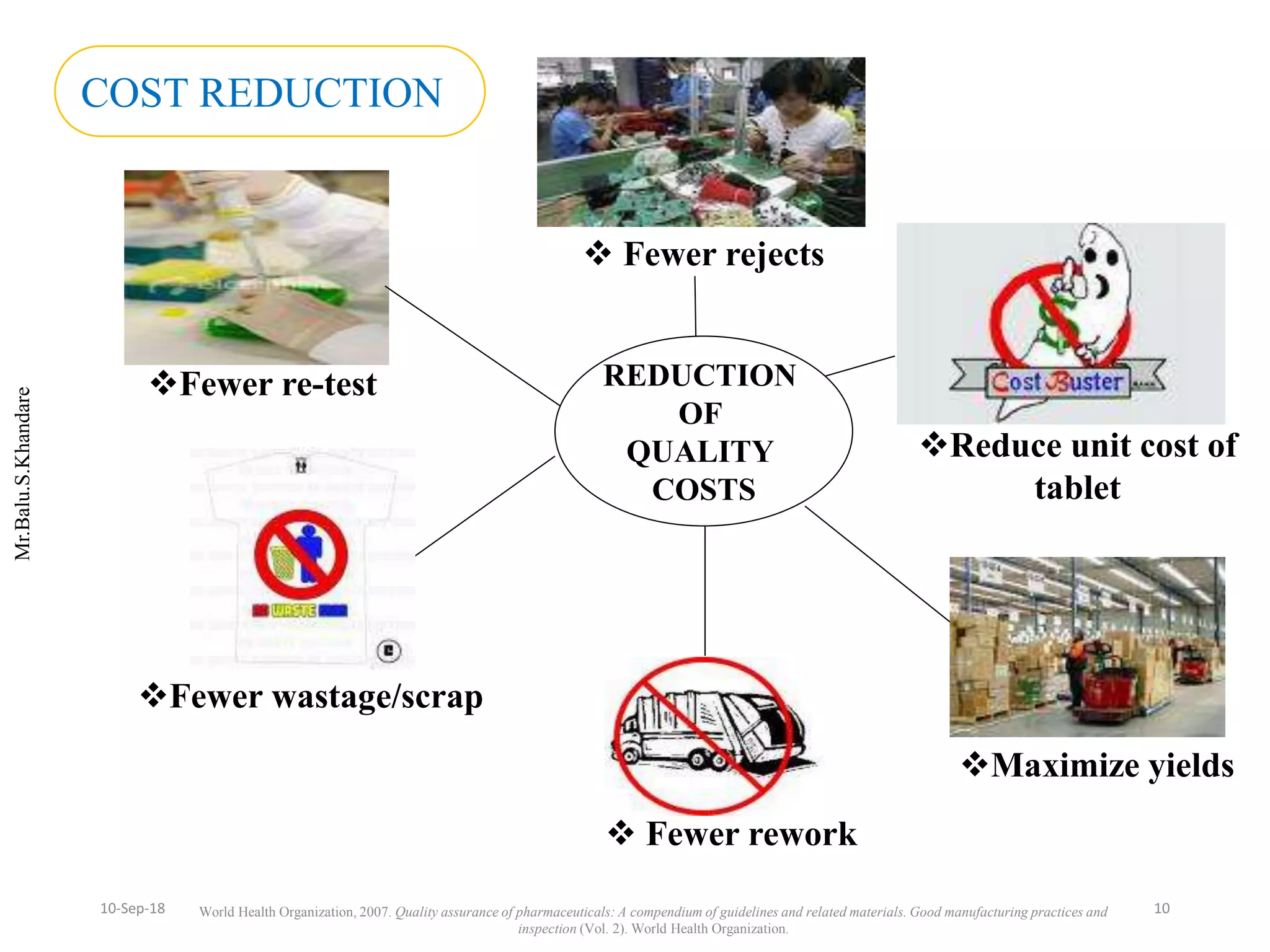
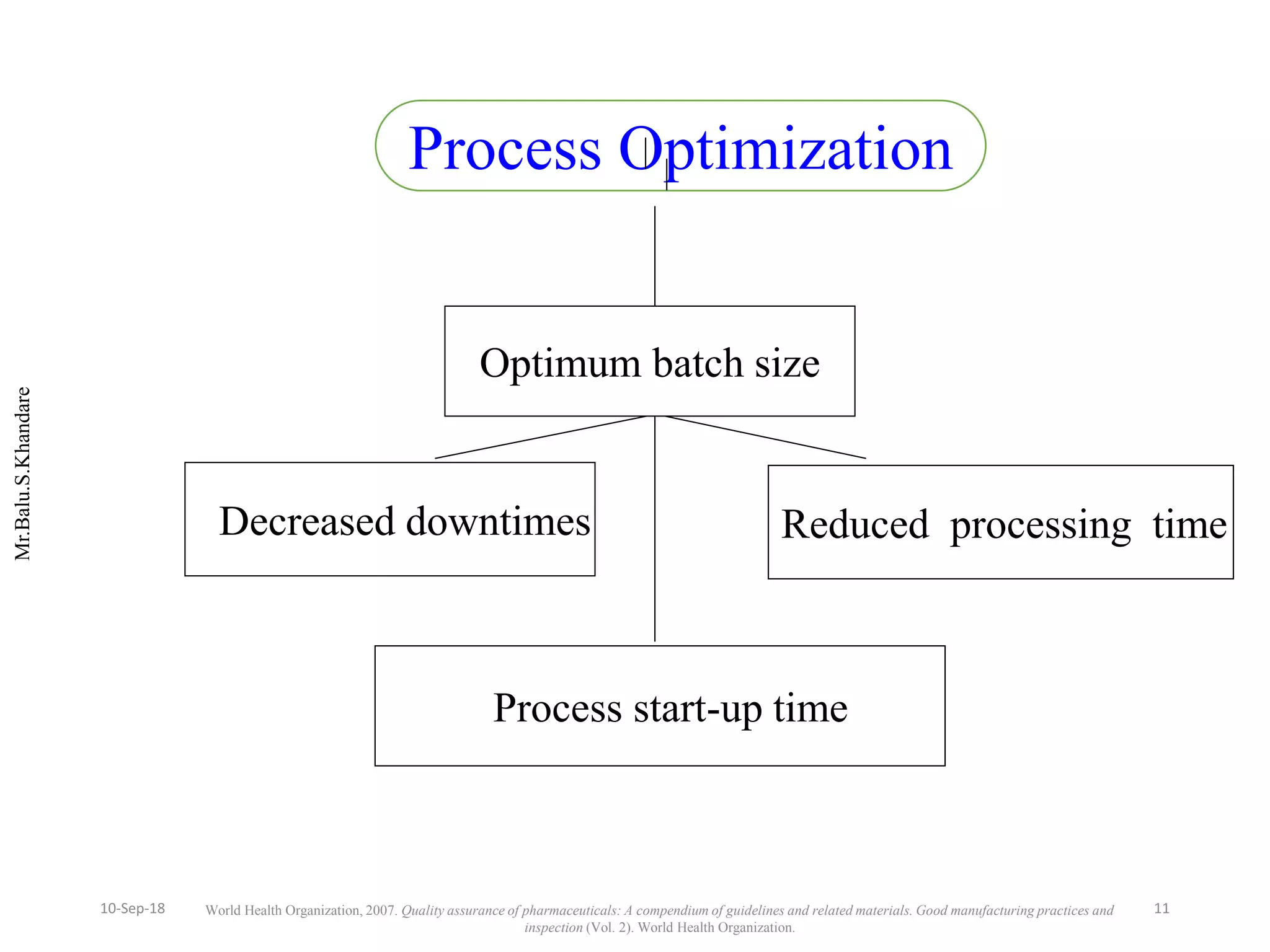
