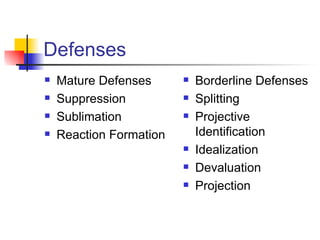
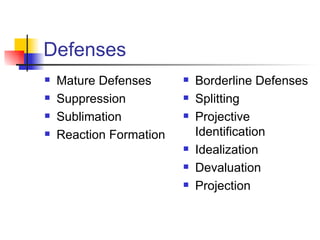
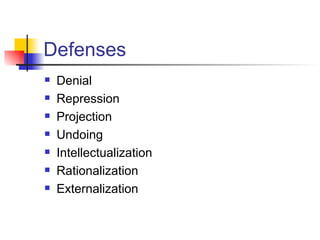
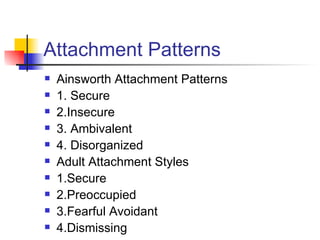
The document discusses psychodynamic formulation as a crucial tool for managing therapeutic alliances, highlighting various defenses such as mature and borderline defenses, and the importance of differential diagnosis and ego function assessment. It also emphasizes attachment patterns, including Ainsworth's categories, and the roles of transference and countertransference in therapy. Lastly, it outlines therapeutic strategies and prognosis factors that influence treatment outcomes.