Embed presentation
Download to read offline

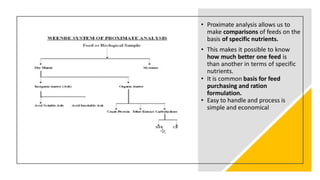

Proximate analysis determines the percentage of key nutrients like fat, carbohydrates, protein, moisture and ash in a feed. It was developed in 1865 and separates feed components into six fractions: moisture, ash, crude protein, ether extract, crude fiber, and nitrogen-free extract. It provides important information about a feed's ability to meet animal nutrient requirements and allows comparisons between feeds based on specific nutrients, making it useful for purchasing and ration formulation decisions.