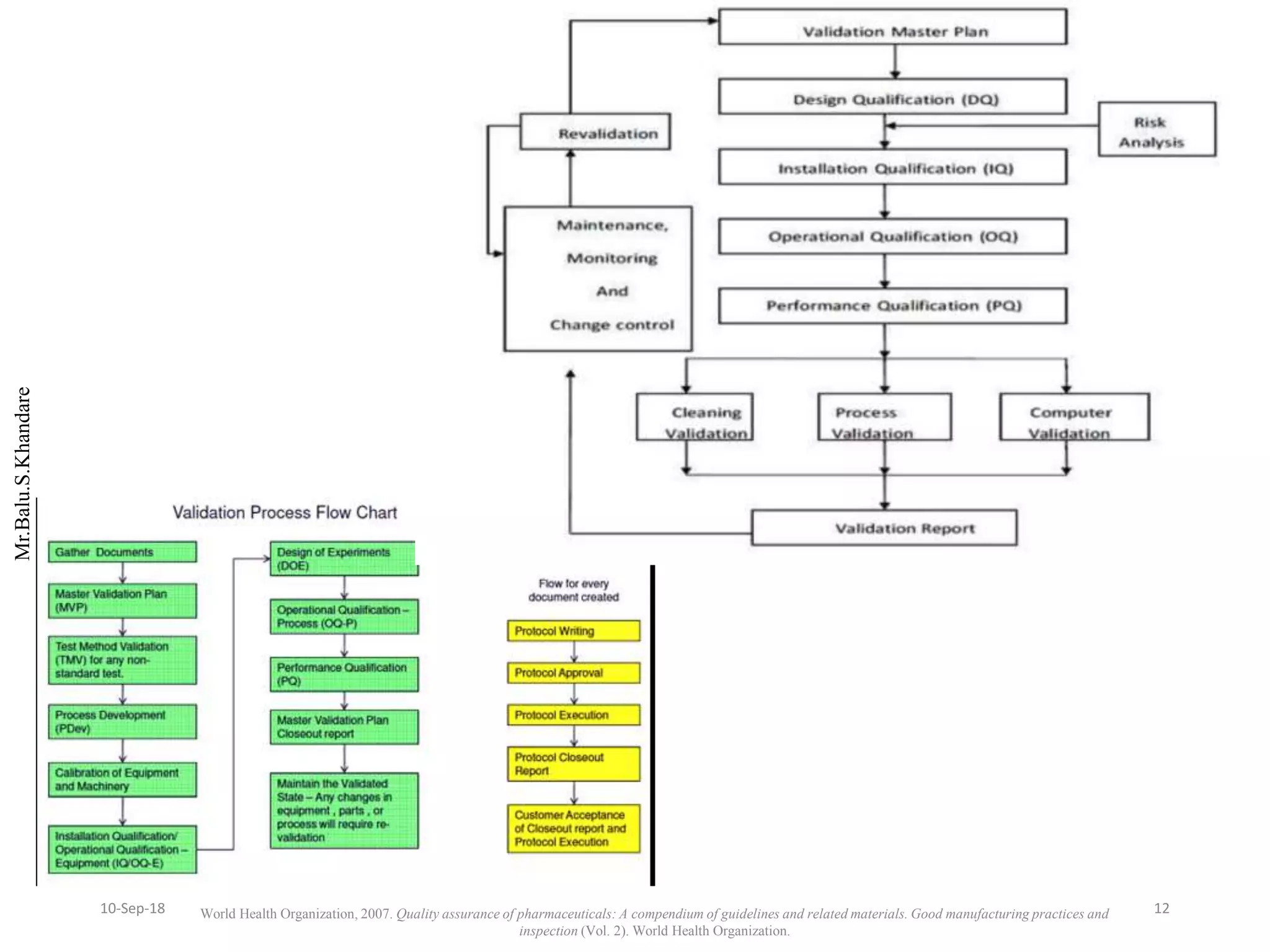
