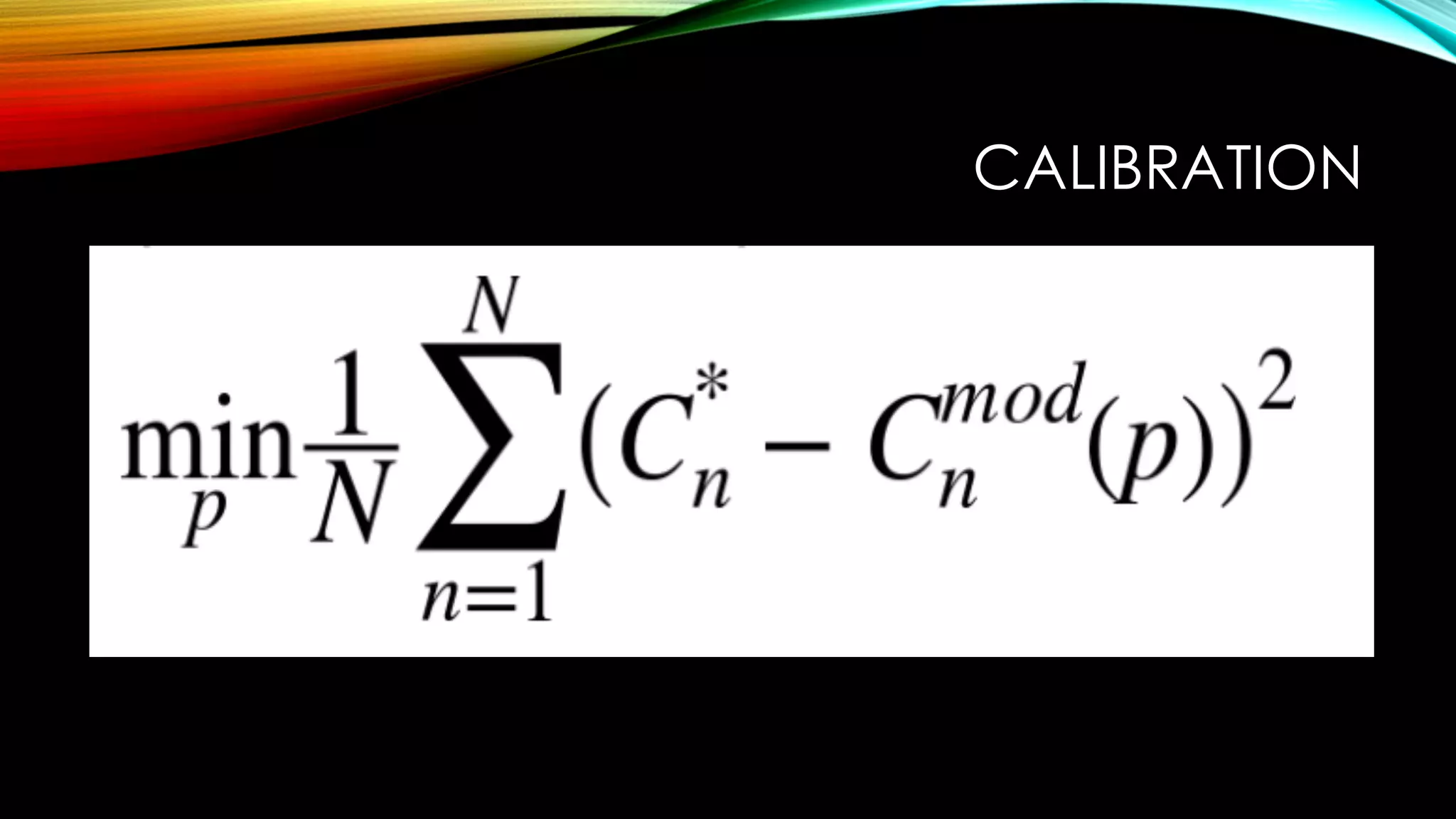Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




