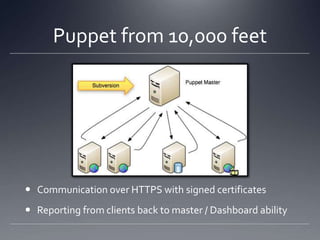
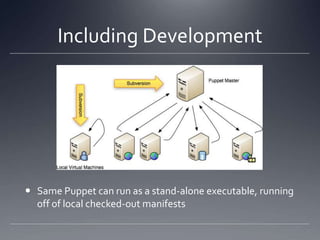
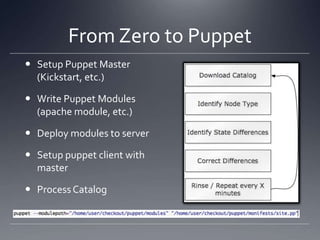
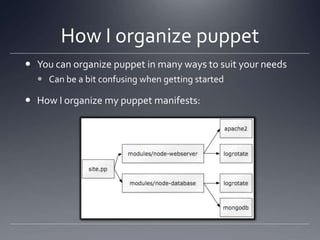
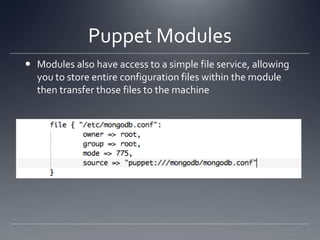
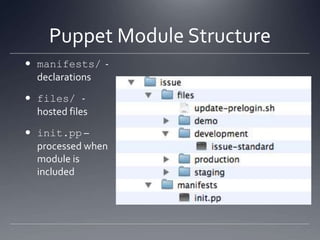
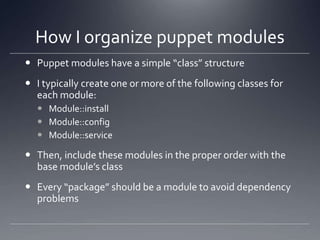
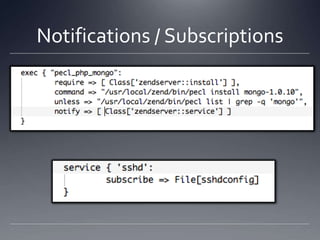
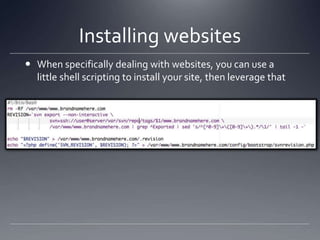
The document provides an overview of Puppet, a centralized and scalable configuration management tool for server deployment. It explains key concepts such as nodes, modules, and resources, along with practical steps for setting up Puppet, managing configurations, and structuring manifest files. Additionally, it highlights security considerations with certificate management and offers resources for further learning.