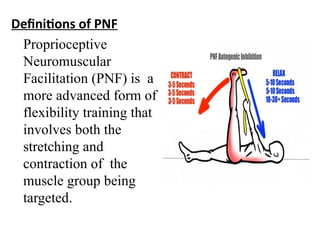
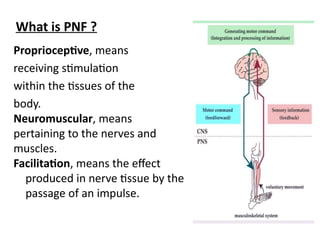
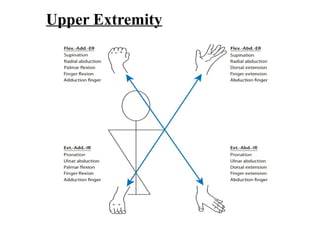
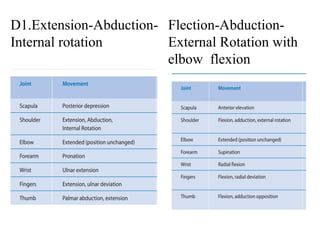
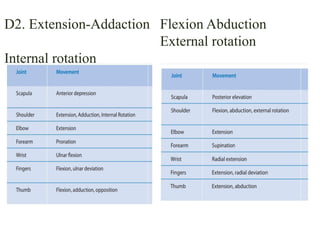
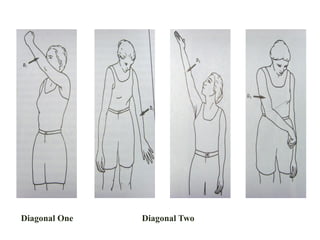
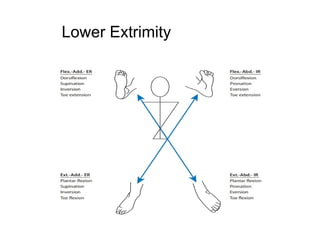
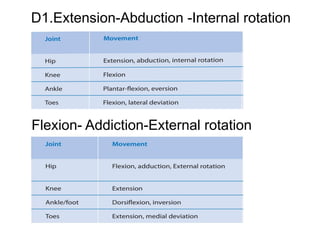
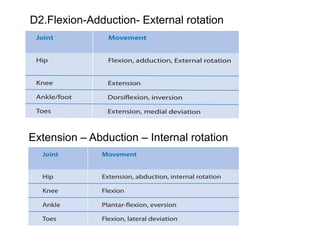
The document is a presentation about Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) techniques in physiotherapy, explaining its definitions and physiological basis. PNF is an advanced flexibility training method that involves muscle stretching and contraction, utilizing principles such as resistance and manual contact to facilitate muscle control and rehabilitation. Various PNF techniques like rhythmic initiation and contract-relax are outlined, emphasizing their application in restoring motor function post-injury.