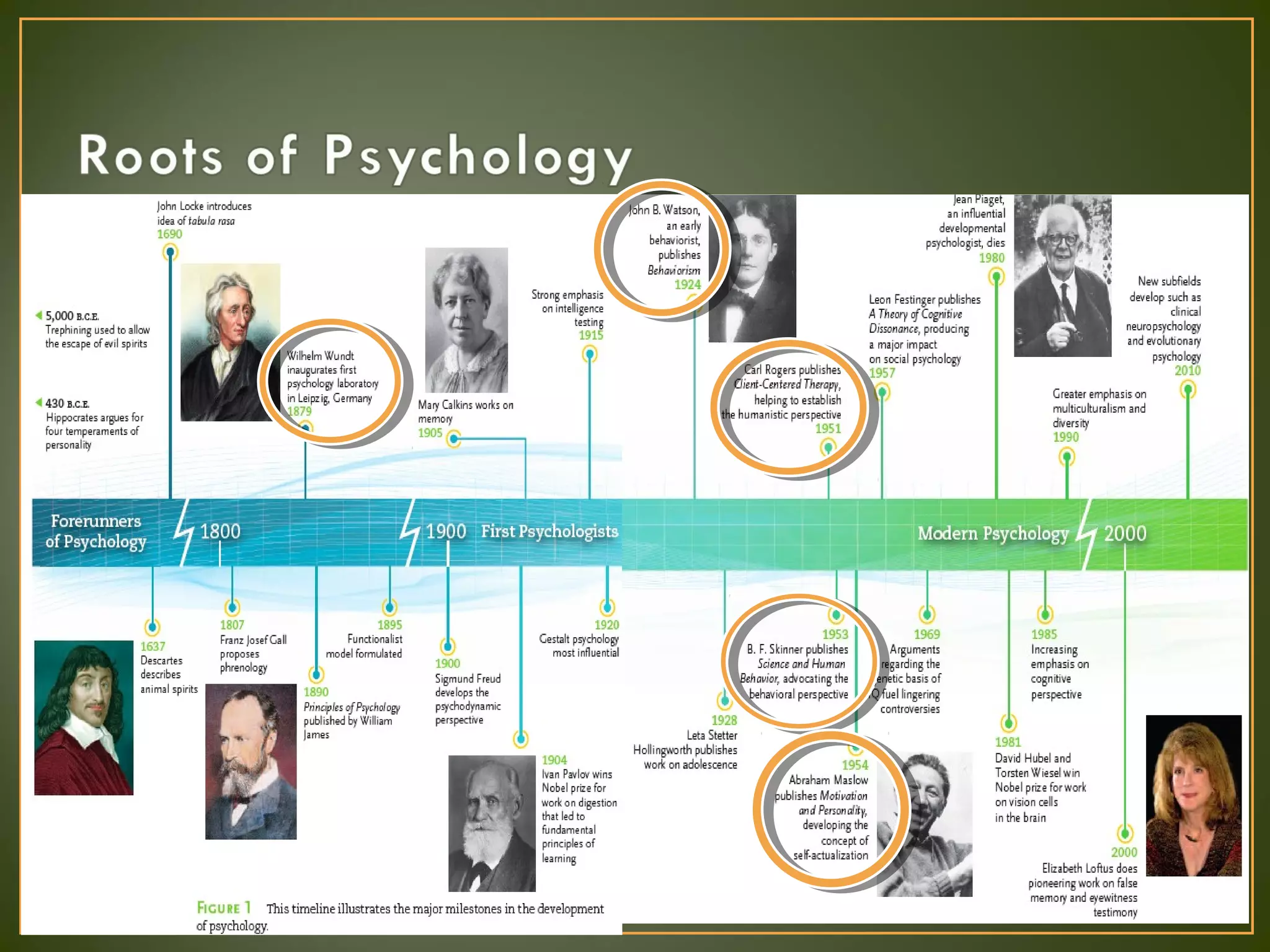
The document discusses the major psychological perspectives in psychology. It defines psychology as the scientific study of mental processes and behavior. It outlines five main perspectives: neuroscience which studies biological functioning and heredity; psychodynamic which focuses on unconscious drives and childhood experiences; behavioral which examines observable behavior and conditioning; cognitive which views people as information processors; and humanistic which emphasizes free will and self-actualization. Each perspective is described in one to two sentences with their key theorists and approaches.