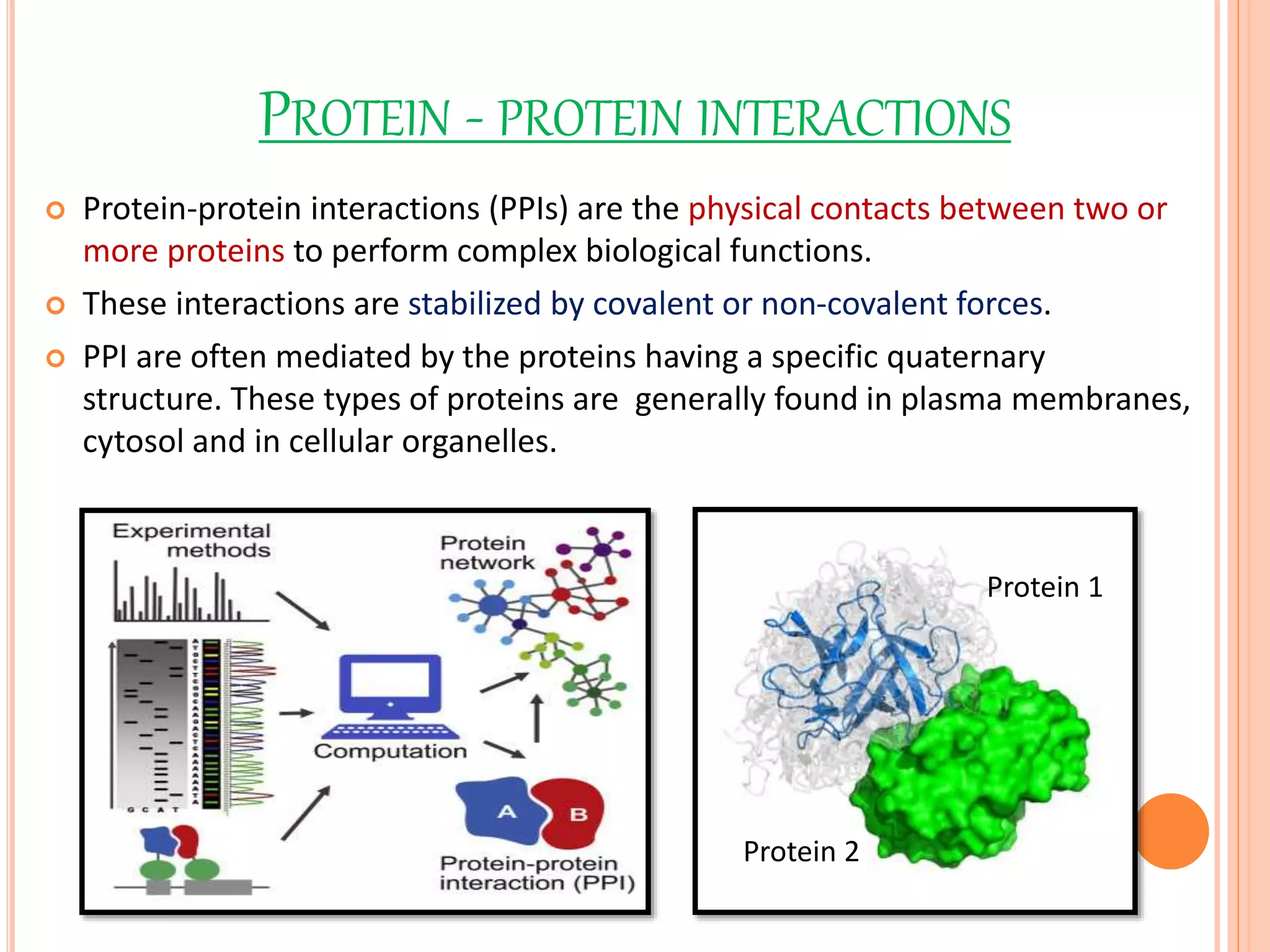
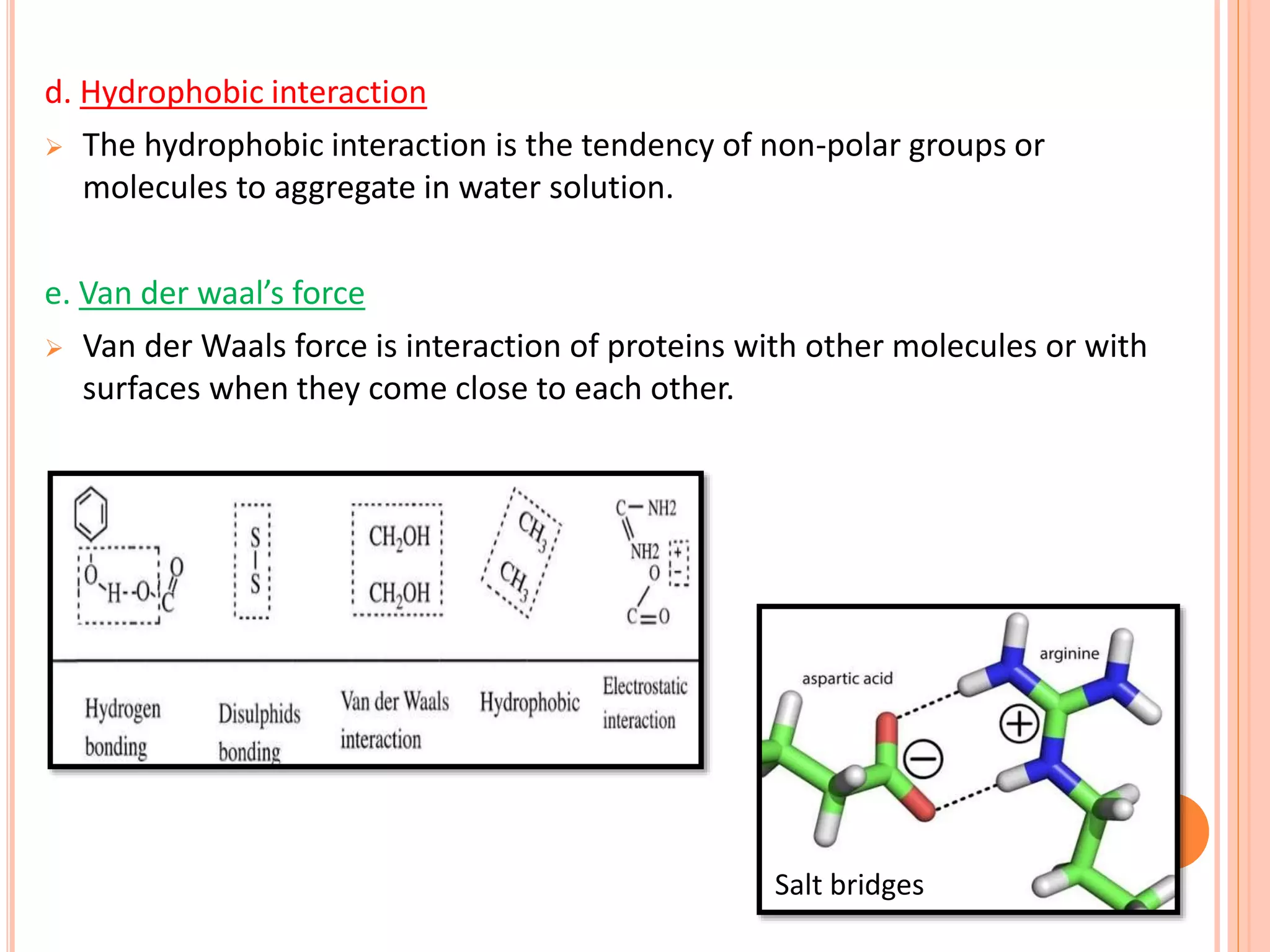
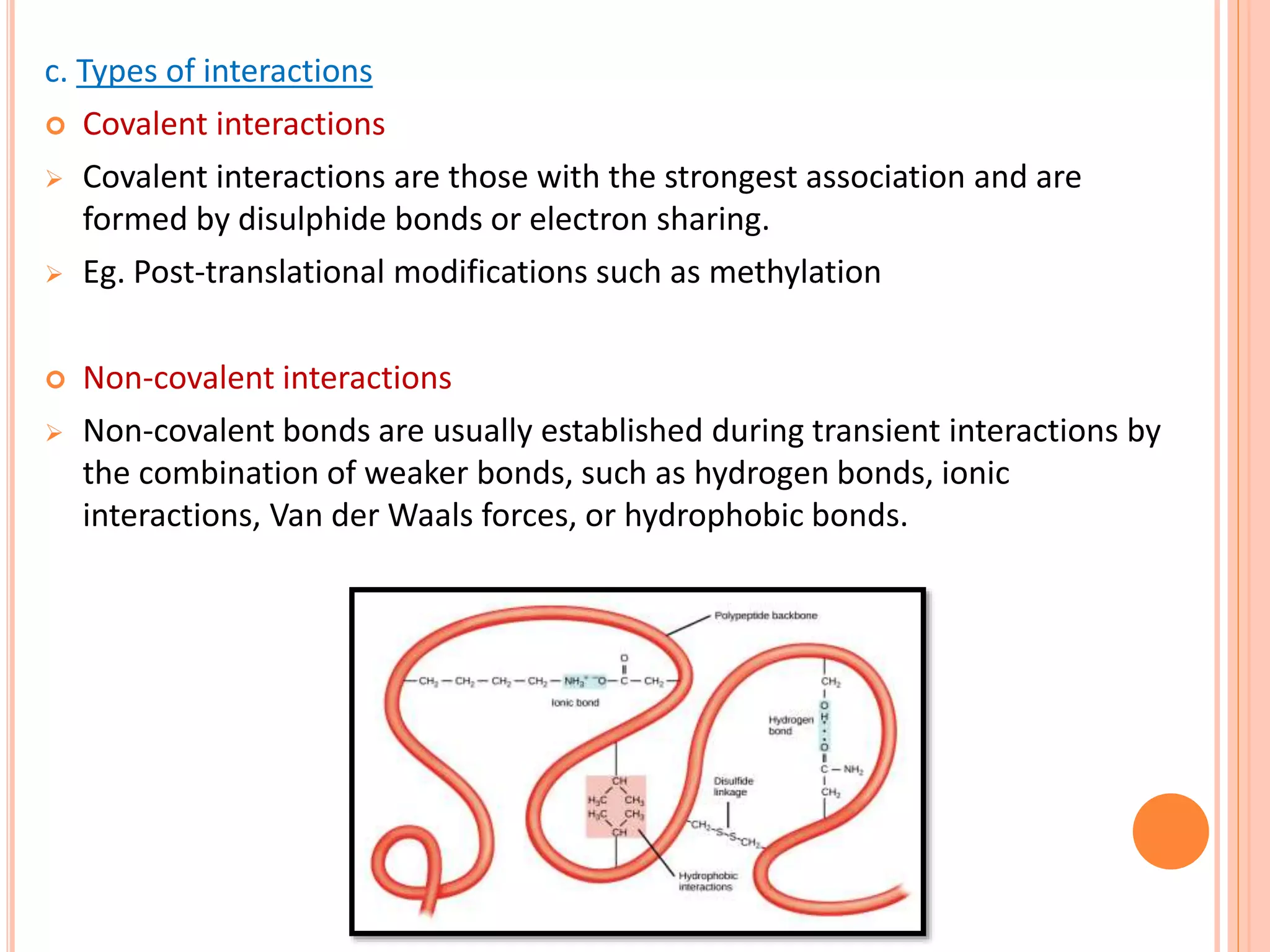
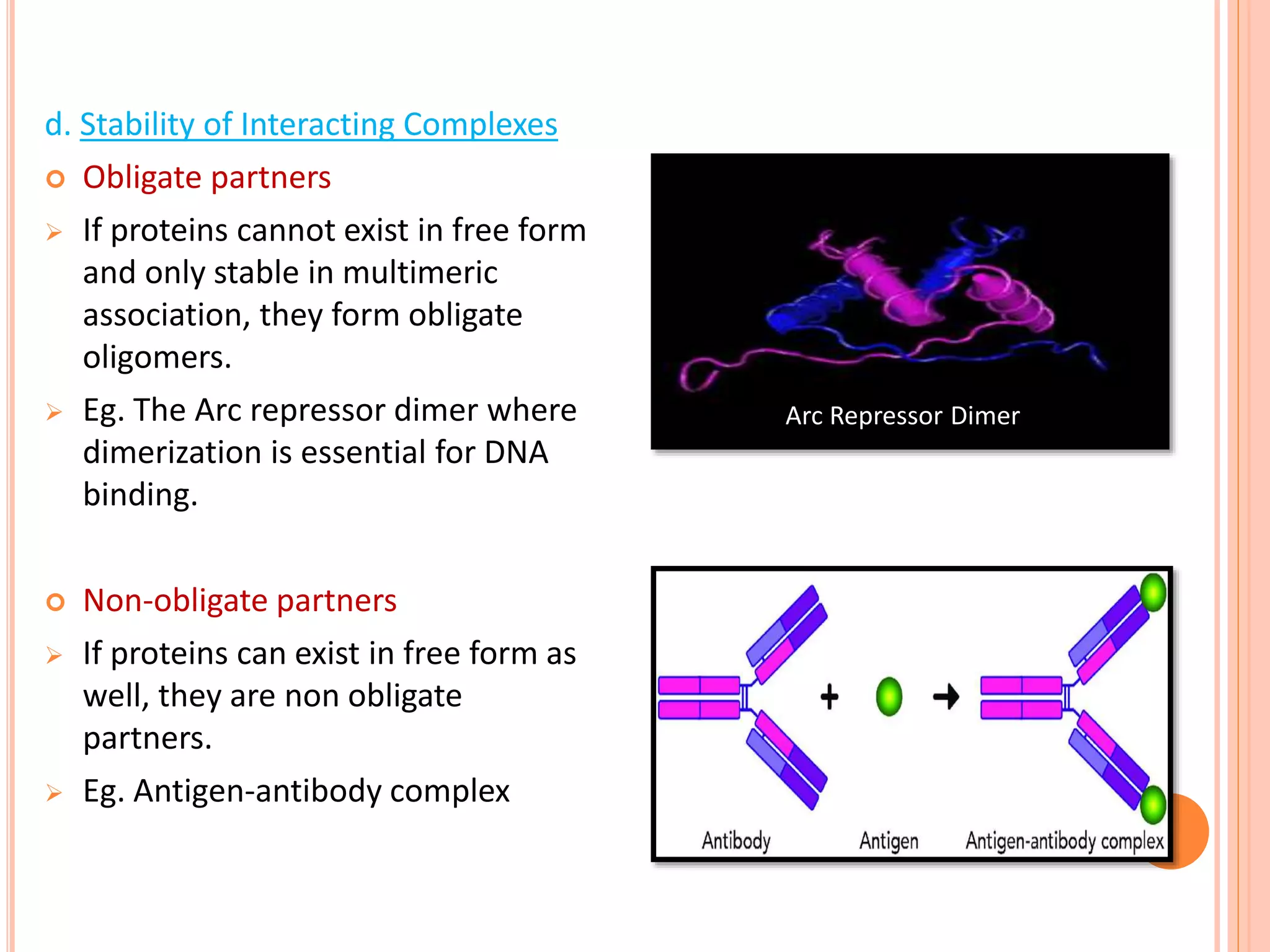
