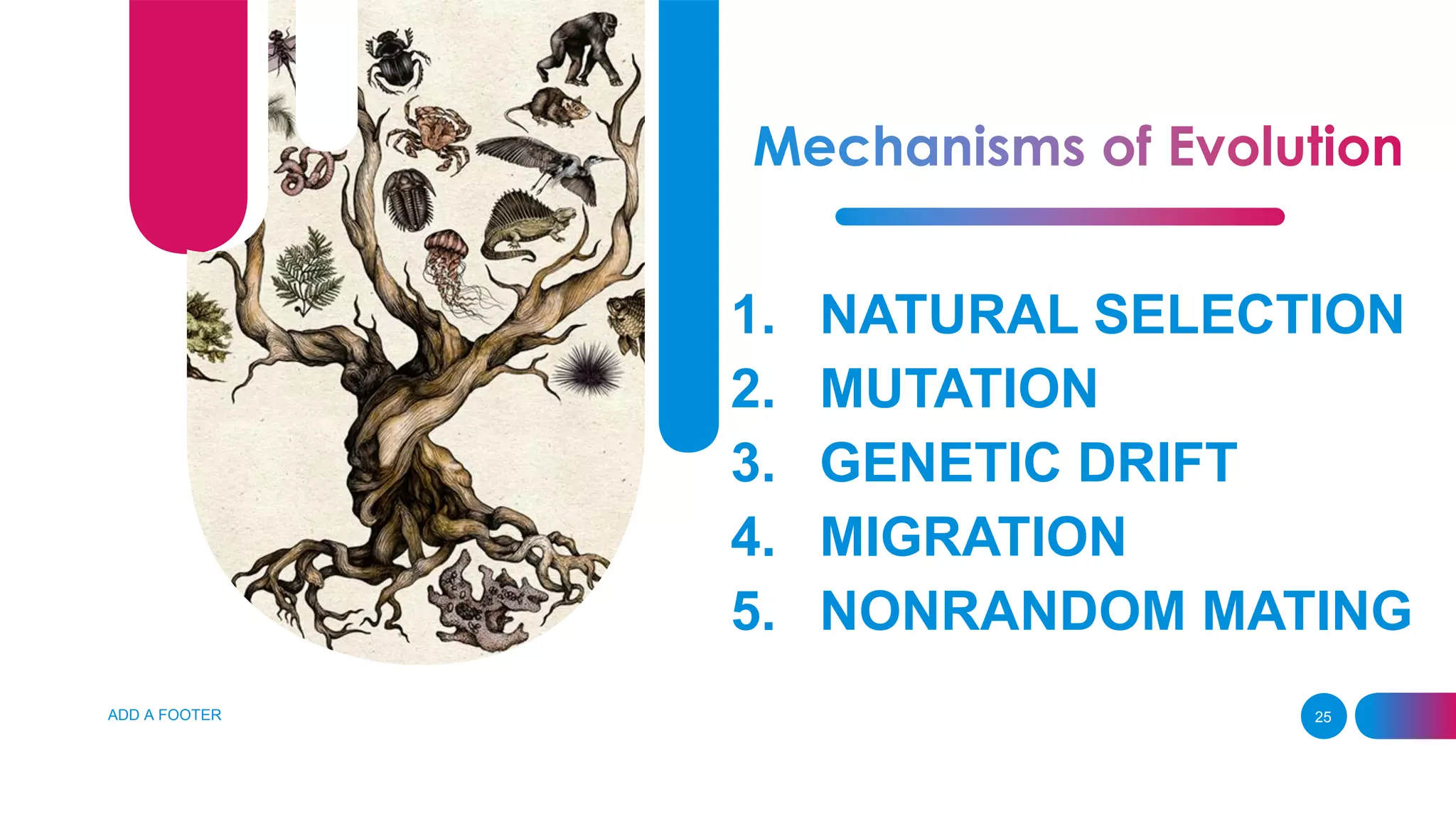
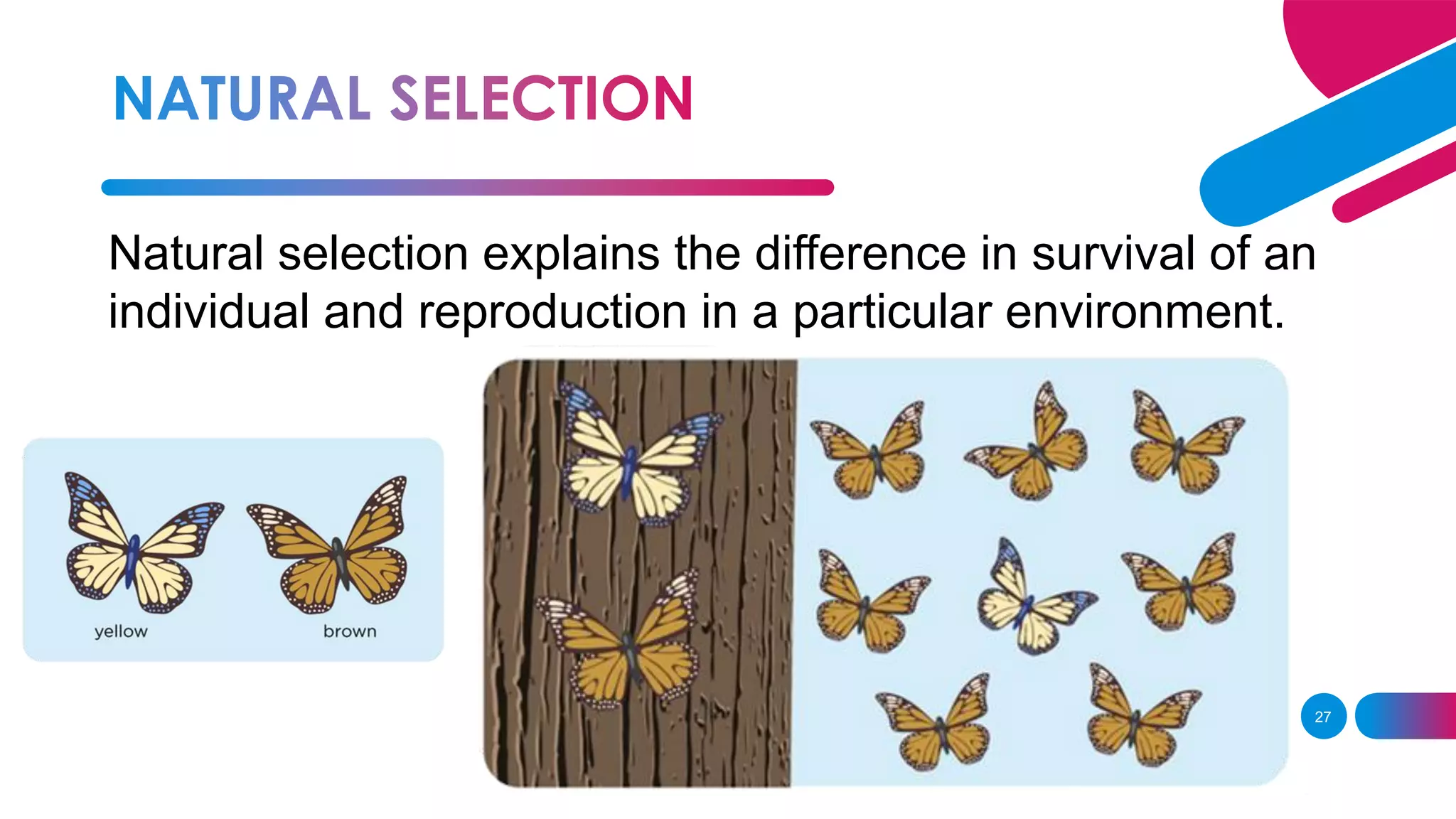
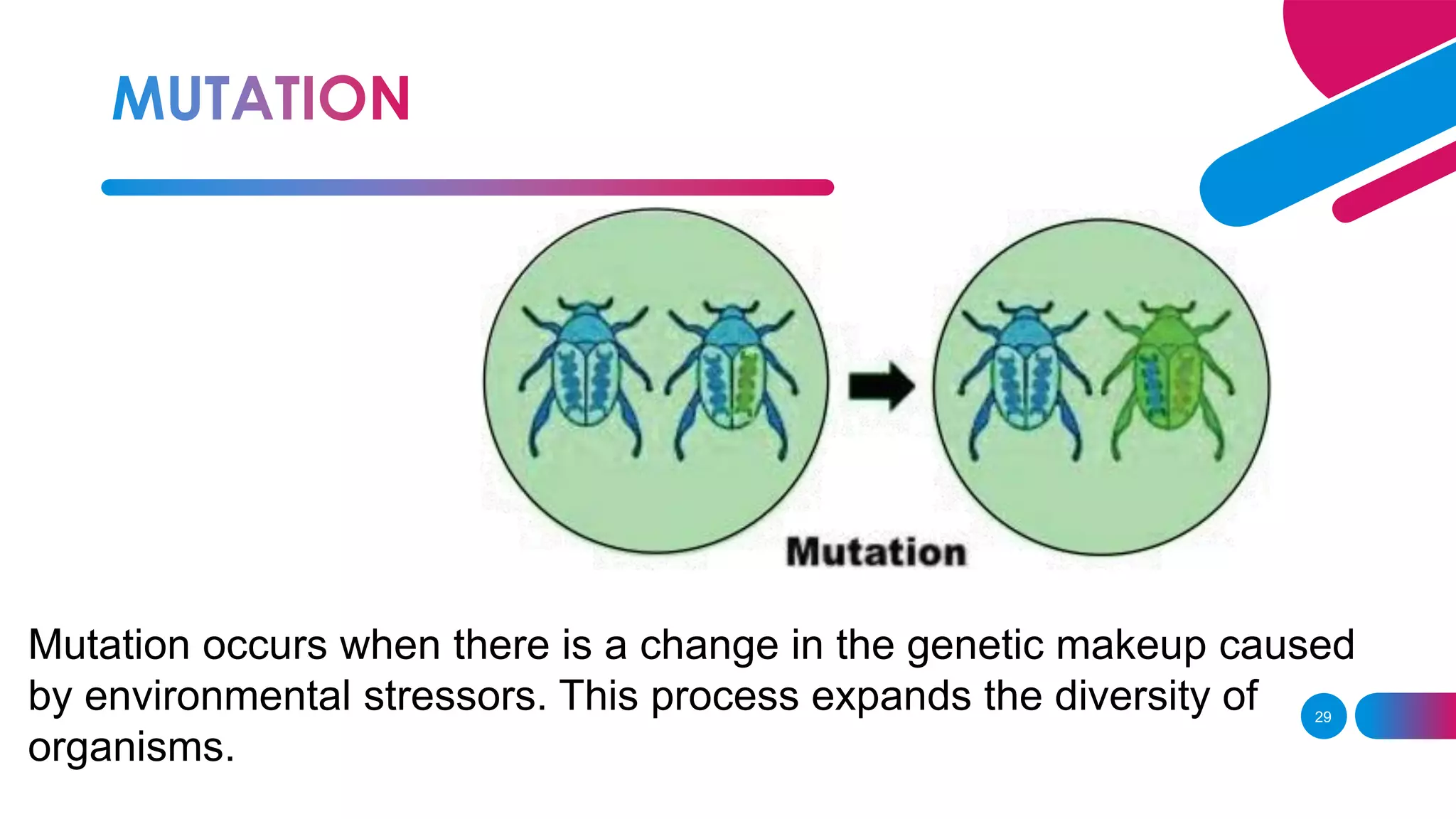
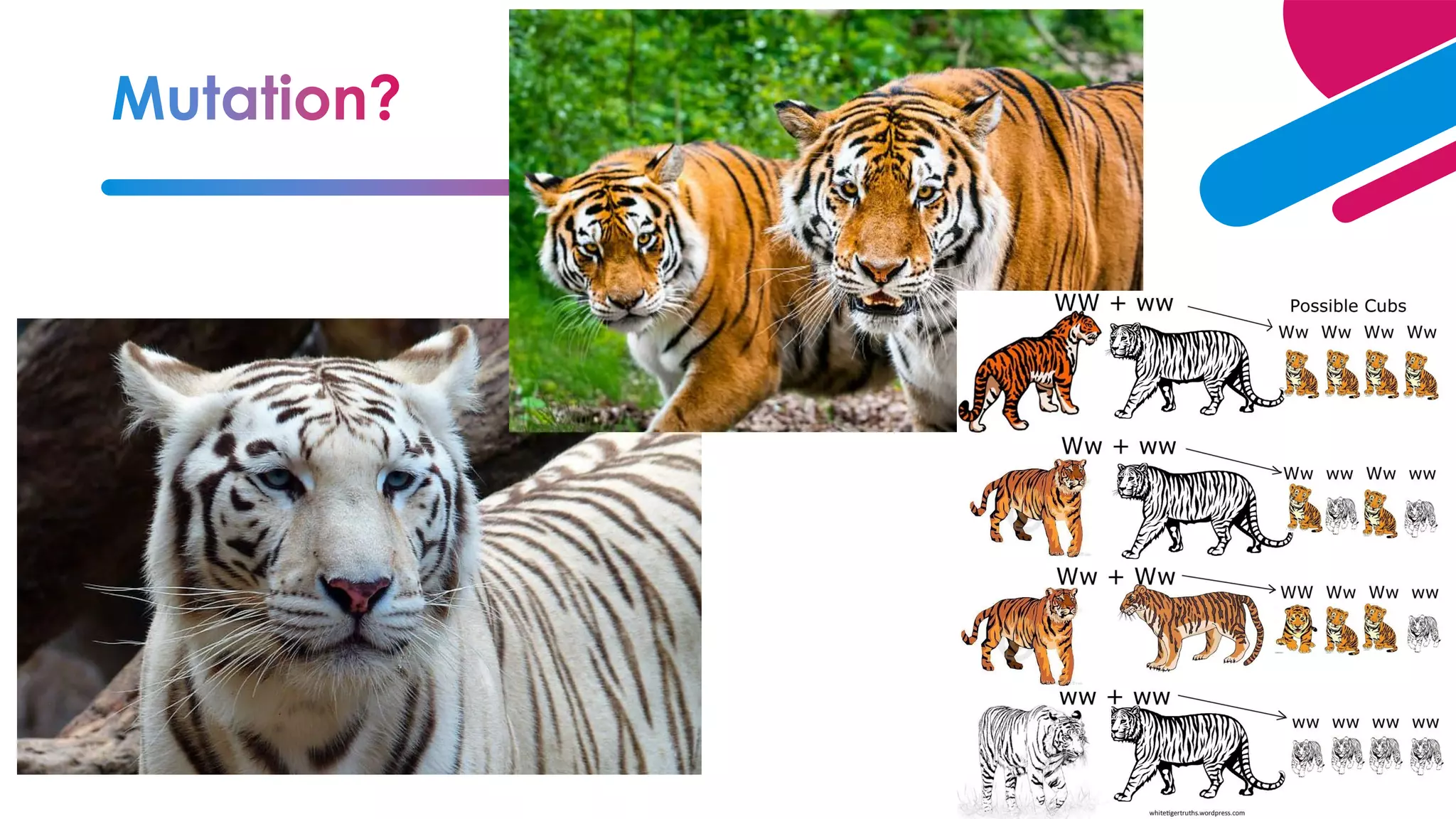