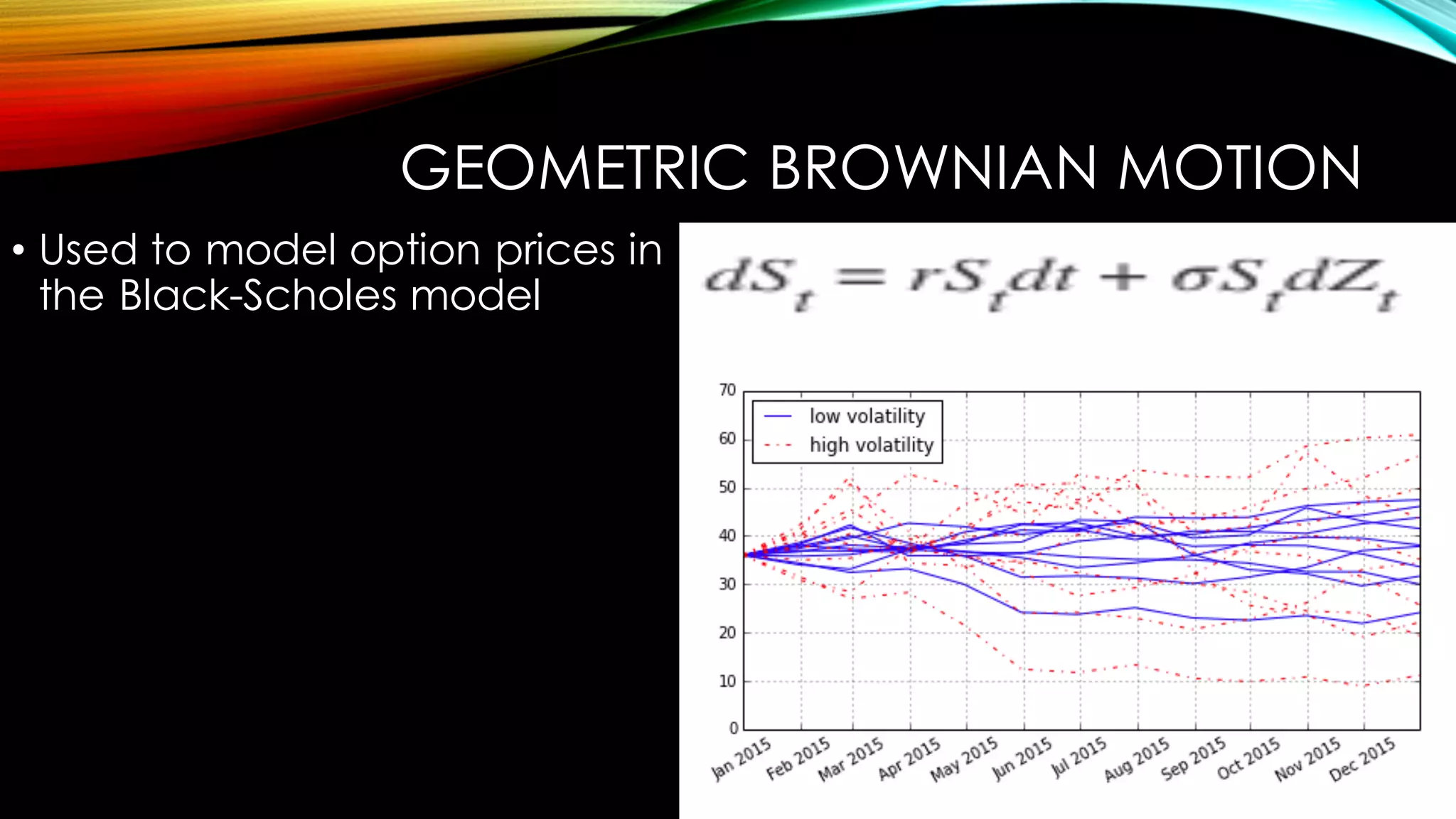
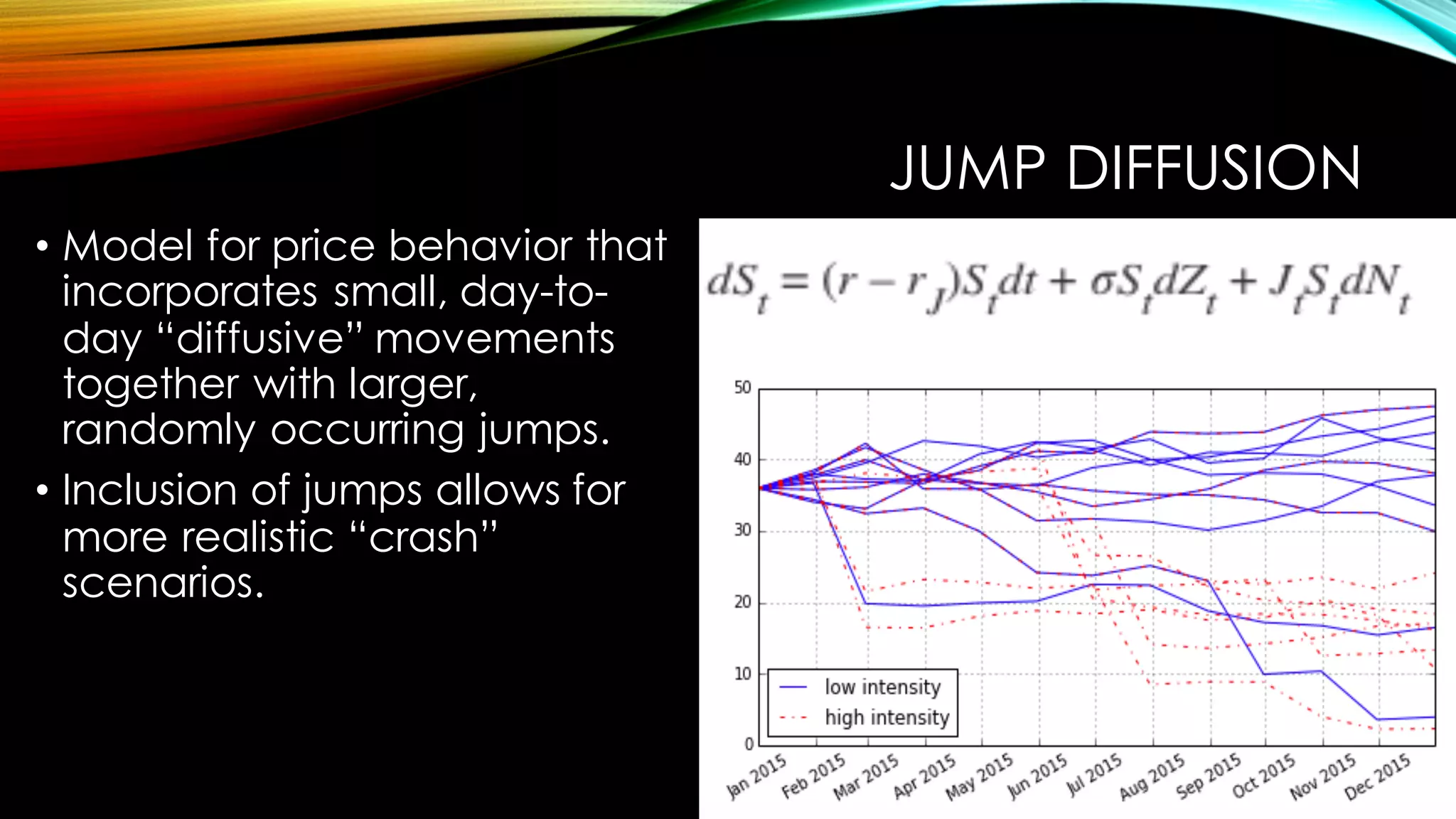
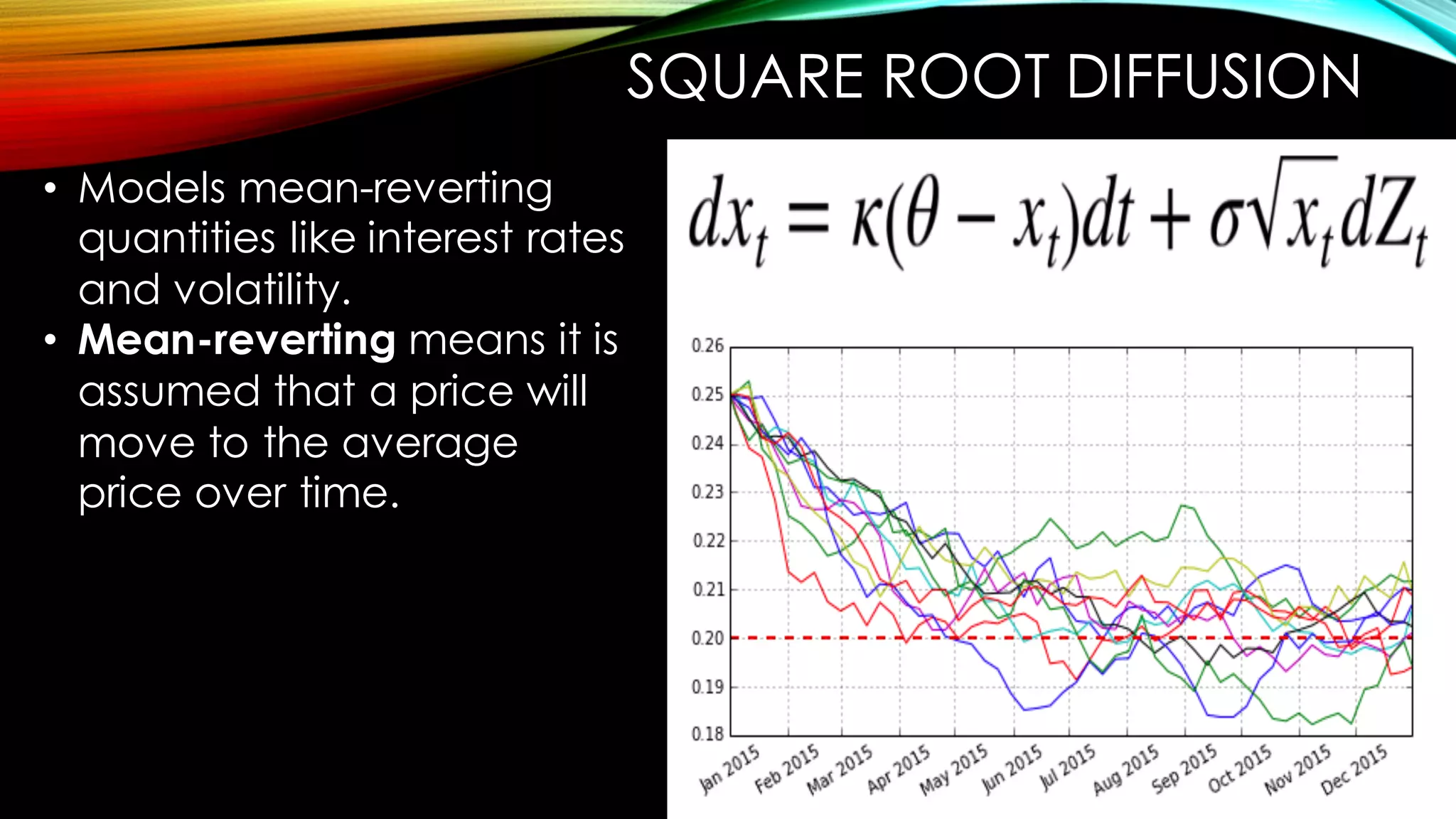