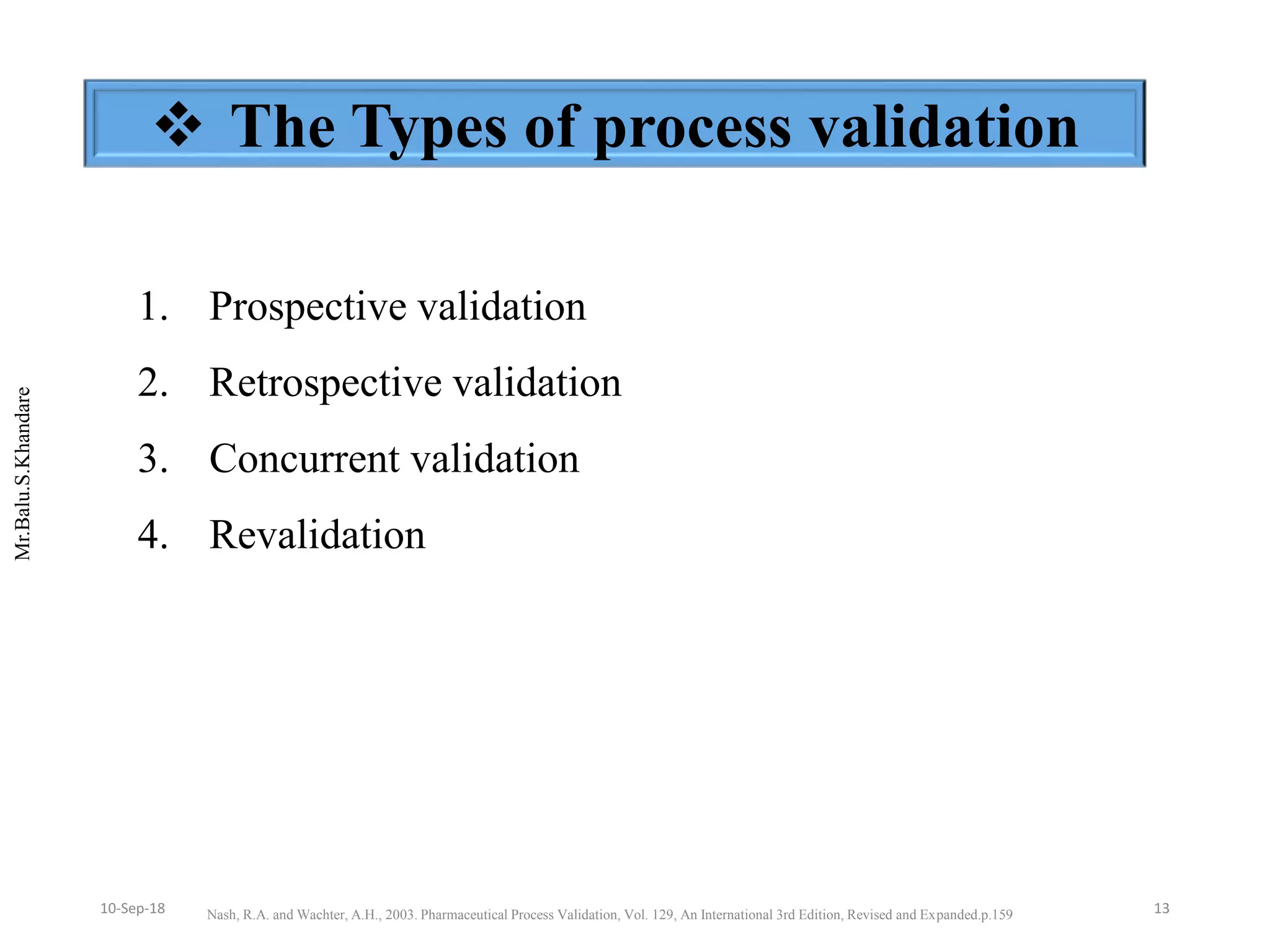
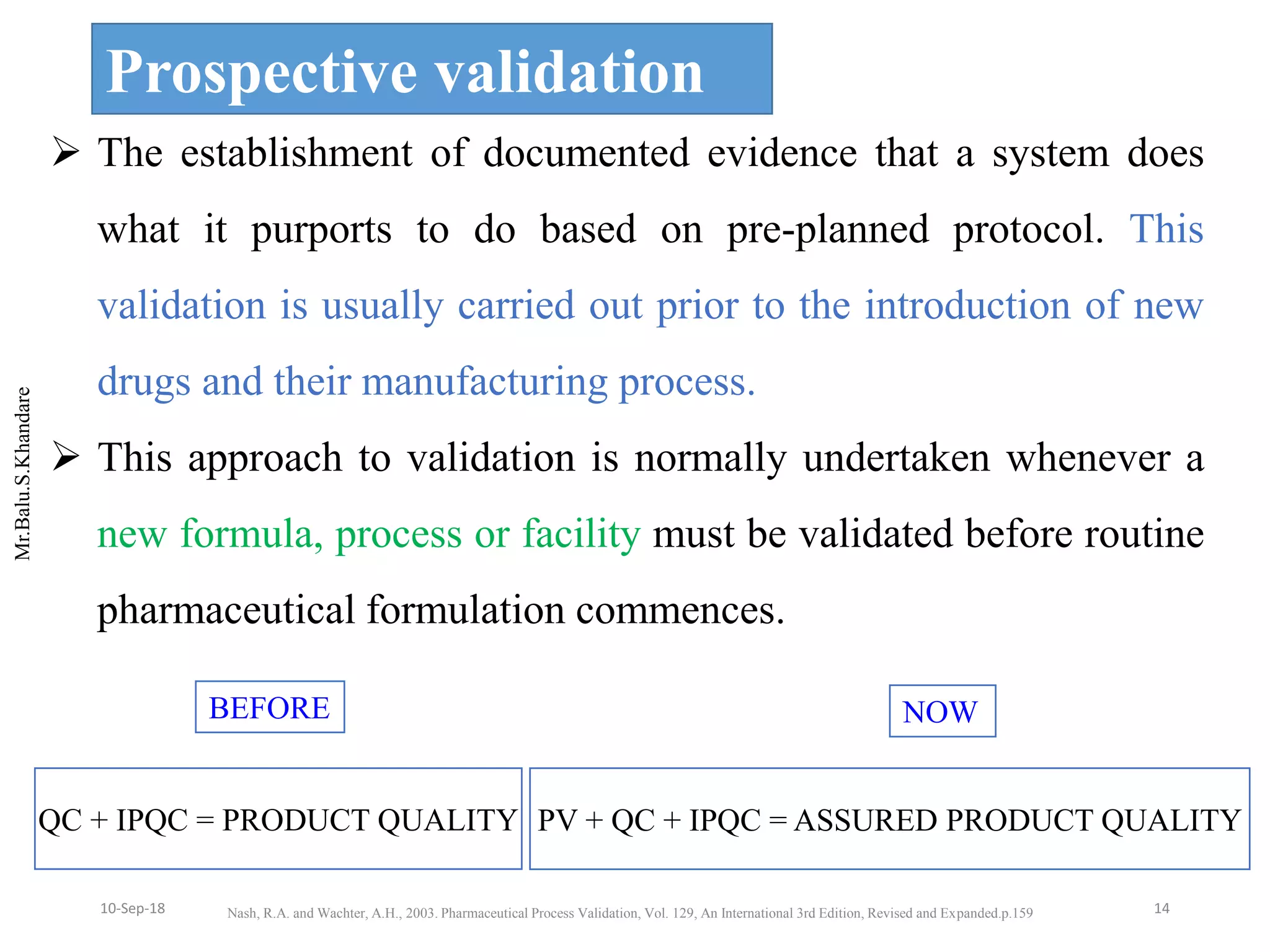
