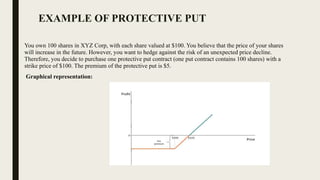
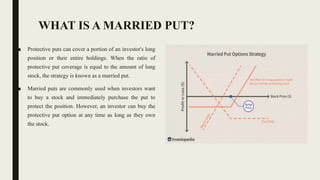
A protective put is a risk-management strategy where investors buy a put option to hedge against potential losses while remaining bullish on a stock. The protective put sets a floor price to limit losses, allowing the investor to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price before expiration. This strategy can involve varying strike prices and premiums, and it can be fully or partially utilized alongside a long position in a stock.