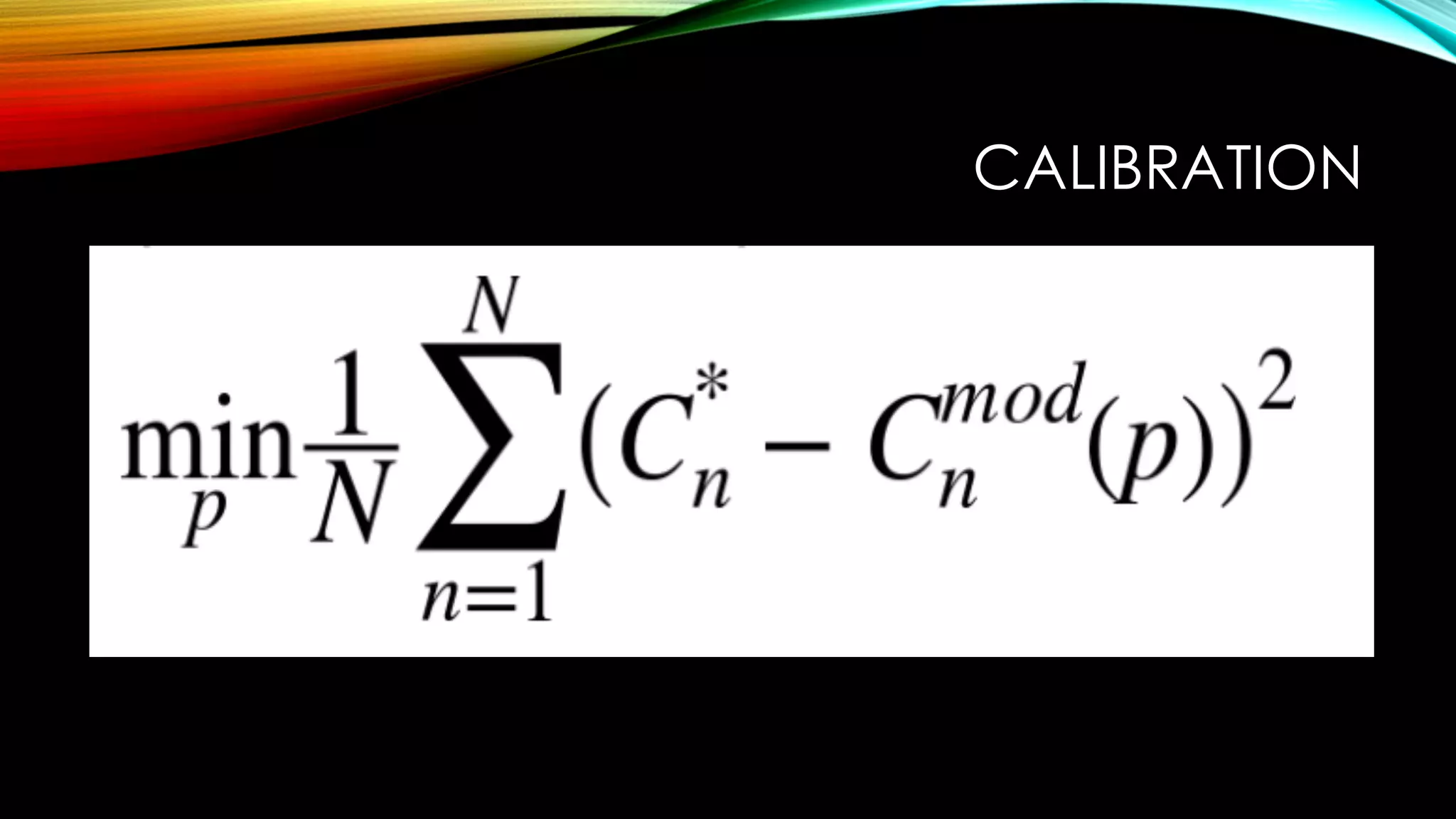
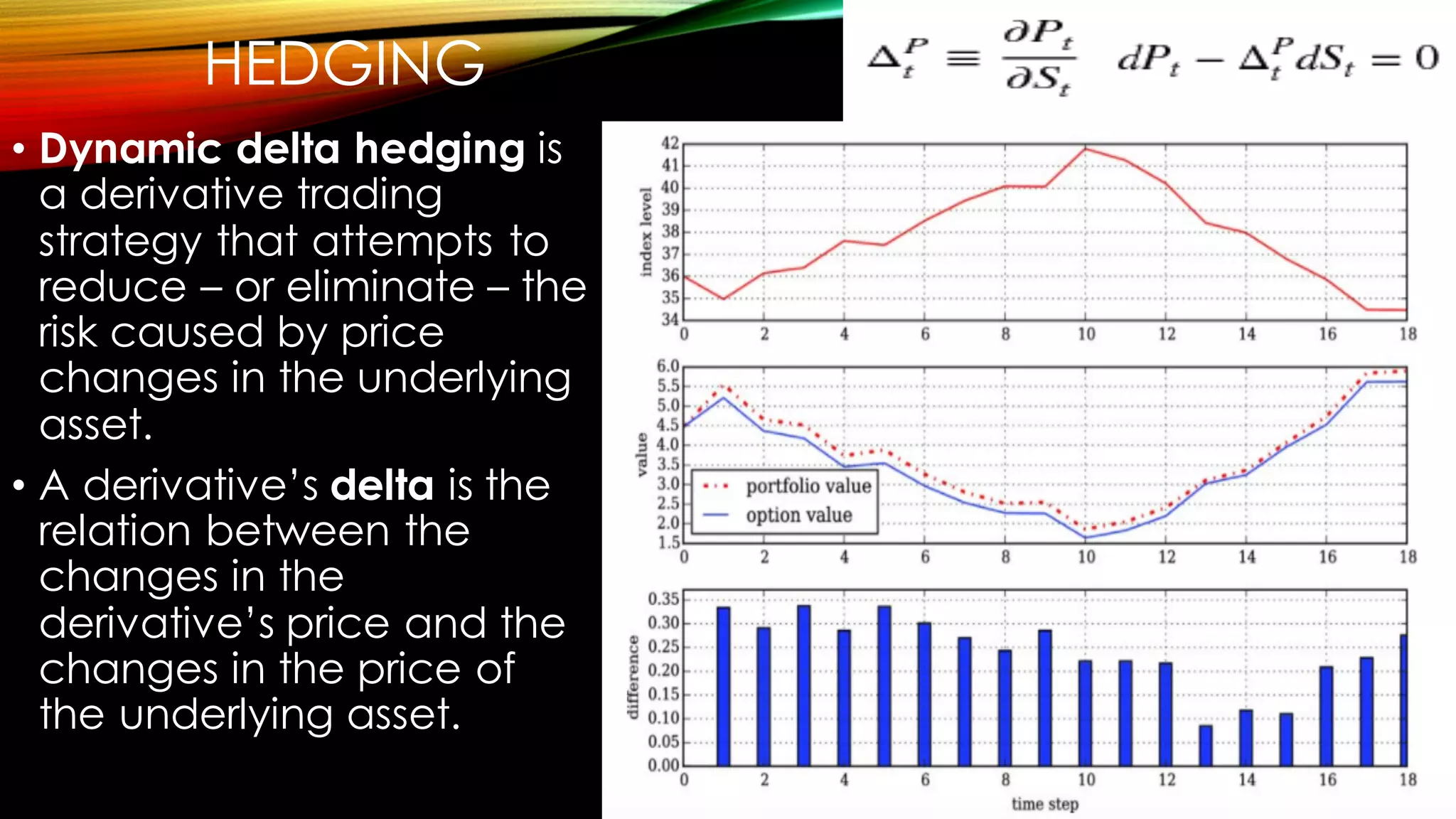

This document discusses using the Python library DX for modeling complex derivatives and portfolios. It describes simulation classes for modeling relevant risk factors like geometric Brownian motion, jump diffusion, and square root diffusion. It also mentions calibration and hedging strategies like dynamic delta hedging to reduce risk from changes in the underlying asset's price.