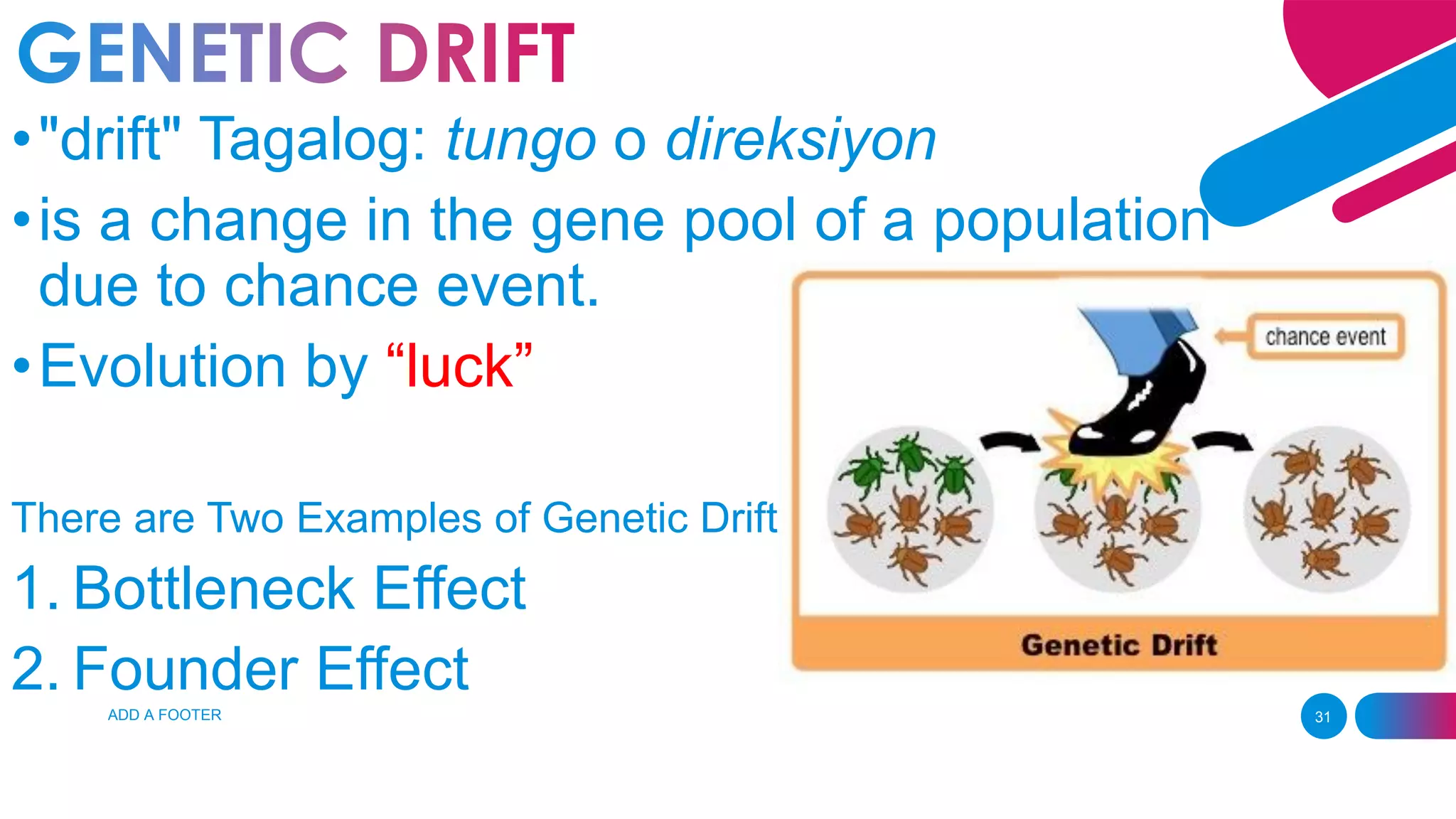
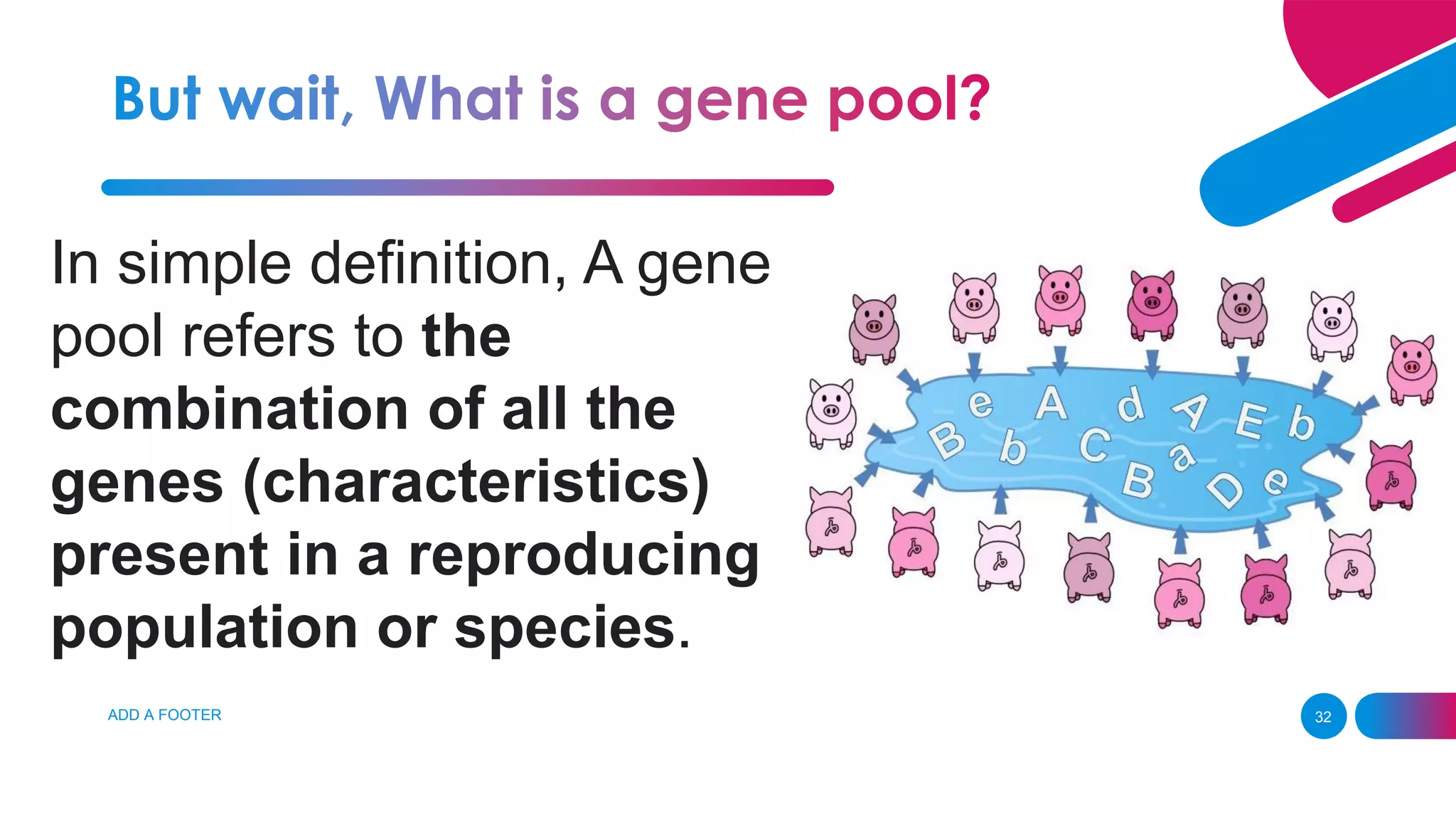
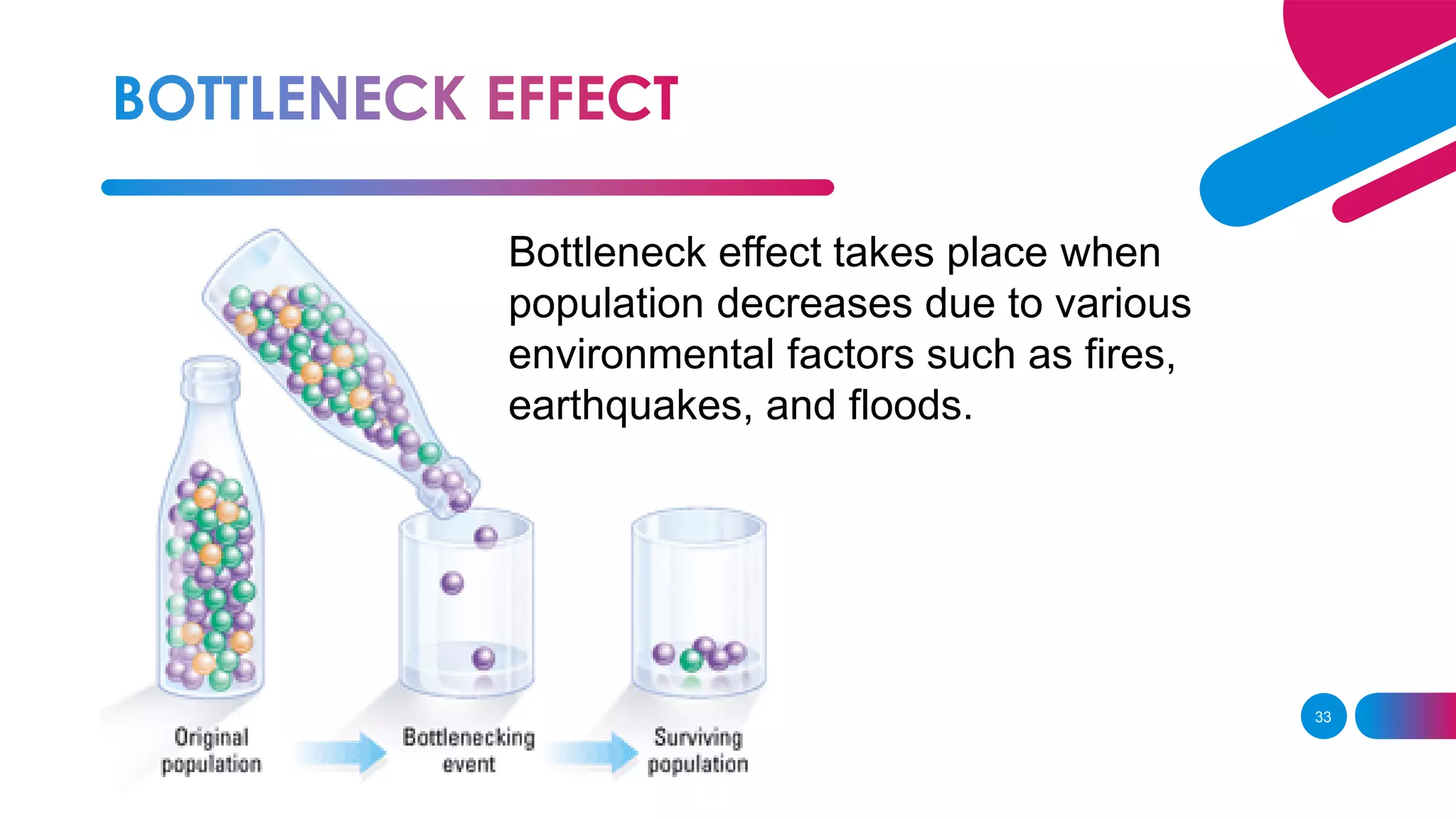
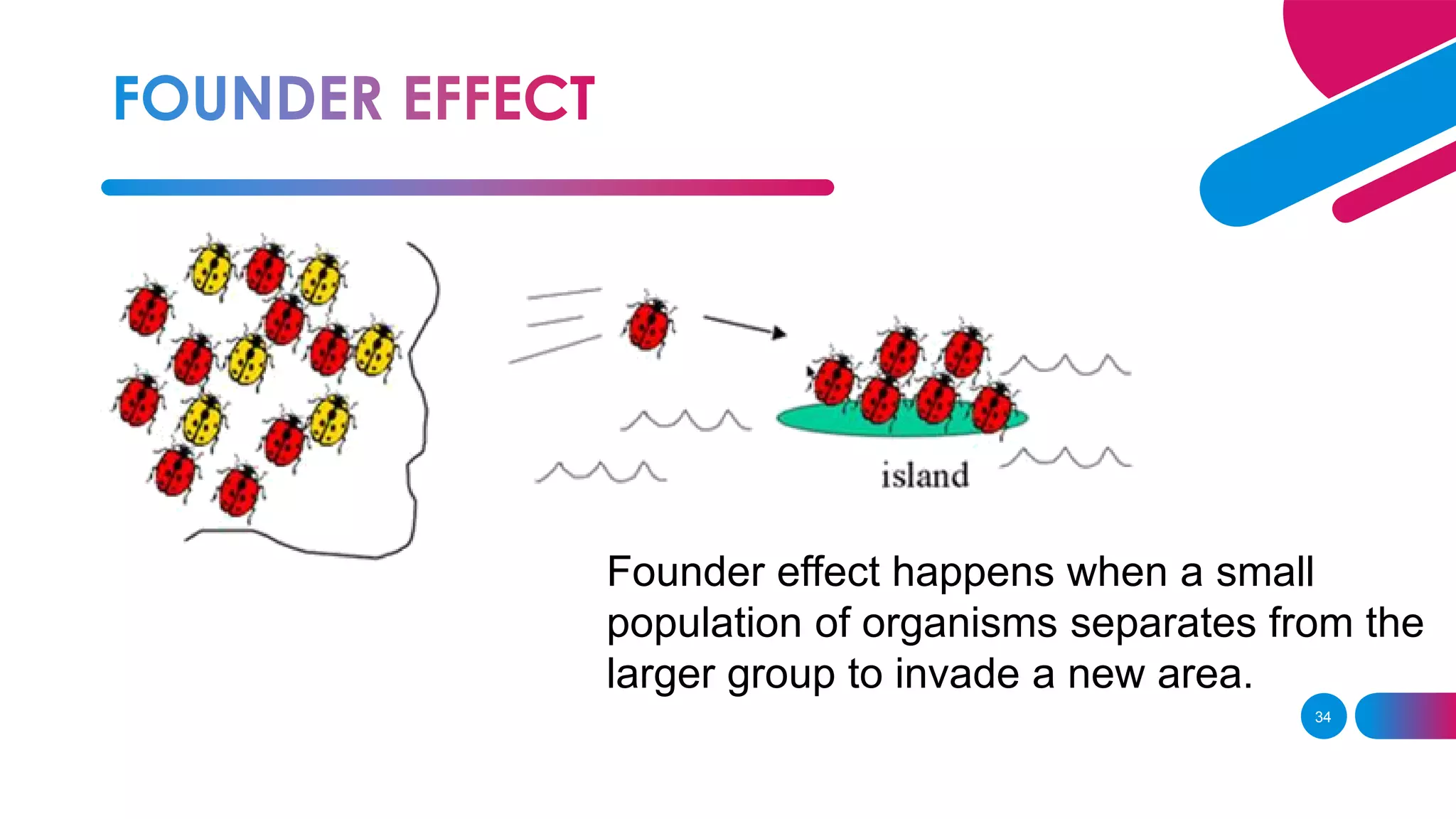
