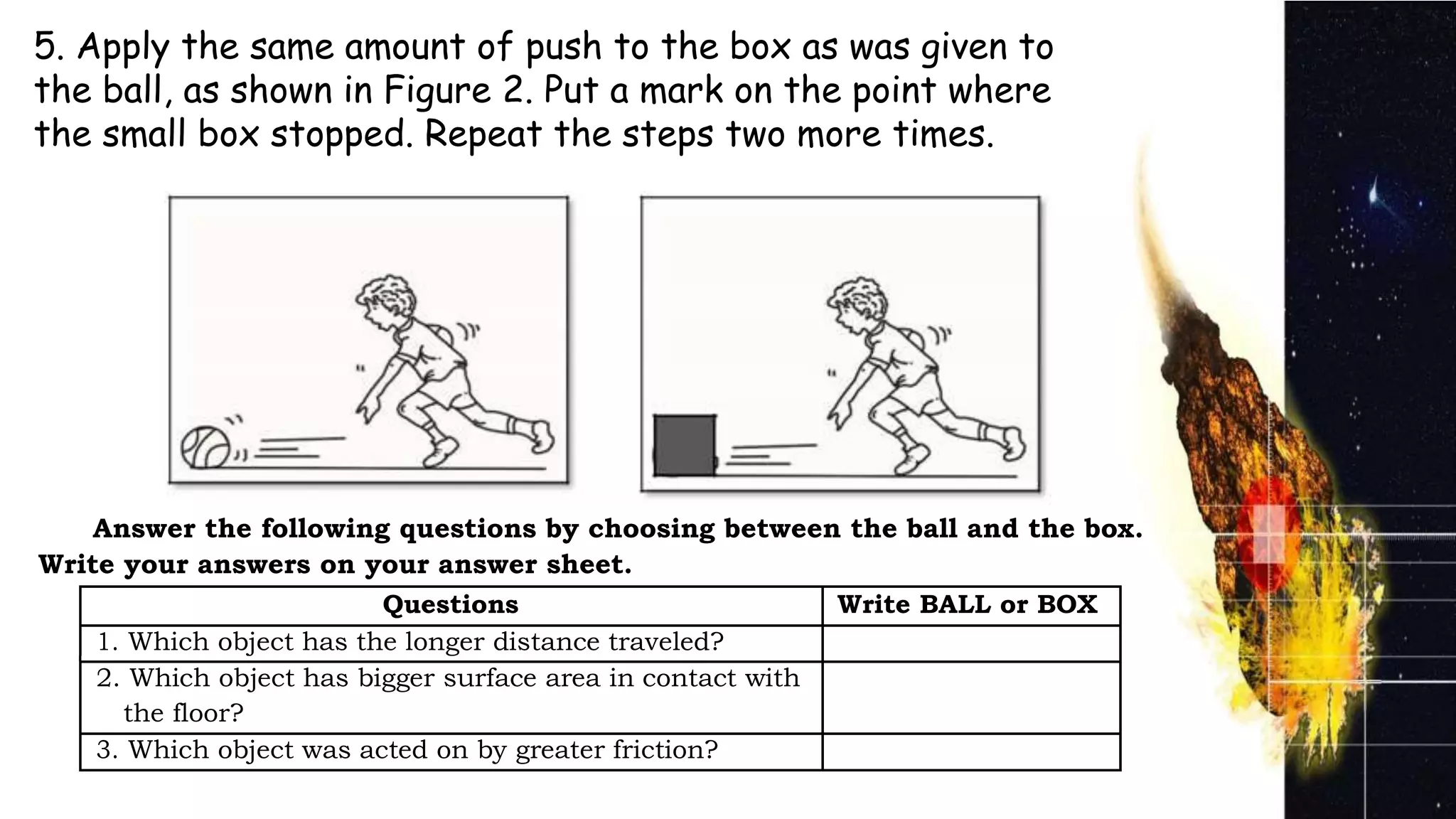
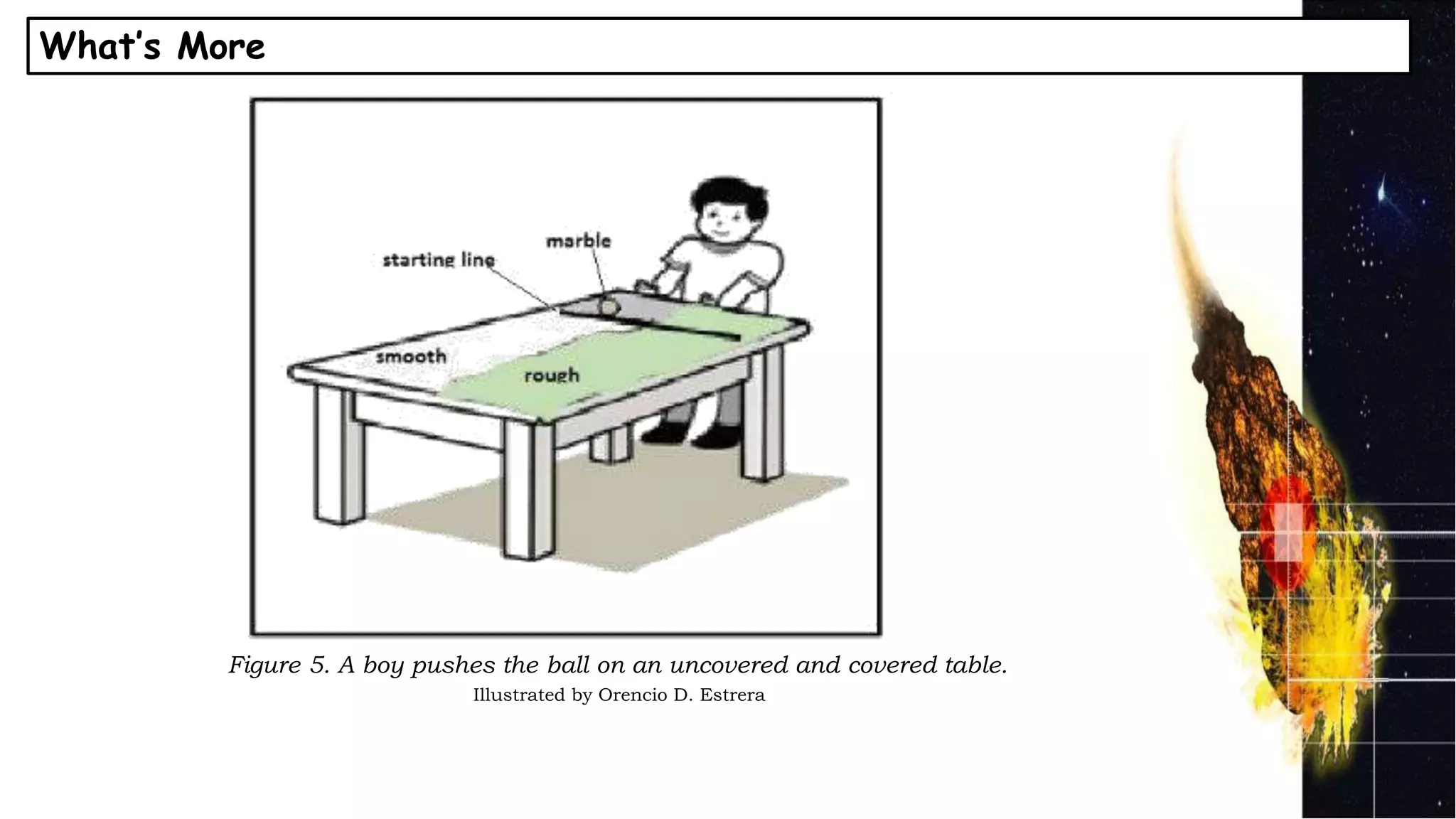
Friction affects the movement of objects in several ways:
1) Friction slows moving objects down and can cause them to stop by acting in the opposite direction of motion. Greater friction leads to slower movement.
2) Friction is greater on surfaces with larger contact areas and rougher textures, causing objects to slow down more quickly. Lesser friction occurs on surfaces with smaller contact areas and smoother textures, allowing for faster movement.
3) Air resistance, a type of friction, also slows down falling objects, with greater air resistance occurring for objects with larger surface areas exposed to the air.