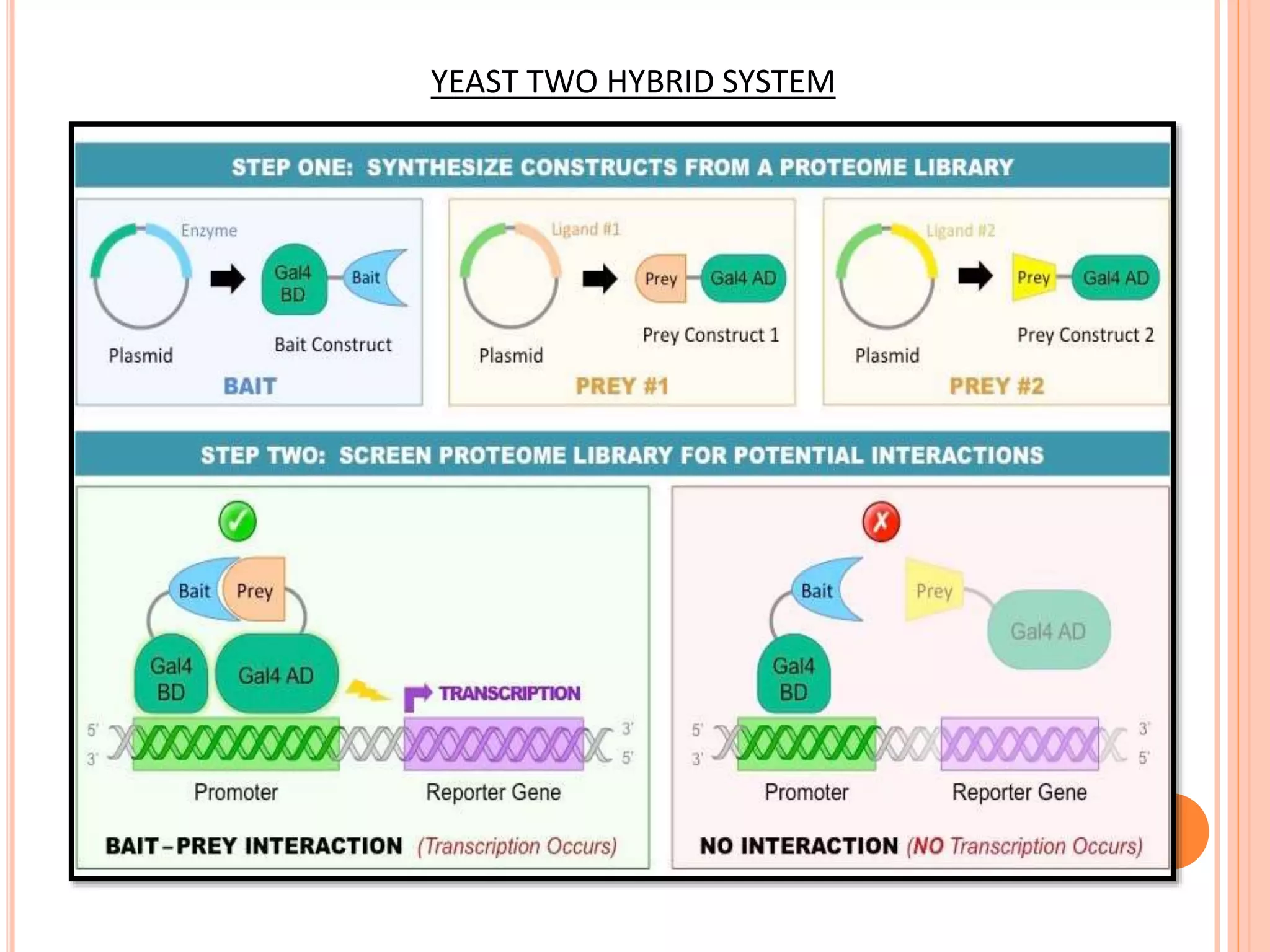
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts between two or more proteins that allow them to perform biological functions. PPIs are stabilized by covalent or non-covalent forces and often involve proteins with specific quaternary structures. Examples of PPIs include muscle contraction mediated by actin, myosin, and other proteins, as well as biosignaling pathways. PPIs can be studied experimentally using methods like yeast two-hybrid systems, fluorescence resonance energy transfer, and affinity chromatography, or computationally using protein interaction databases. Understanding PPIs is important for developing new drugs that target protein interactions.