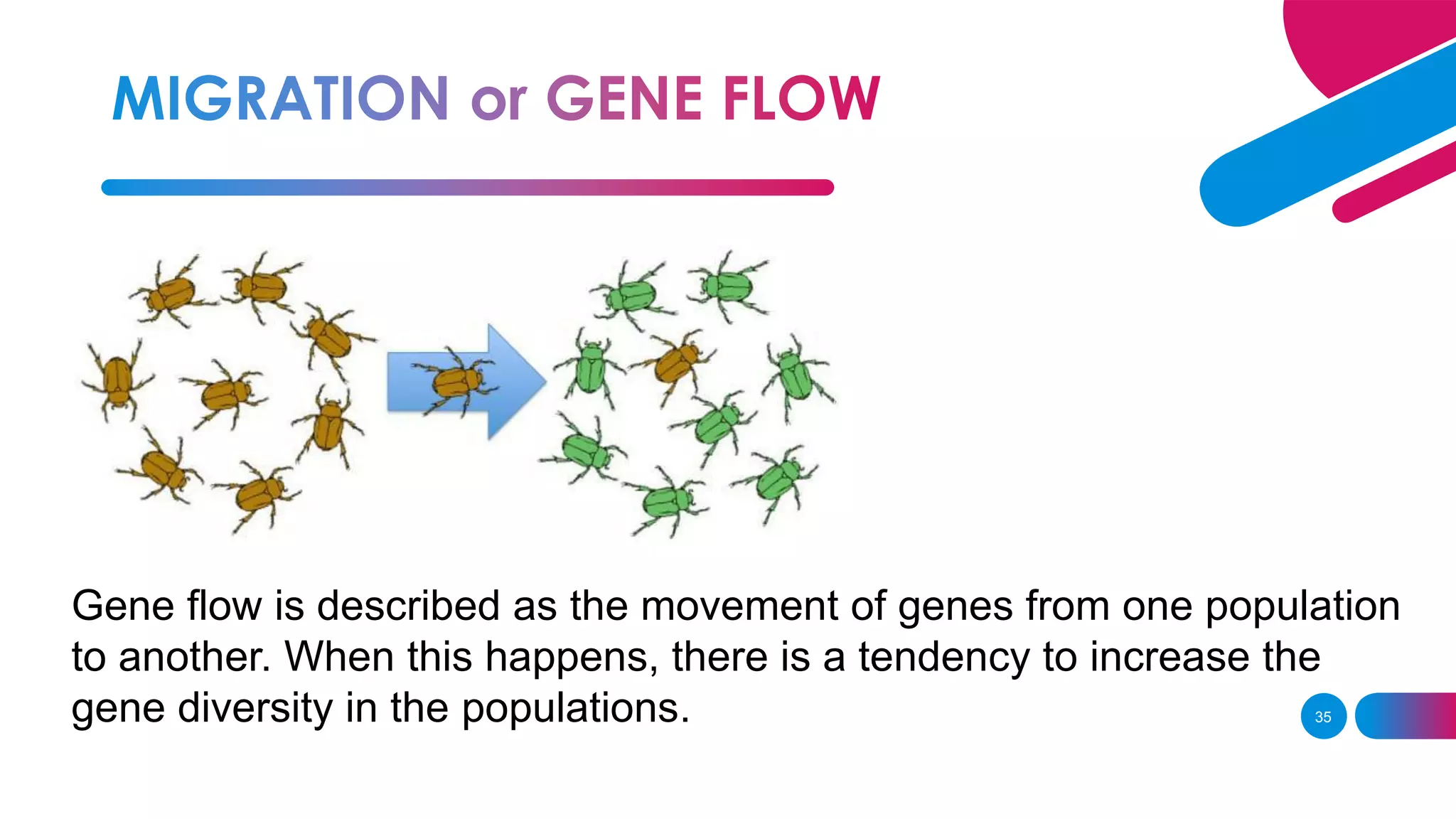
The document summarizes key concepts relating to evolution, including:
1. It outlines the process of evolution and scientists