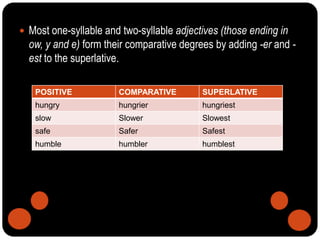
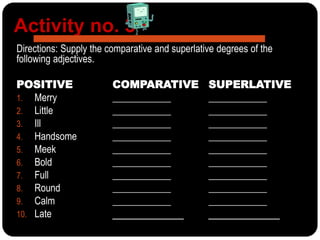
The document provides a thorough overview of adjectives, including their classifications, functions, and degrees of comparison. It details types like descriptive and limiting adjectives, and encompasses lessons on comparative and superlative forms, as well as adjectives used in series. Activities are included for practice in identifying and using adjectives correctly.