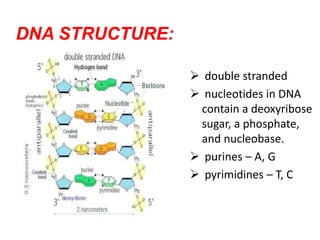
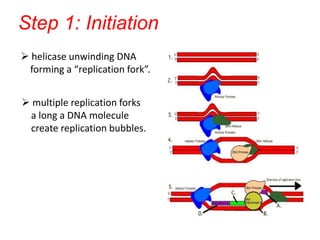
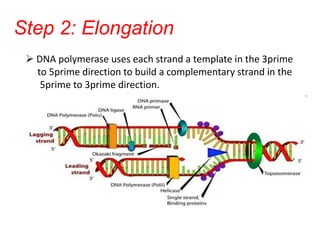
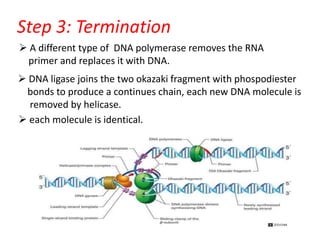
DNA replication is the process by which DNA duplicates itself to produce two identical copies. It occurs during the S-phase of the cell cycle and involves three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, helicase unwinds the DNA double helix to form a replication fork. During elongation, DNA polymerase uses each DNA strand as a template to build a complementary new strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Termination involves removing RNA primers, replacing them with DNA, and ligating the fragments together to produce two complete DNA molecules identical to the original.