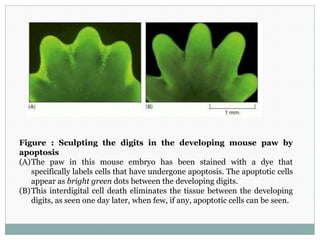
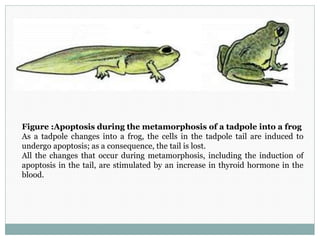
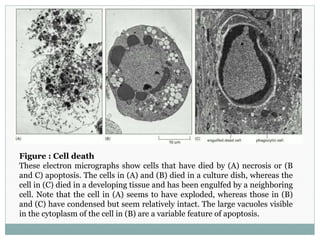
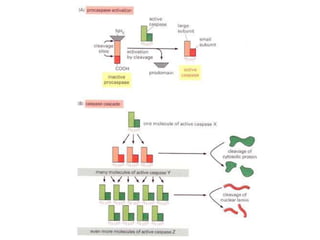
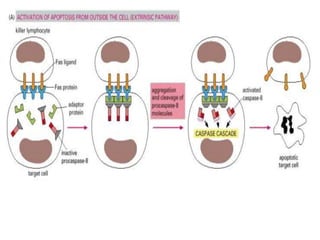
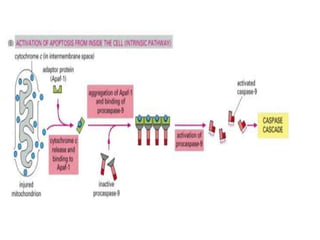
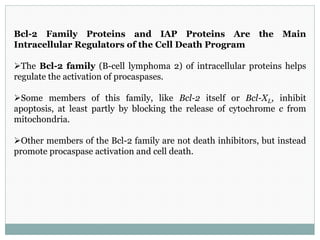
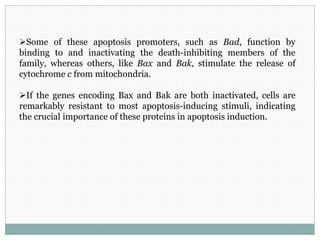
Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is a tightly regulated process where cells commit suicide through an intracellular death program. This process is important for sculpting tissues during development and maintaining cell numbers in adult tissues. Apoptosis is mediated by caspases, a family of proteases that activate in a cascade to dismantle the cell in a controlled manner. The caspase cascade is triggered by adaptor proteins that aggregate initiator procaspases. Mitochondria can also induce apoptosis by releasing proteins like cytochrome c that activate caspases. The Bcl-2 family and IAP proteins are key intracellular regulators that can both promote and inhibit apoptosis.