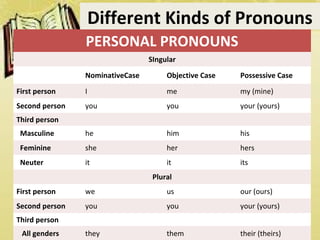
Pronouns are words that replace nouns, with their usage dependent on the noun being substituted and its function in a sentence. Different types of pronouns include personal, reflexive, intensive, interrogative, demonstrative, indefinite, numerical, reciprocal, and relative pronouns, each serving distinct roles in grammar. Examples are provided for each type, illustrating their application in various contexts.