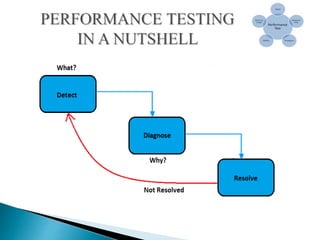
The document discusses performance testing, which is done to evaluate how a system performs under certain workloads. It aims to determine a system's speed, scalability, stability and other quality attributes. The document outlines different types of performance tests like load testing and stress testing. It explains key performance metrics such as response time, throughput and how performance testing helps improve quality and reduce risks. Overall, performance testing is important to ensure applications meet expectations before release.