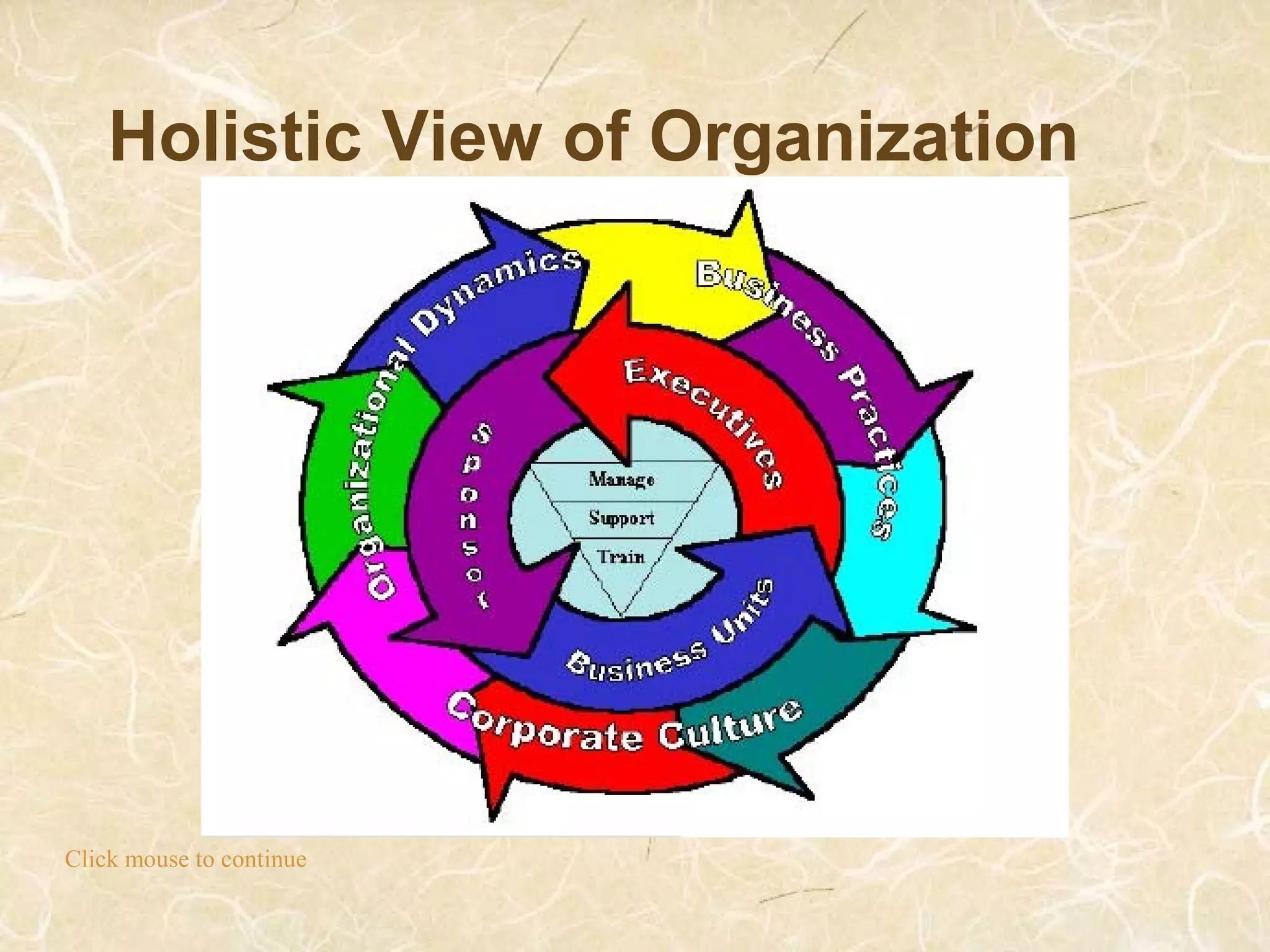
This document discusses project management and the challenges of managing projects in today's rapidly changing business environment. It argues that project management is as much an art as it is a science, requiring both hard technical skills as well as soft interpersonal skills. Soft skills like clear communication, understanding organizational culture, and effectively managing stakeholders are identified as being crucial for project success alongside traditional project management frameworks, tools and techniques. The document advocates for a holistic, iterative approach to project management that can adapt to changing needs and deliver value to customers.