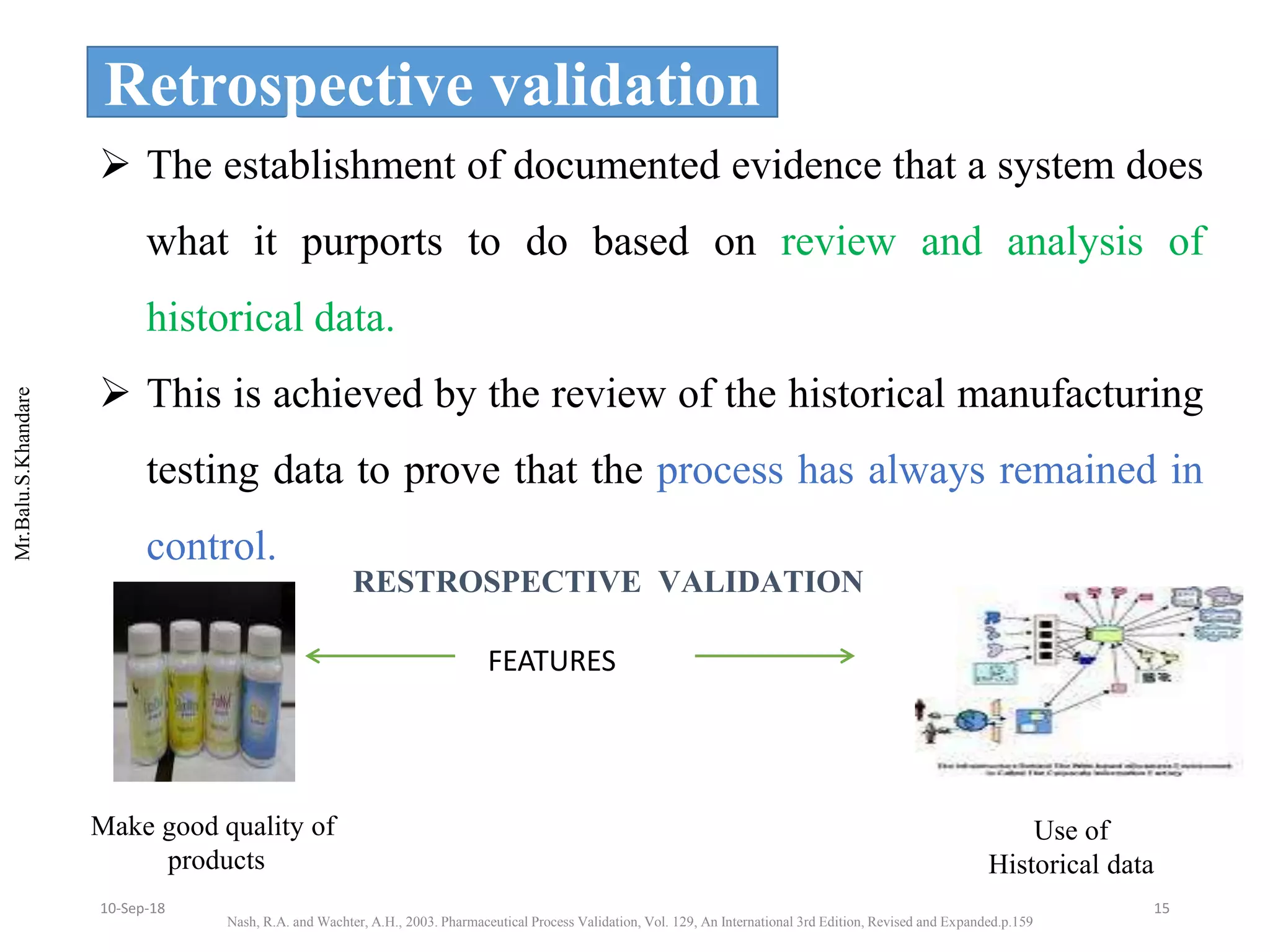
