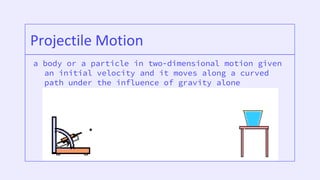
The document compares Aristotle and Galileo's concepts of horizontal and vertical motion. Aristotle believed horizontal motion required a continuous force, while Galileo believed objects in motion stay in motion due to inertia unless acted on by an external force. For vertical motion, Aristotle believed heavier objects fall faster, while Galileo demonstrated that all objects accelerate at the same rate when in free fall, defined as motion only due to gravity. The document also discusses projectile motion, quantities used to describe motion, and examples of motion concepts.