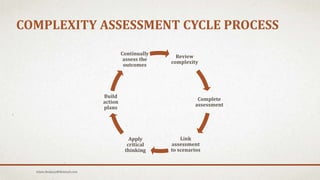
The document discusses project complexity and its management, highlighting the factors impacting projects such as human behavior, organizational structure, and diverse stakeholder agendas. It emphasizes the importance of effective communication, risk analysis, and continuous complexity assessment to navigate challenges in project management. Additionally, it provides practical solutions and scenarios for addressing complexities that arise during project execution.