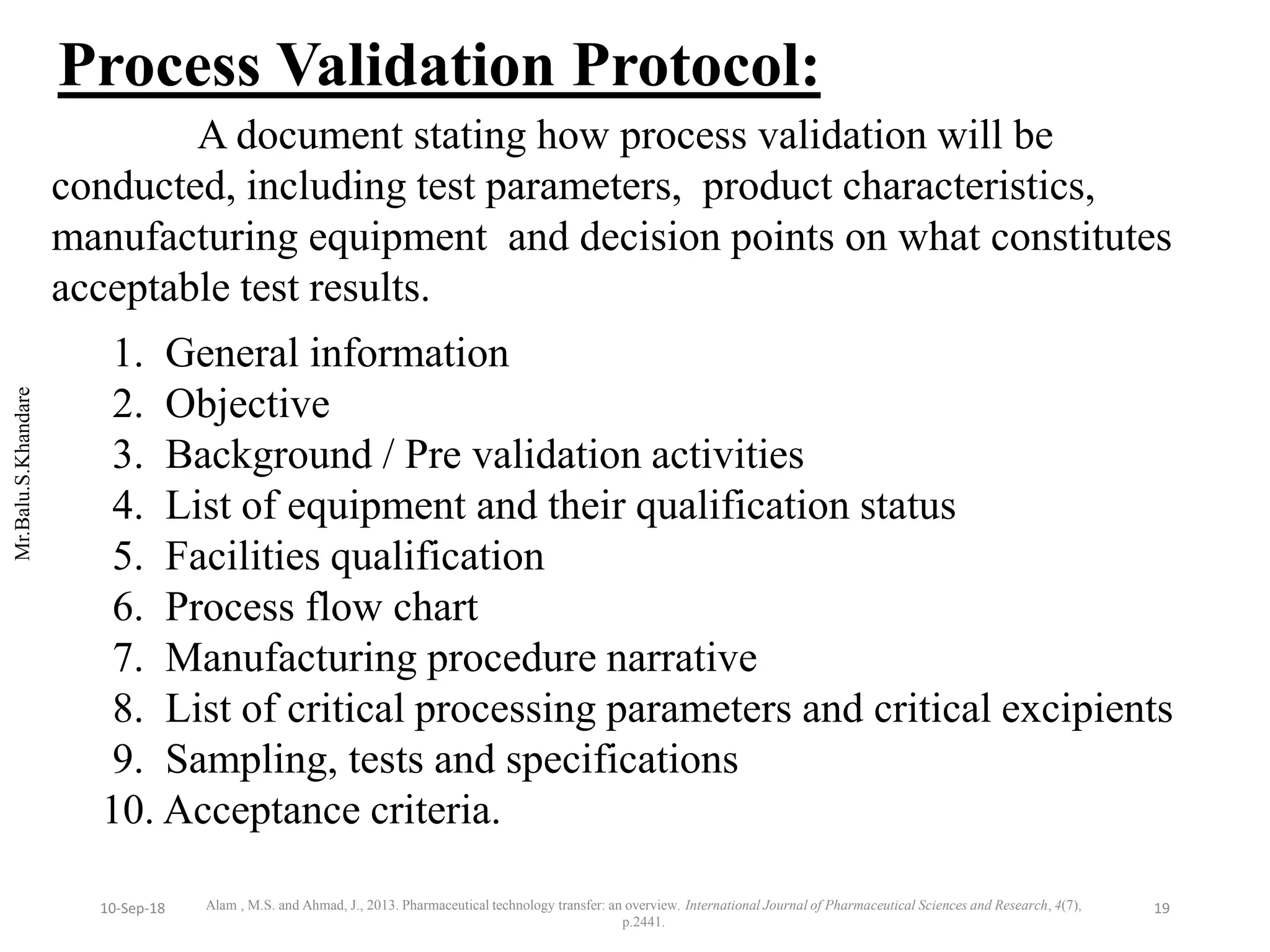
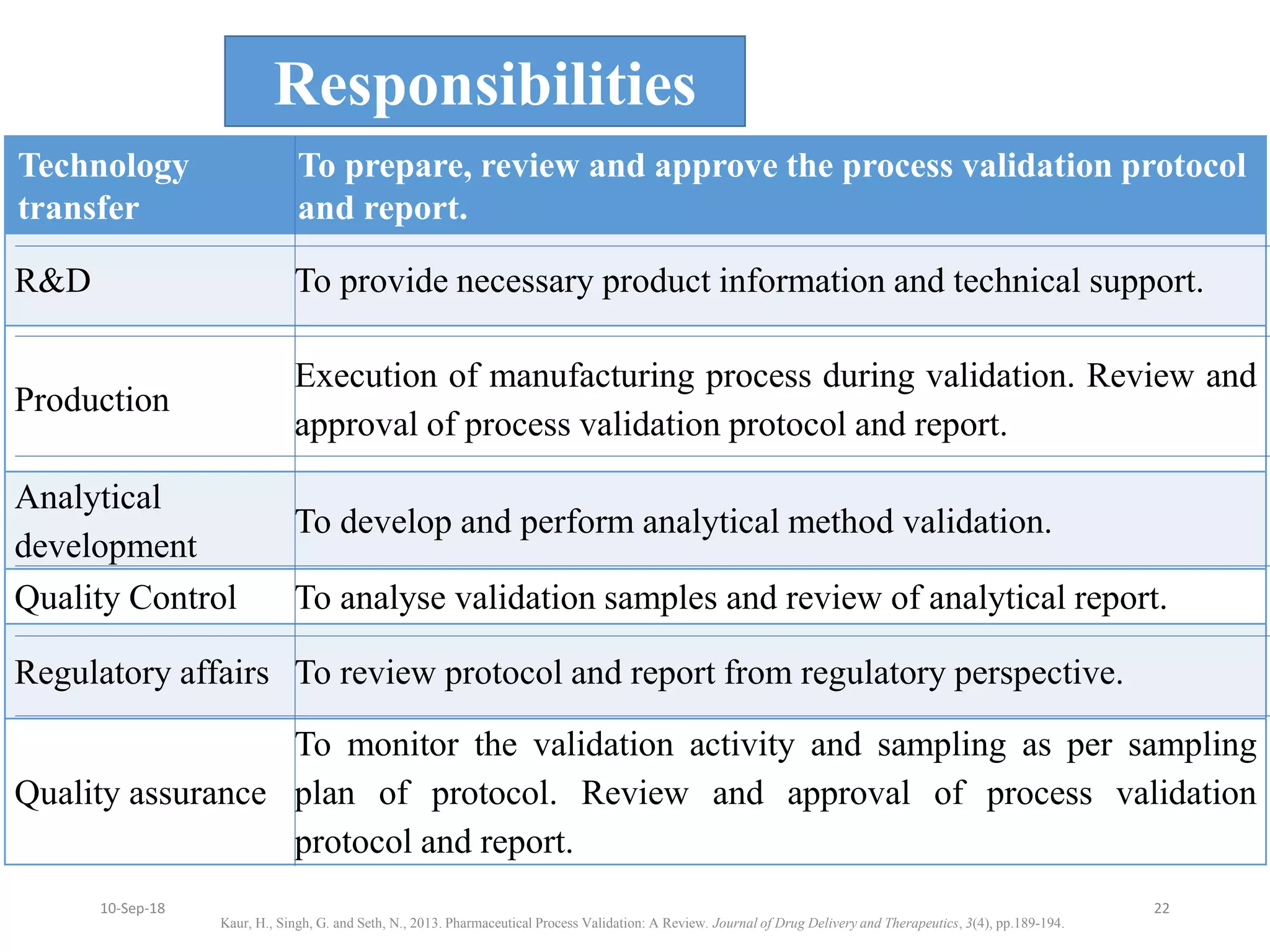
