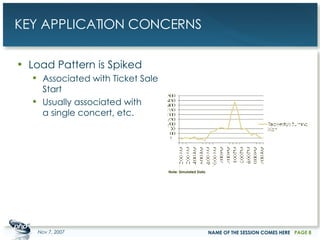
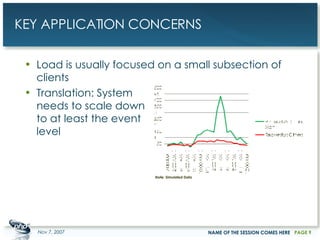
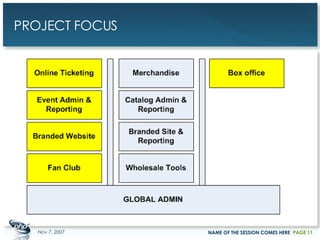
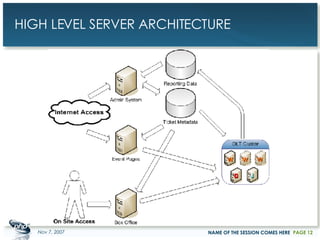
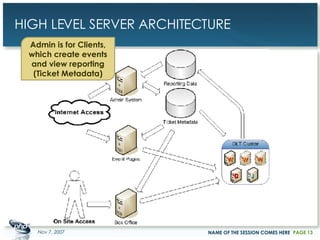
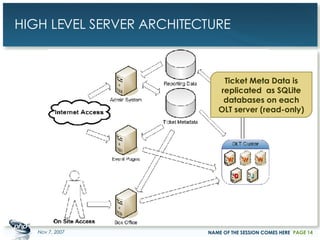
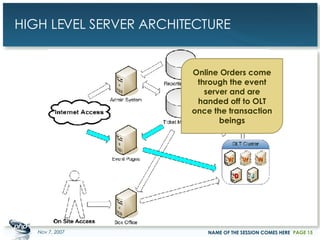
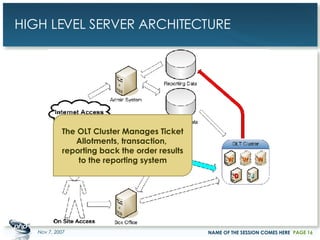
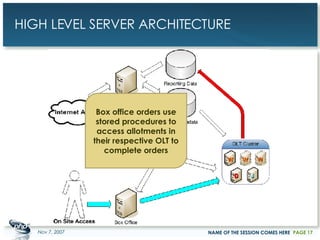
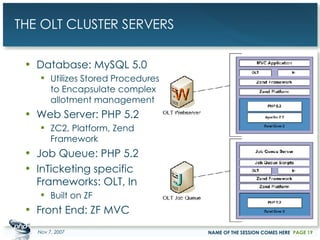
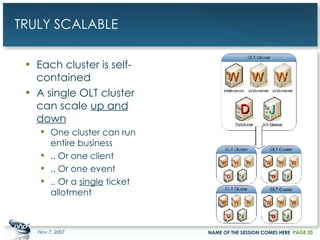
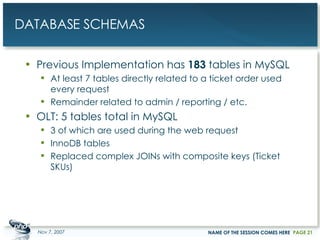
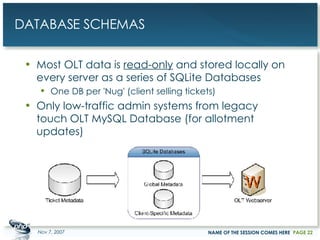
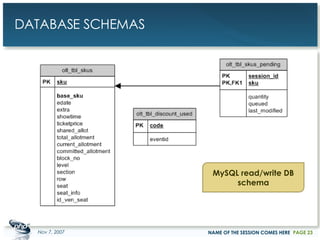
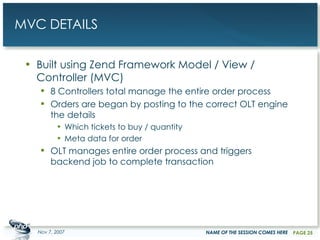
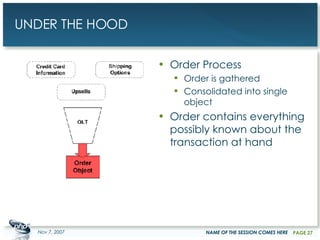
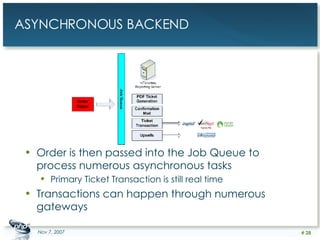
The document outlines a case study on enterprise PHP applications, focusing on a ticketing system developed by John Coggeshall and Marc Urbaitel. It discusses the challenges faced in scaling the existing PHP/MySQL application and details the architectural solutions implemented to improve ticket transaction processing capabilities. Key improvements included a restructured online ticketing engine, enhanced database management, and a scalable cluster system to handle greater transaction volumes efficiently.