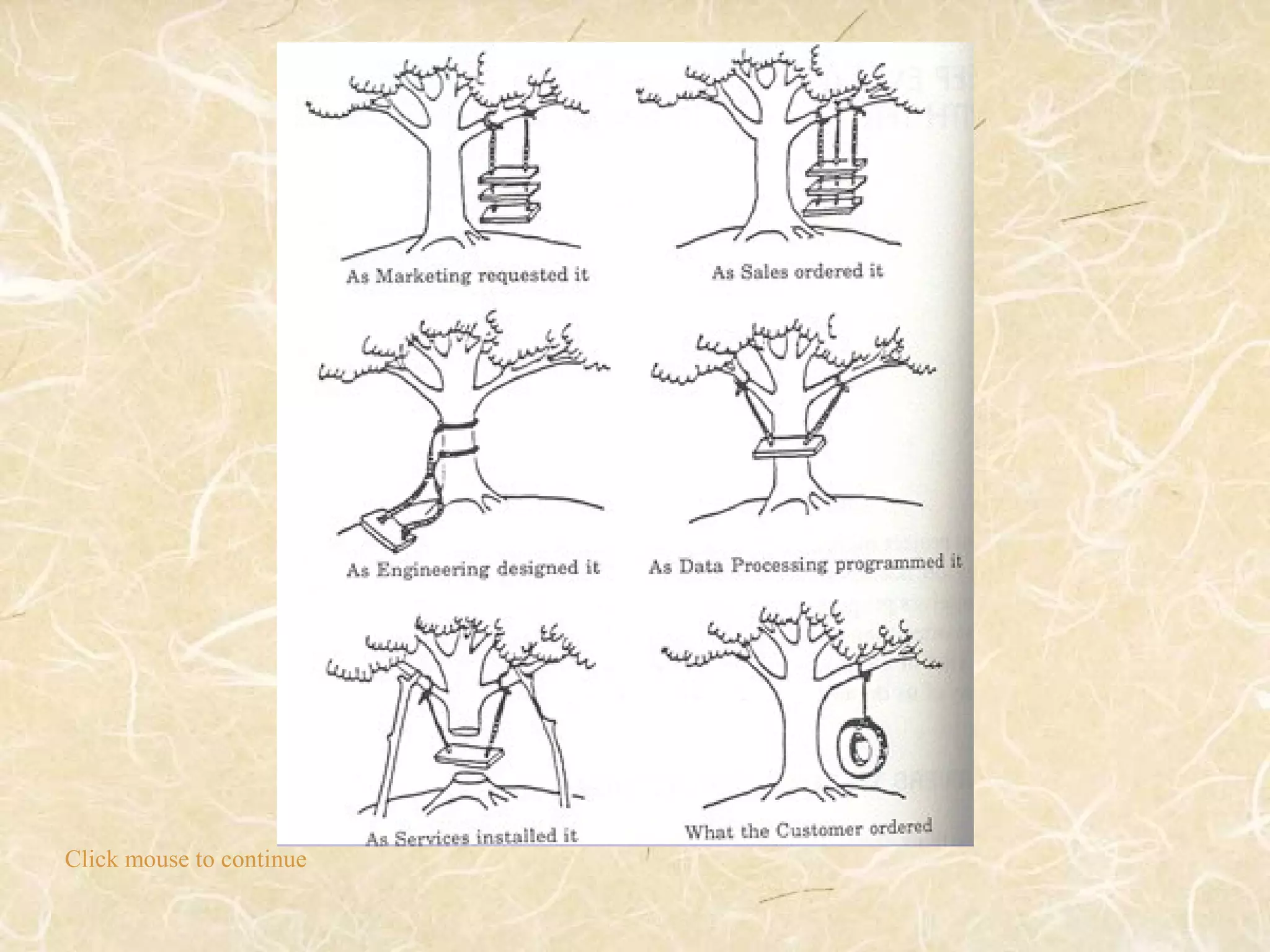





![What Makes a Project
Successful?
Click mouse to continue
Plan-Do-Check-Act [PDCA] (Walter Shewhart)
- Limited knowledge, improving as we go
- Velocity of change through iterations
Use processes, tools, and techniques
Soft skills
- Working within the organization
Hard Skills (Supplemental Information)
- Project Management Institute’s (PMI):
- Five Process Groups
- Nine Knowledge Areas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stillmoreartthanscience-101130060243-phpapp01/75/project-management-8-2048.jpg)