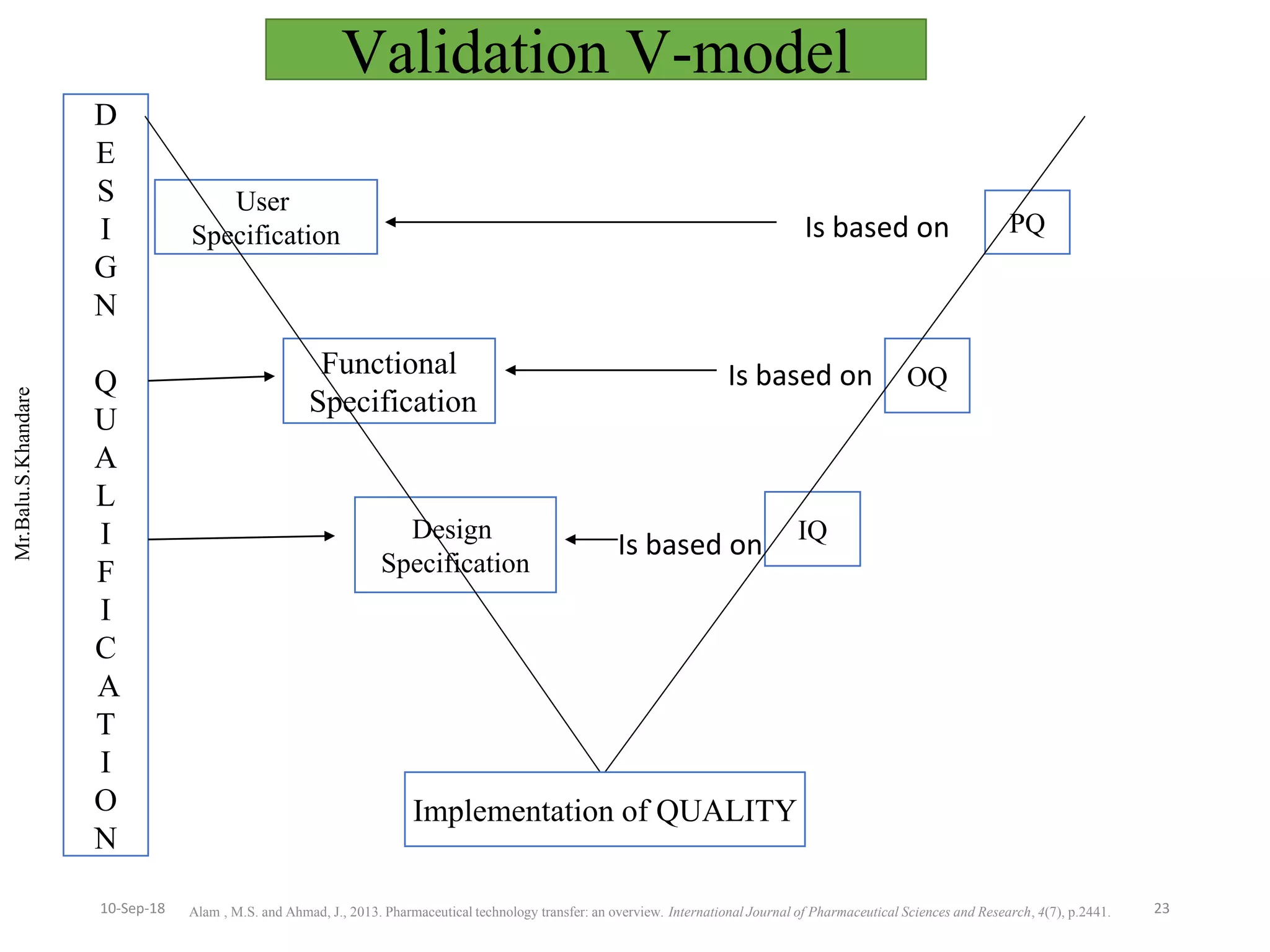
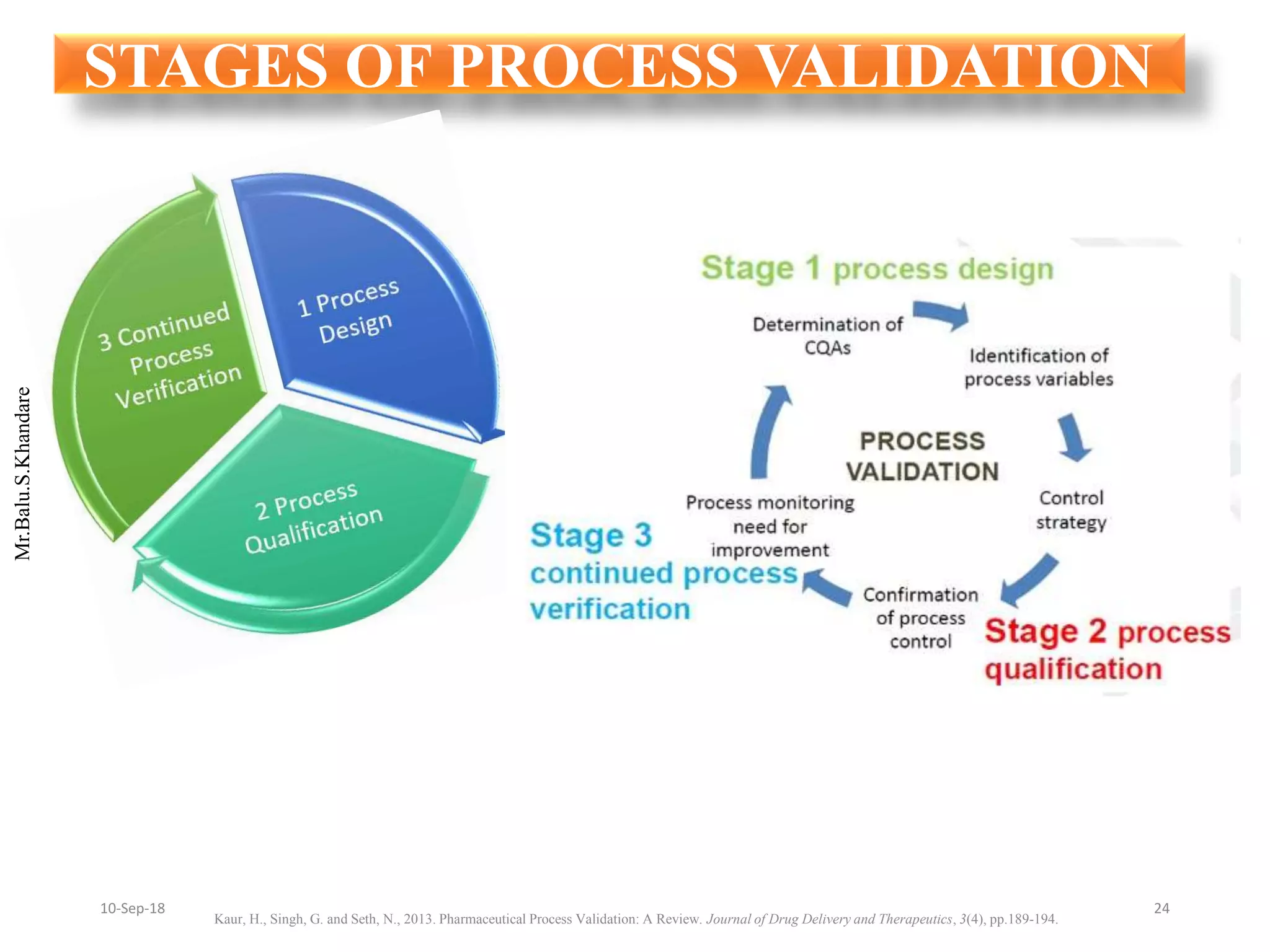
