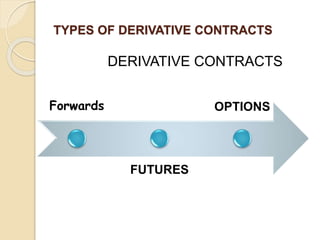
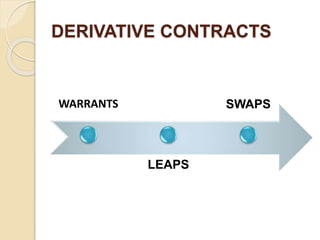
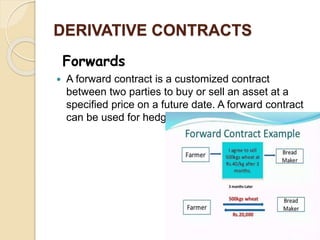
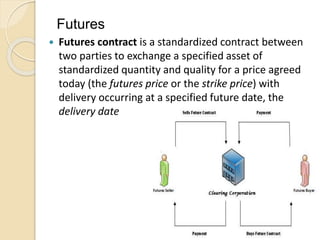
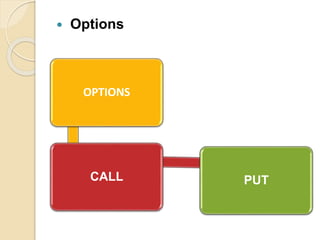
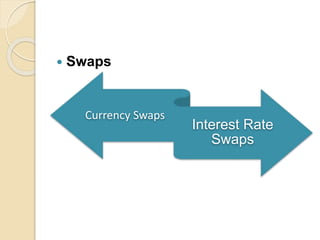
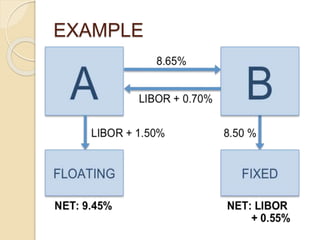
This document defines derivatives and describes different types of derivative contracts. It states that a derivative is a contract whose price is dependent on an underlying asset such as a security, commodity, or index. It provides examples of derivative contracts including forwards, futures, options, warrants, LEAPS (long-term equity anticipation securities), and swaps. The document also discusses exchange-traded versus over-the-counter derivatives and describes participants in derivative markets such as hedgers, speculators, and arbitrageurs.