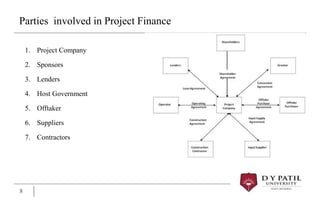
Project finance deals with analyzing the financial feasibility of a particular project based on expected cash flows. It is a form of financing used for long-term infrastructure and industrial projects that often involve governments. Key features include risk sharing between multiple parties and better management. The different stages of project finance include feasibility, structuring, and implementation. Advantages are reducing lender recourse and maximizing leverage, while disadvantages include higher costs and disclosure requirements. Parties typically involved are the project company, sponsors, lenders, host government, offtaker, suppliers, and contractors. Sources of finance include loans, equity, retained profits, and sale/leaseback arrangements.