like Darwin, Wallace, and Lamarck who contributed to evolutionary thought.
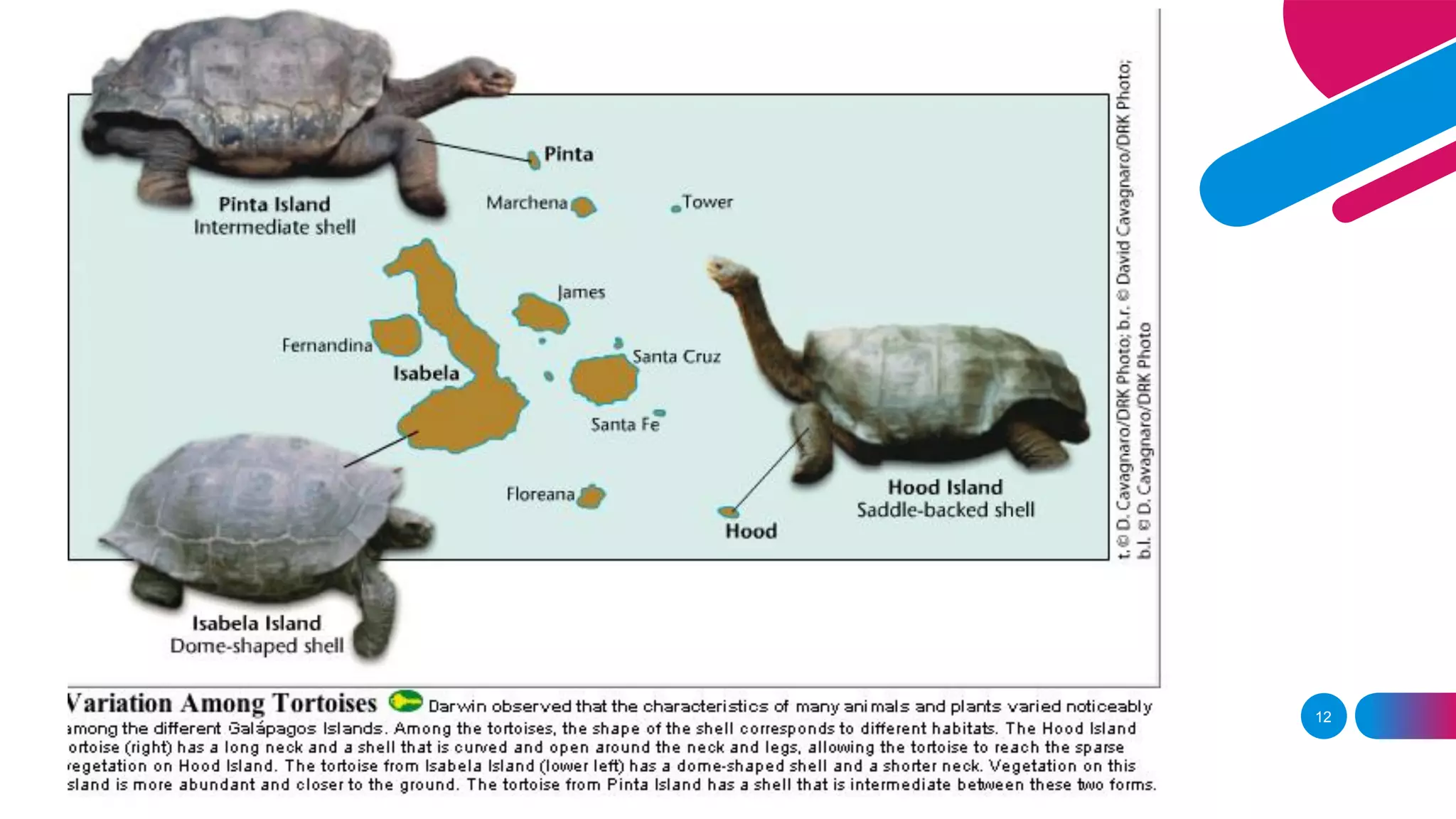
2. Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection proposed that organisms change over generations through natural selection of beneficial traits, leading to descent with modification from common ancestors.
