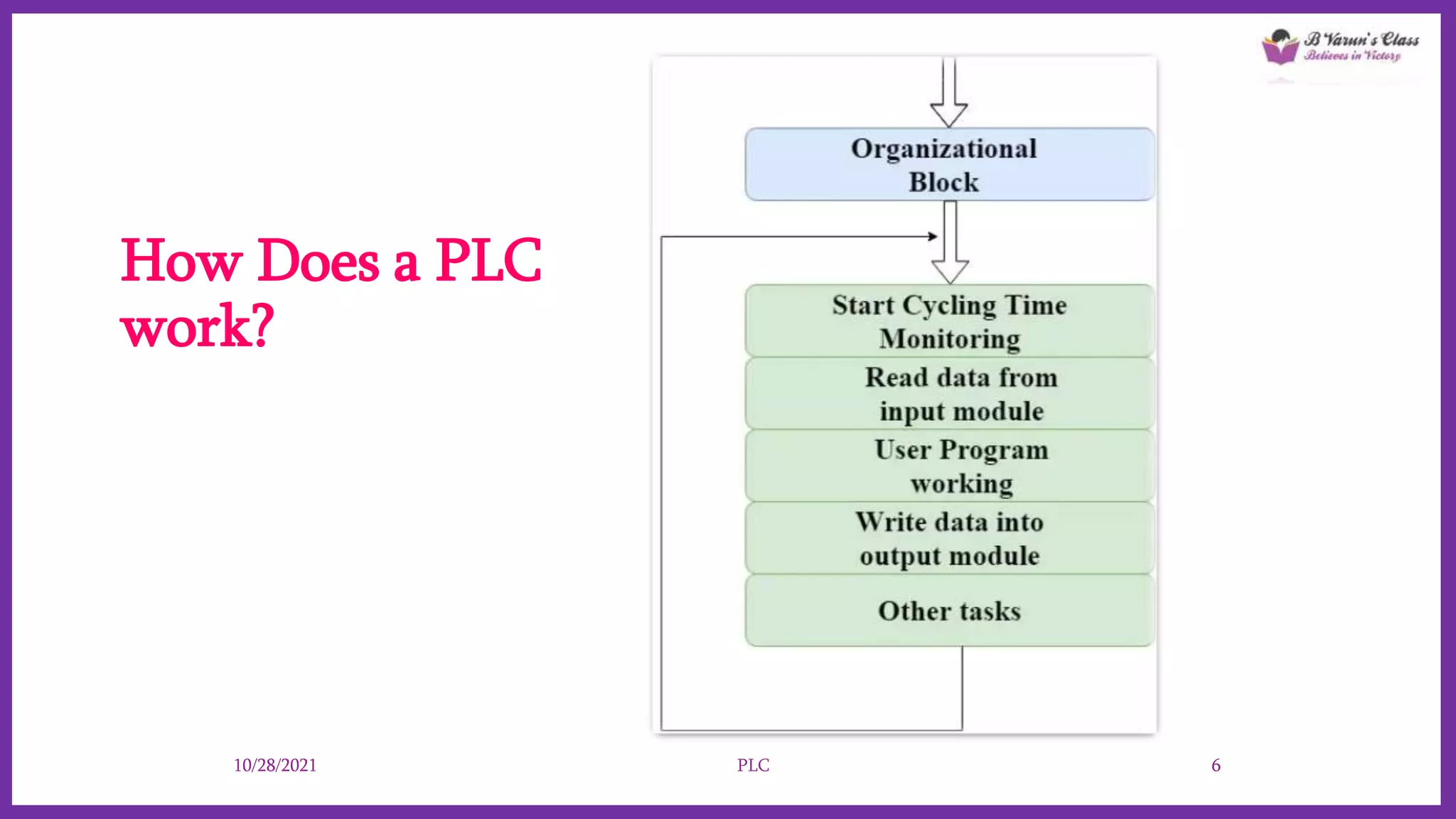
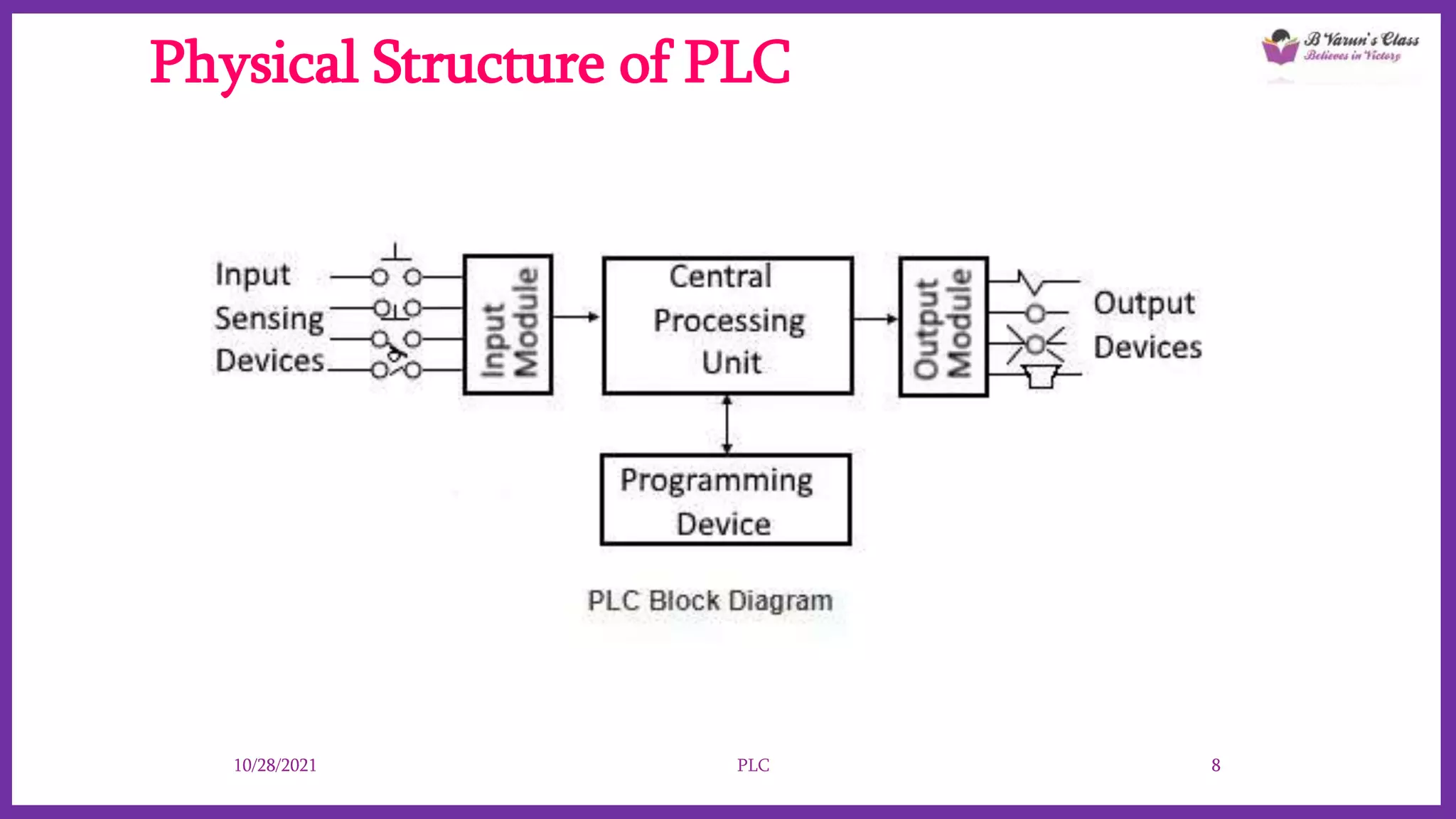
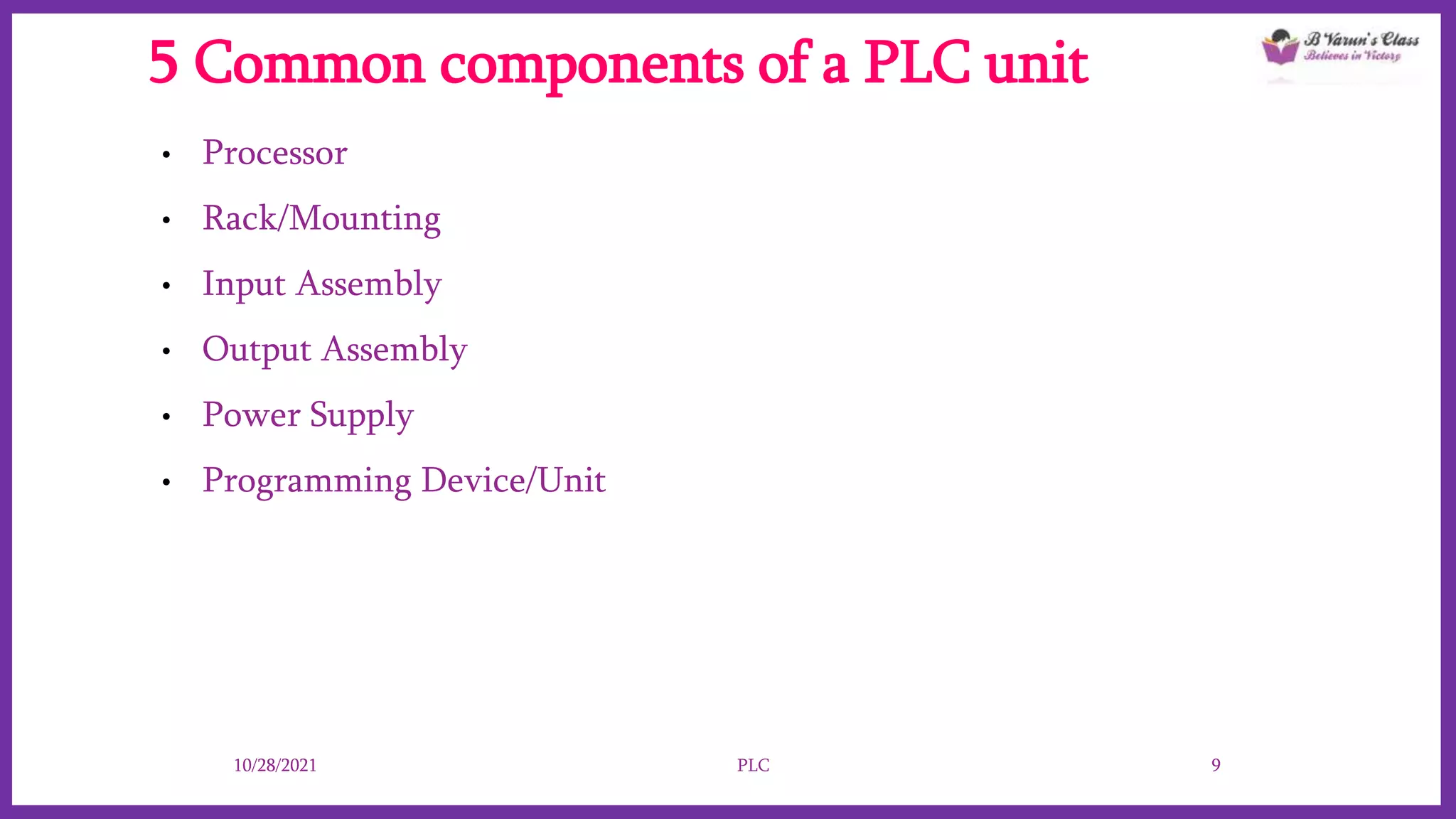
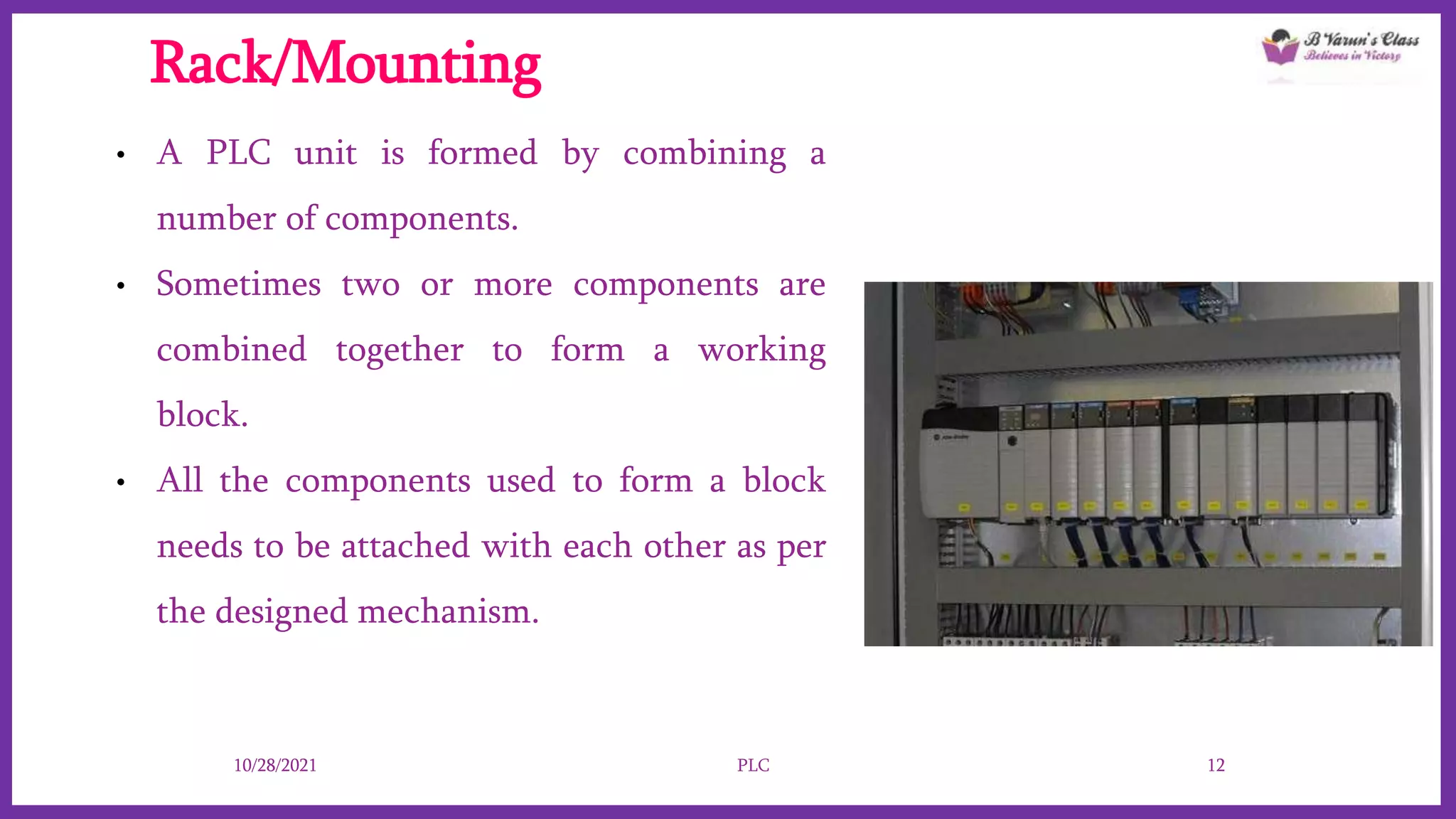
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are advanced control systems replacing traditional hard-wired logic relays in industrial automation, programmed to manage electromechanical processes. They consist of key components like a processor, input/output assemblies, and power supply, allowing for flexibility and ease of reprogramming as production needs change. PLCs enhance functionality, save space, and simplify troubleshooting, making them cost-effective for controlling complex systems.