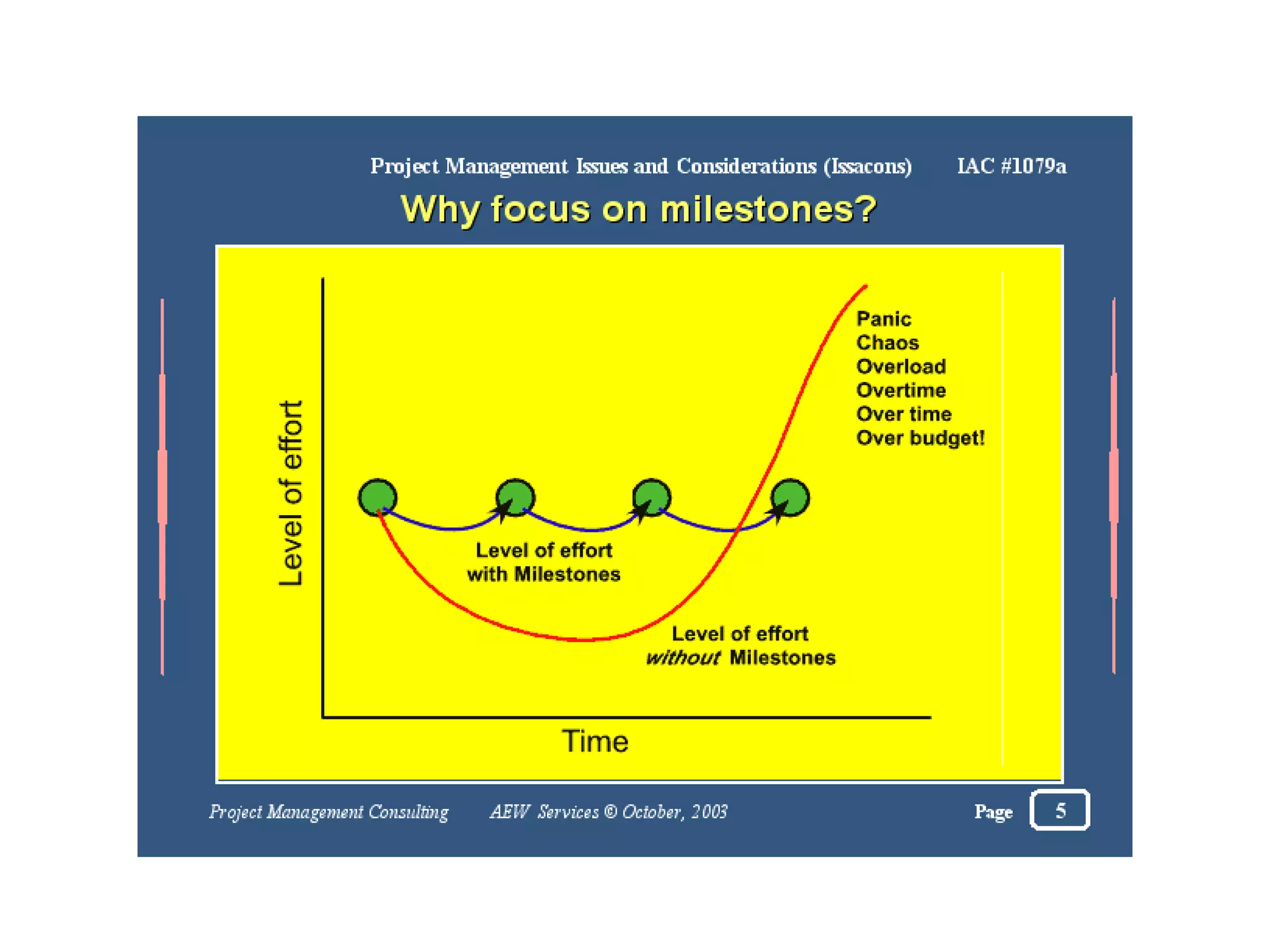
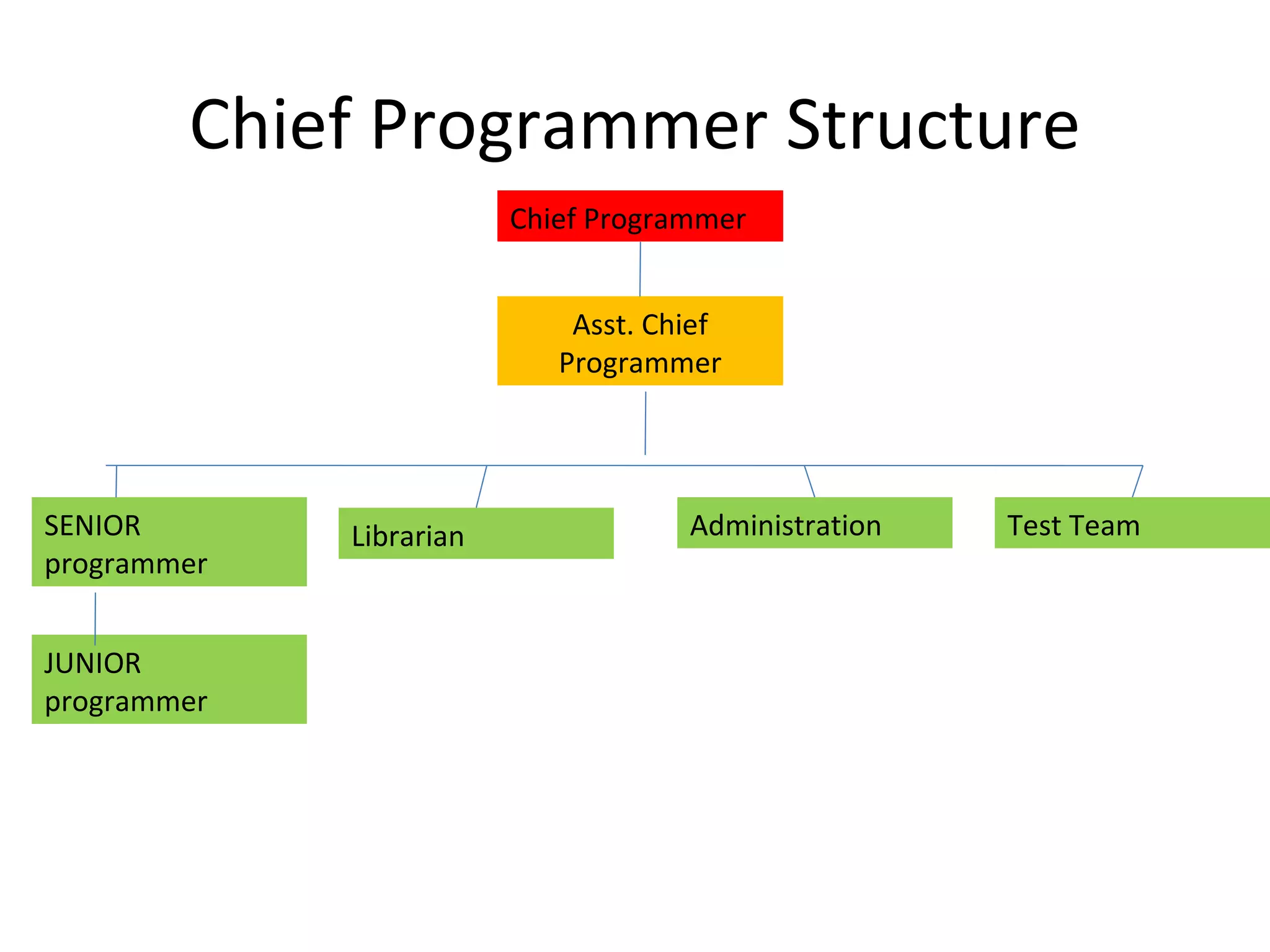
Project management involves carefully planning and organizing resources to successfully complete specific goals and objectives within constraints of scope, time and budget. It includes developing a project plan with tasks to achieve goals, resource needs, budgets and timelines. Project managers must achieve all goals while honoring constraints, and optimally allocate inputs to meet objectives. Key figures in the development of project management techniques include Henry Gantt, known for the Gantt chart, and Henri Fayol for establishing the five management functions. Project management typically involves phases of feasibility, definition, planning, implementation, evaluation and support.

![Project A project is a temporary endeavor, having a defined beginning and end (usually constrained by date, but can be by funding or deliverables [1] ), undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives [2] , usually to bring about beneficial change or added value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-magnt-1277906887-phpapp01/75/project-magnt-2-2048.jpg)