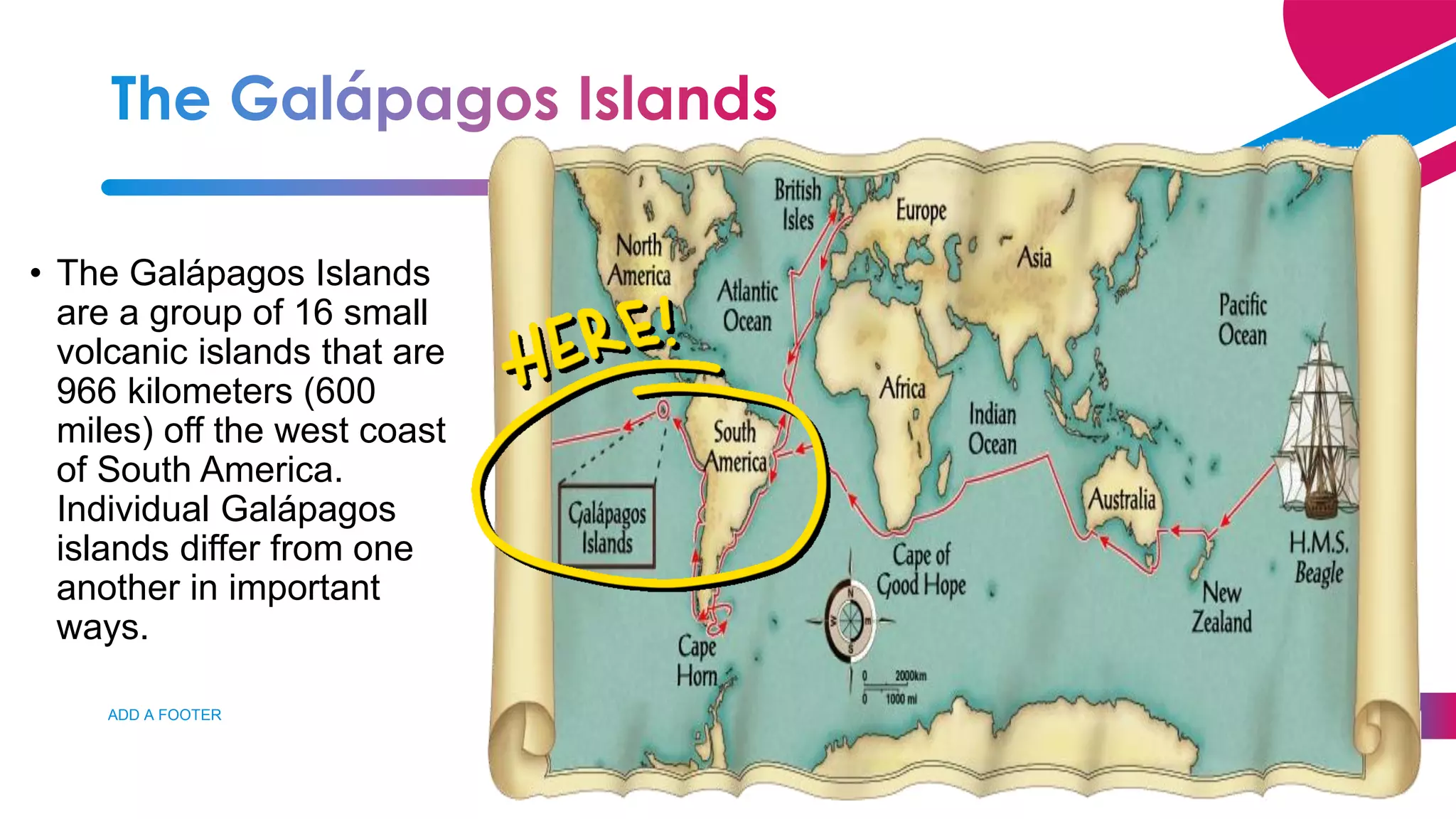
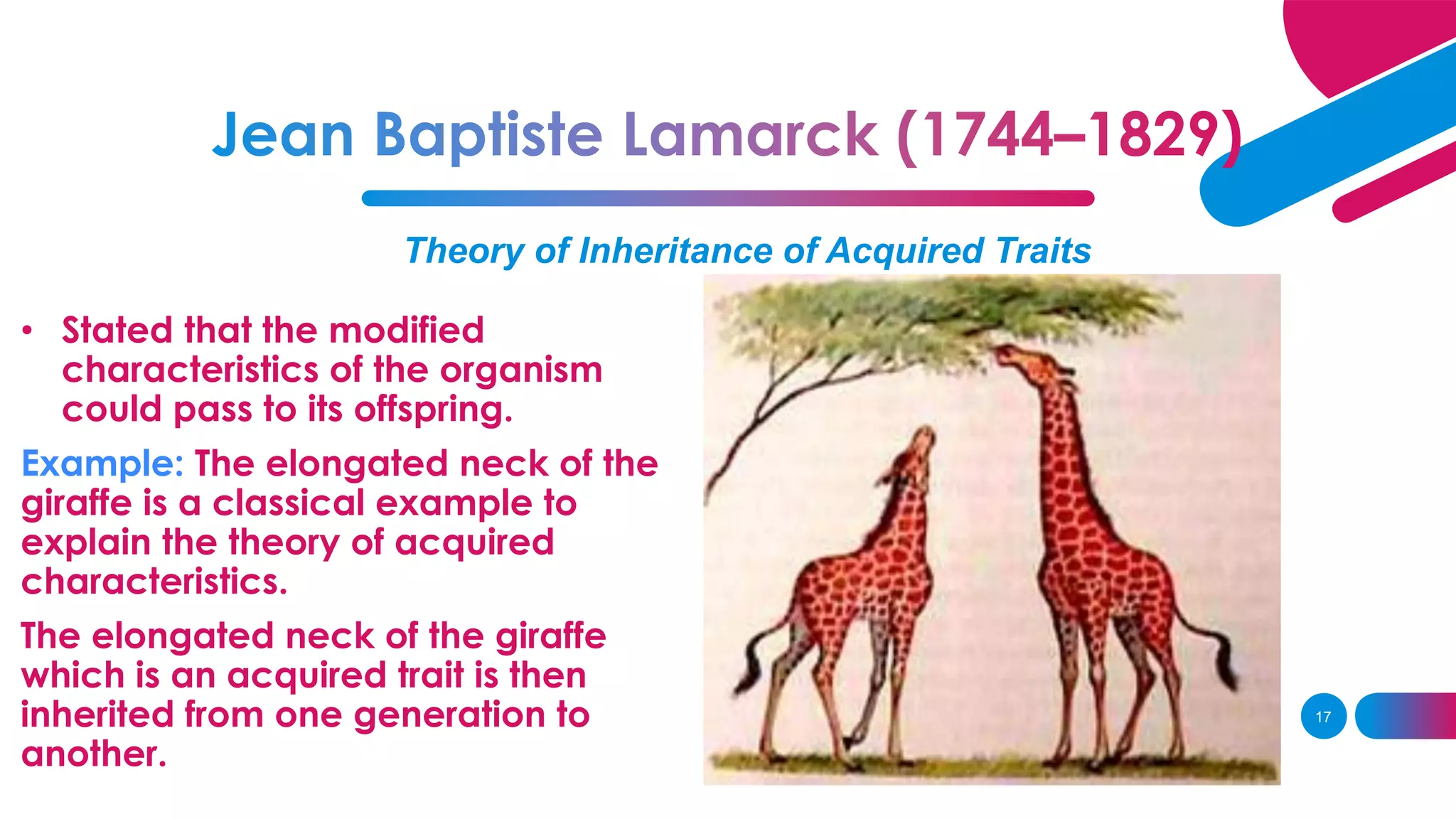
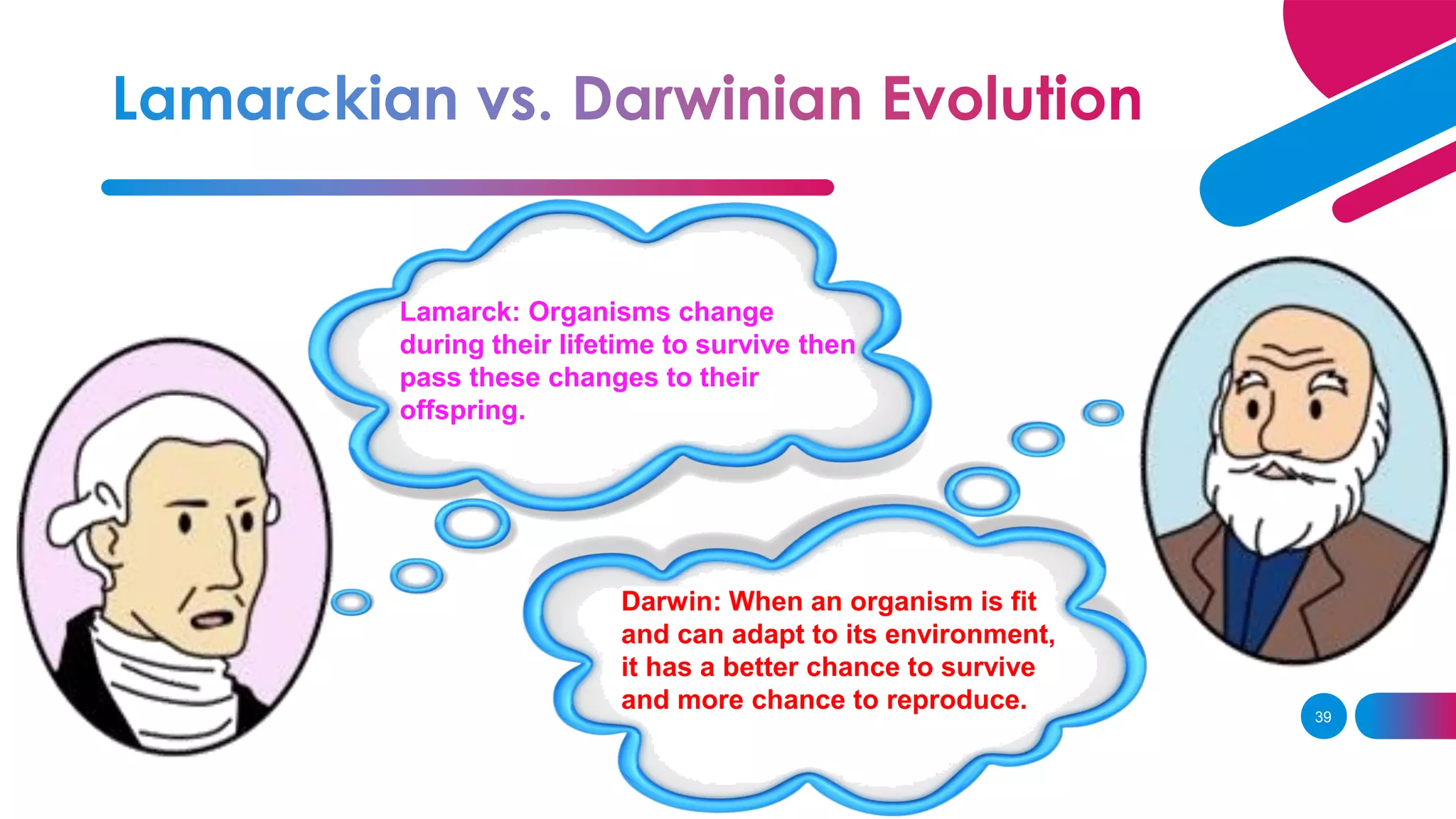
