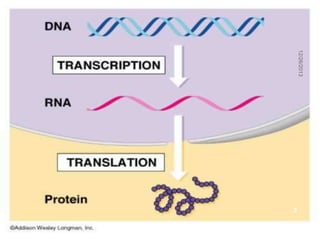
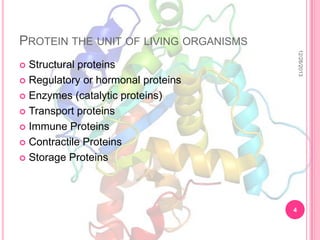
Proteins are one of the basic building blocks of the human body and are made through the process of translation. There are many types of proteins that serve different functions, including structural, regulatory, enzymatic, transport, immune, contractile, and storage proteins. Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body, and deficiencies can lead to health issues like muscle wasting, fatigue, and weakened immunity.