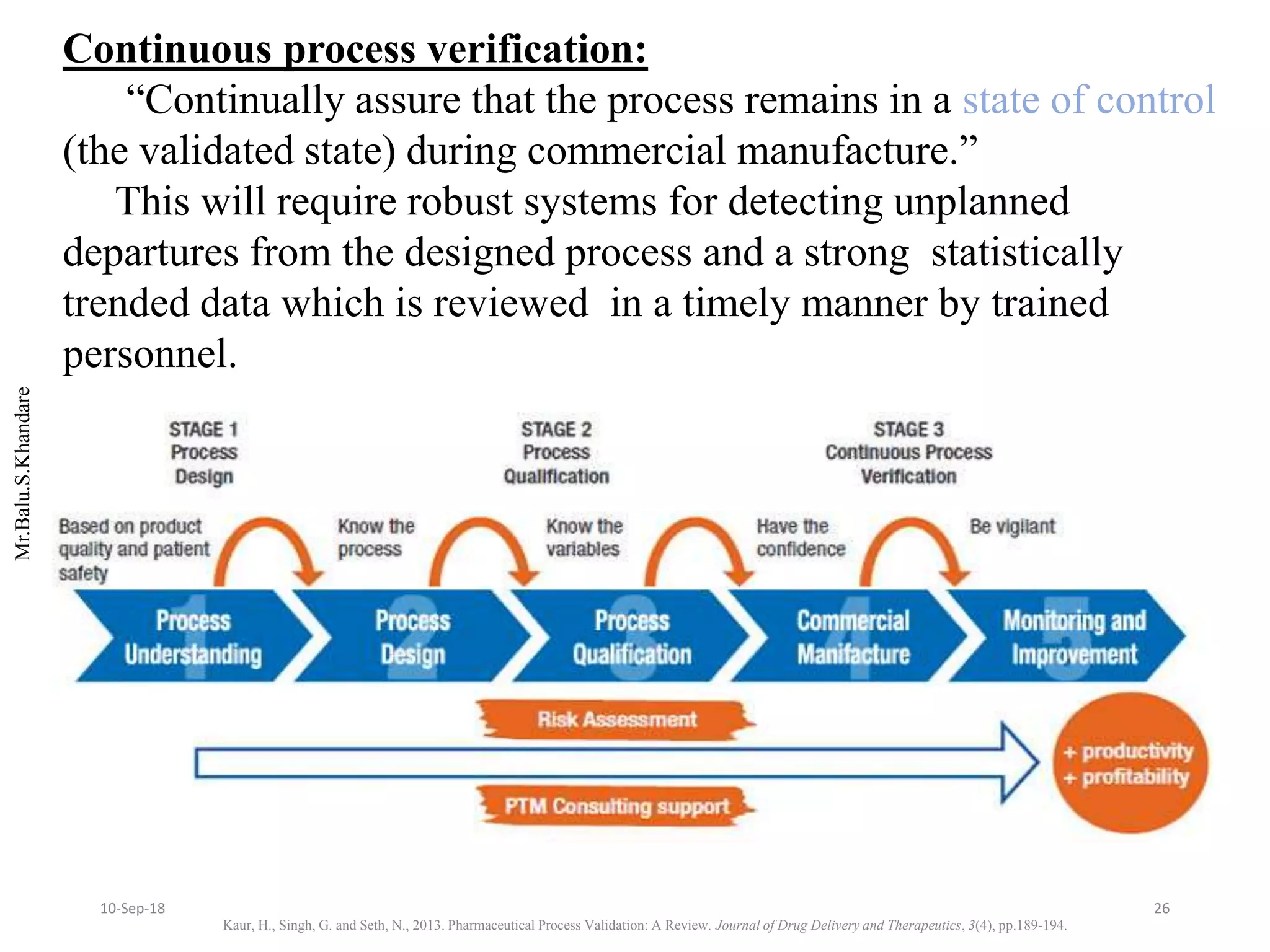