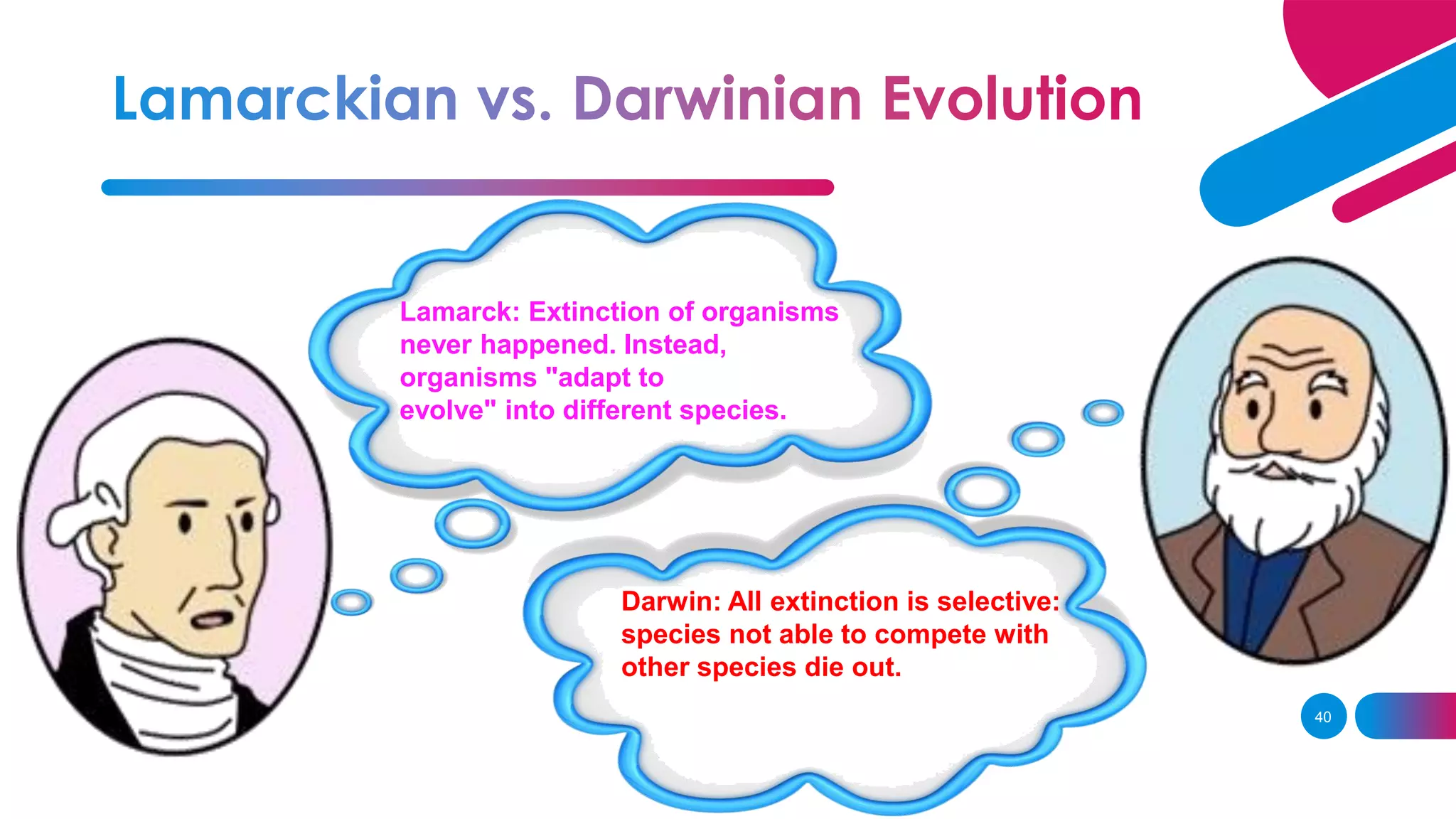
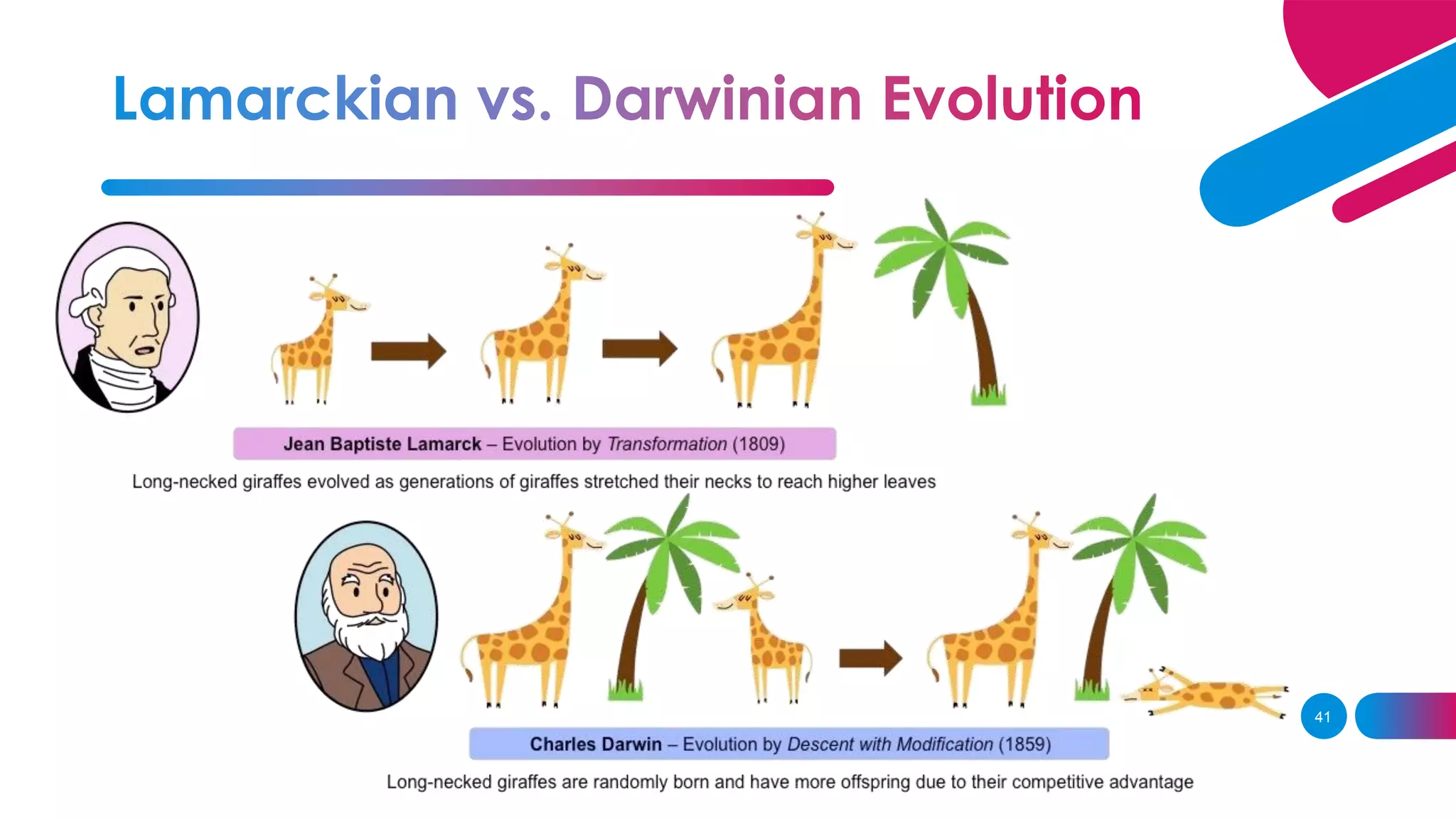
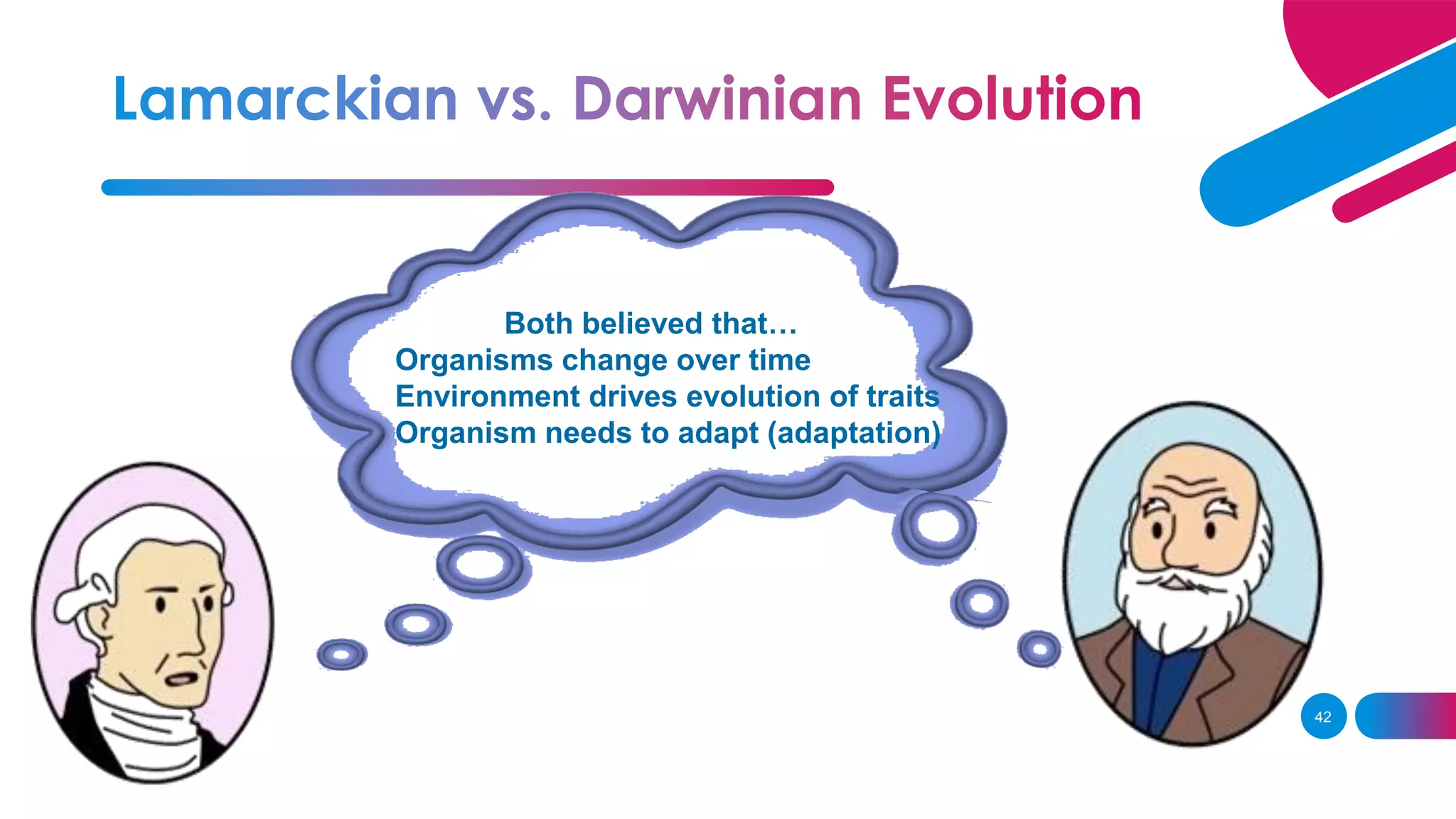
3. Lamarck believed in the inheritance of acquired traits, while Darwin found evidence of evolution through natural selection on his voyage on the HMS Beagle.