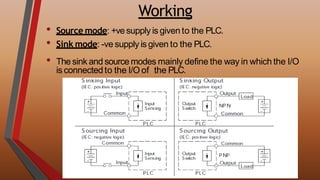
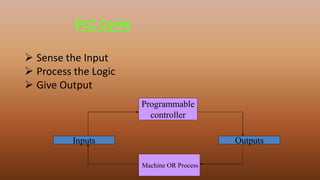
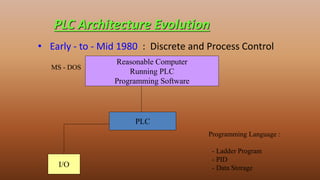
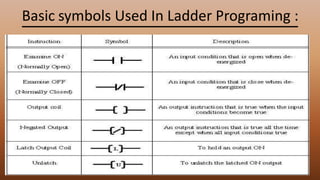
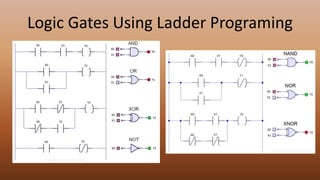
This document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It discusses the basic architecture of PLCs, including their input and output modules. The document also covers the advantages of PLCs over traditional relay-based control systems. Additionally, it examines PLC programming standards like ladder logic and the evolution of PLC architecture over time. Examples are provided to demonstrate basic PLC programming concepts like timers, counters, and logic gates using ladder diagrams.
![A
SEMINAR
ON
[PROGRAMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLER]
Submitted for partial fulfillment of the award of
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
Degree
In
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
By
SATYAM SHIVANSH
(1614331083)
ECE Department, IMS Engineering College, Ghaziabad
Dr. A.P.J. ABDUL KALAM TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, LUCKNOW
September 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programablelogiccontroller-200819192841/85/Programmable-Logic-Controller-1-320.jpg)