The document discusses topics related to security and graphics programming in Python. It covers encryption/decryption algorithms, hash functions, classical ciphers, turtle graphics, and Tkinter GUI programming. Specifically, it provides details on encryption/decryption processes, how hash functions work to produce fixed-length strings from inputs, different cipher types (block/stream), and how to perform basic drawing and create GUI windows using the Turtle and Tkinter modules in Python.





![hashlib.new(name[, data]):
Is a generic constructor that takes the string name of the desired
algorithm as its first parameter.
The Use of new() Method
Example:
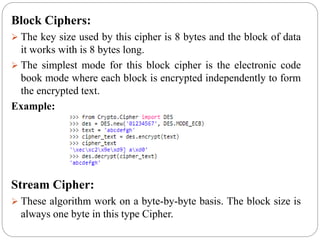
Classical Cipher:
Encryption Algorithm take some text as input & produce Cipher text
using a variable key.
Types of Cipher:
There are two types of ciphers: one is block cipher and other is stream
Cipher. Block ciphers work on blocks of a fixed size (8 or 16 bytes).
Stream ciphers work byte-by-byte or character by character.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-180521173028/85/Python-ppt-6-320.jpg)