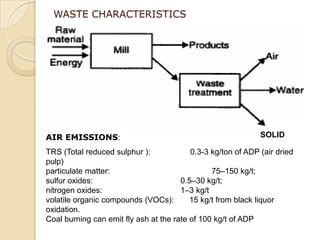
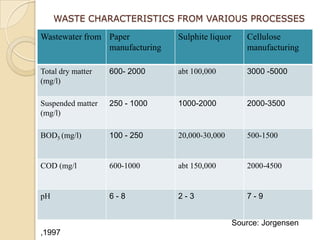
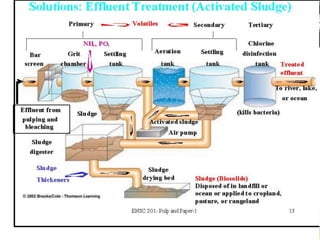
Pulp and paper mills produce large amounts of liquid and solid waste from their pulping and papermaking processes. Liquid waste is characterized by high levels of biochemical oxygen demand, suspended solids, and chemical oxygen demand. Solid waste includes treatment sludge and fly ash. Wastewater treatment involves neutralization, screening, sedimentation, and activated sludge or anaerobic fermentation to remove organic content. Sludge is dewatered and combusted. Alternative technologies also exist for sludge disposal and wastewater treatment.