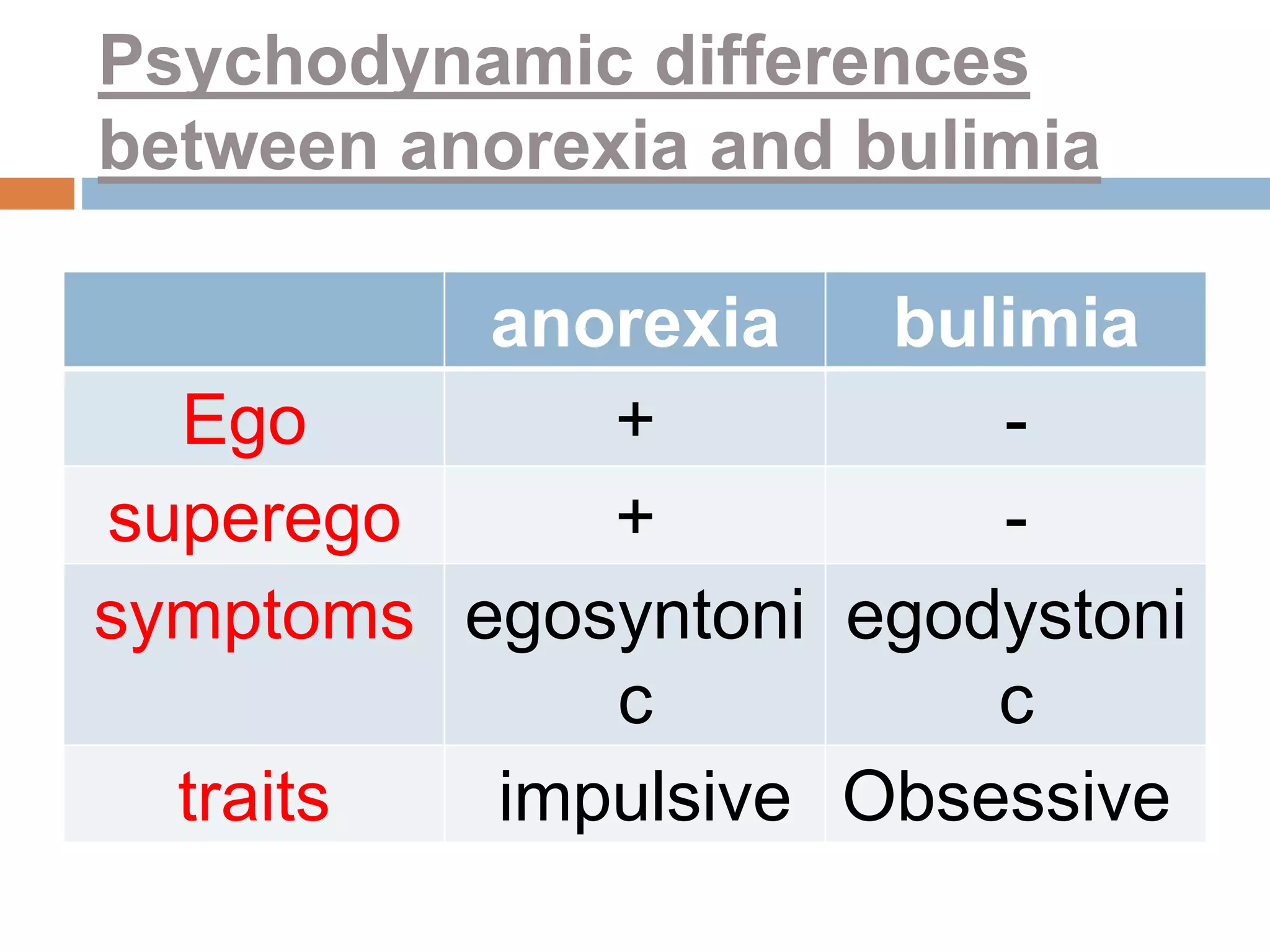
This document discusses the psychopathology of eating disorders. It defines eating disorders and outlines the DSM-5 classification system, which includes pica, rumination disorder, avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder. It then examines psychological theories including psychodynamic, cognitive, and behavioral theories. Key psychodynamic differences between anorexia and bulimia are presented. Cognitive theory focuses on irrational beliefs and schemas while behavioral theory explores conditioning and observational learning influences. Obesity is discussed as an abnormal eating behavior rather than a disorder.