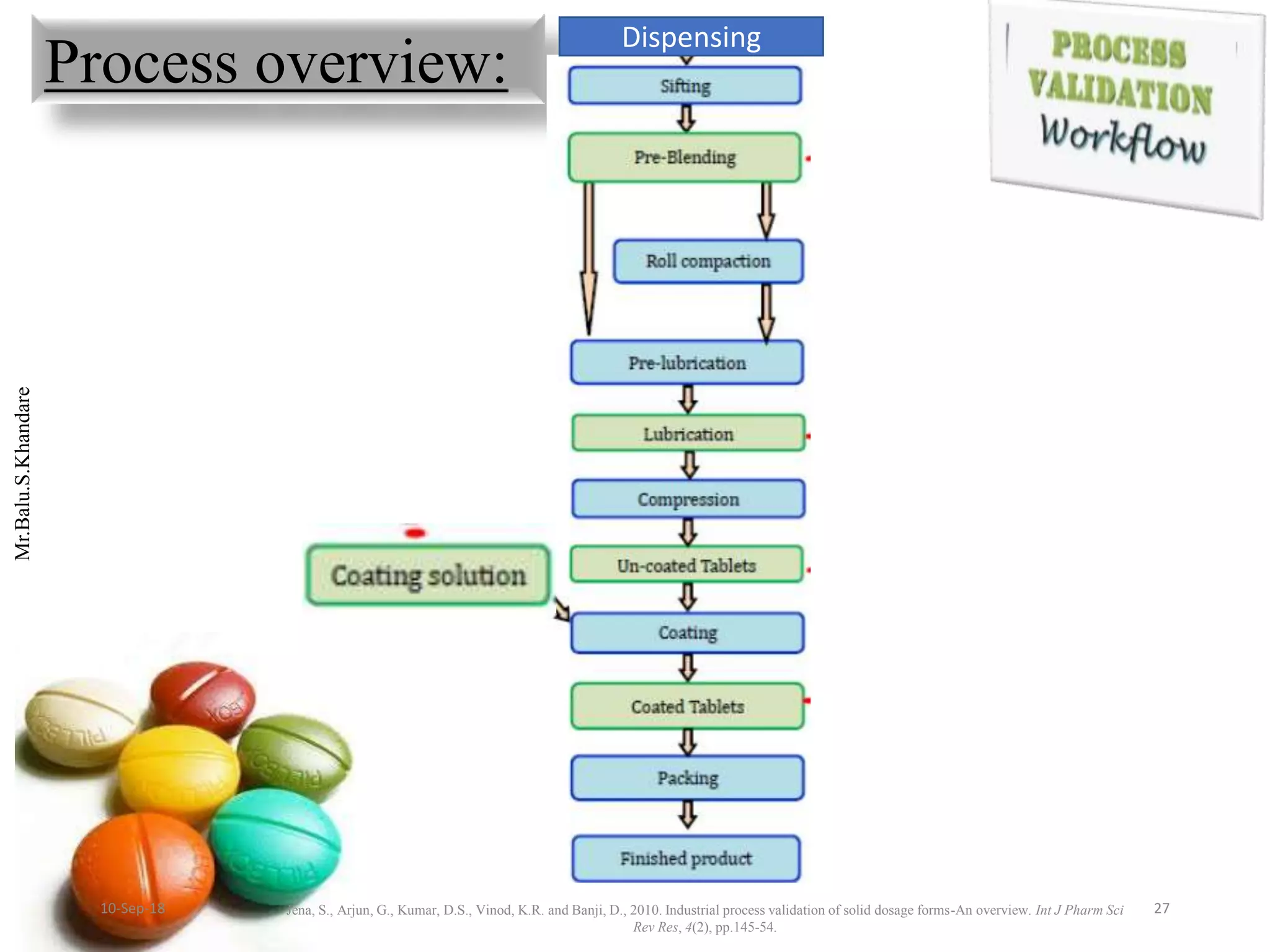
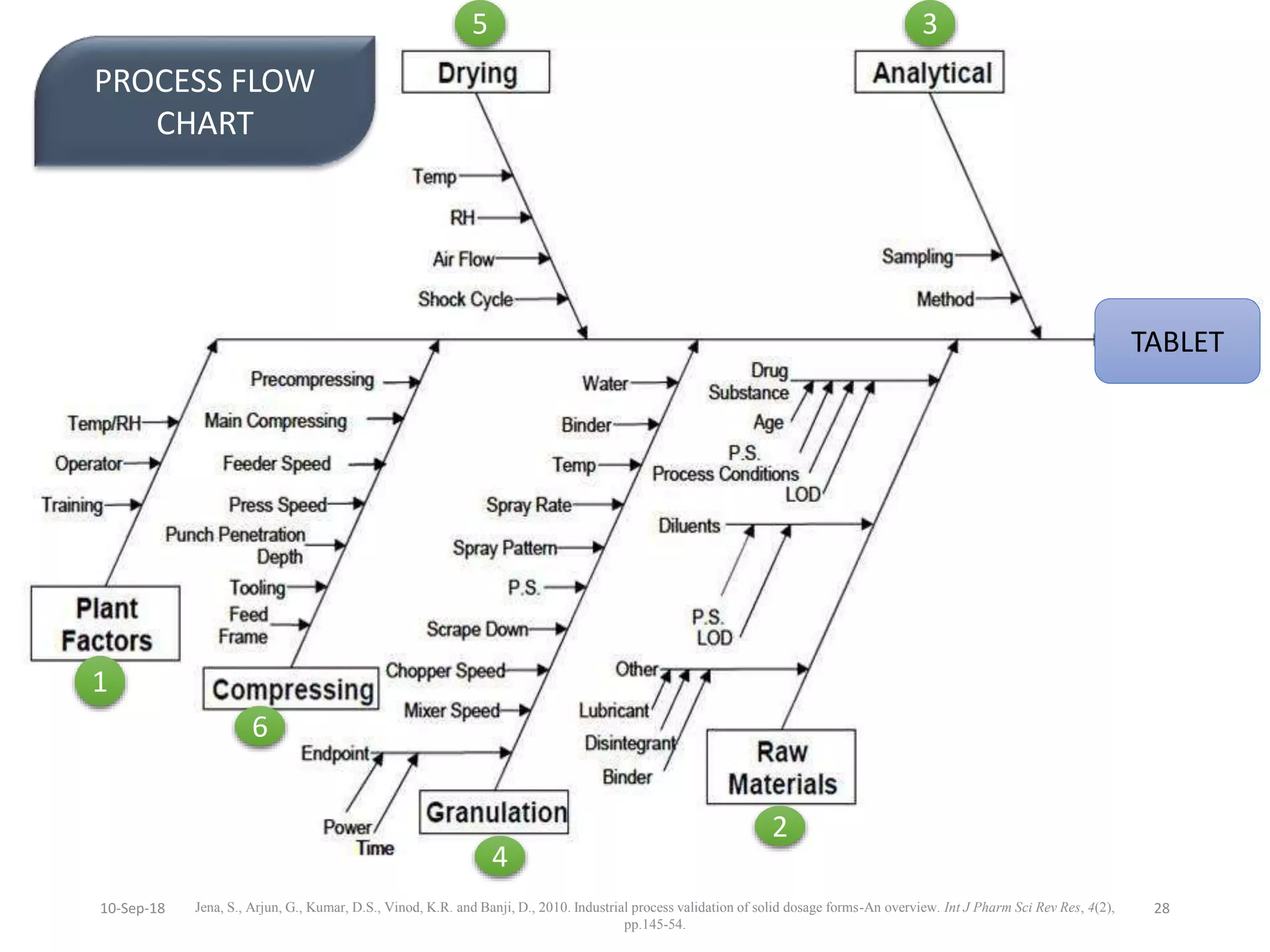
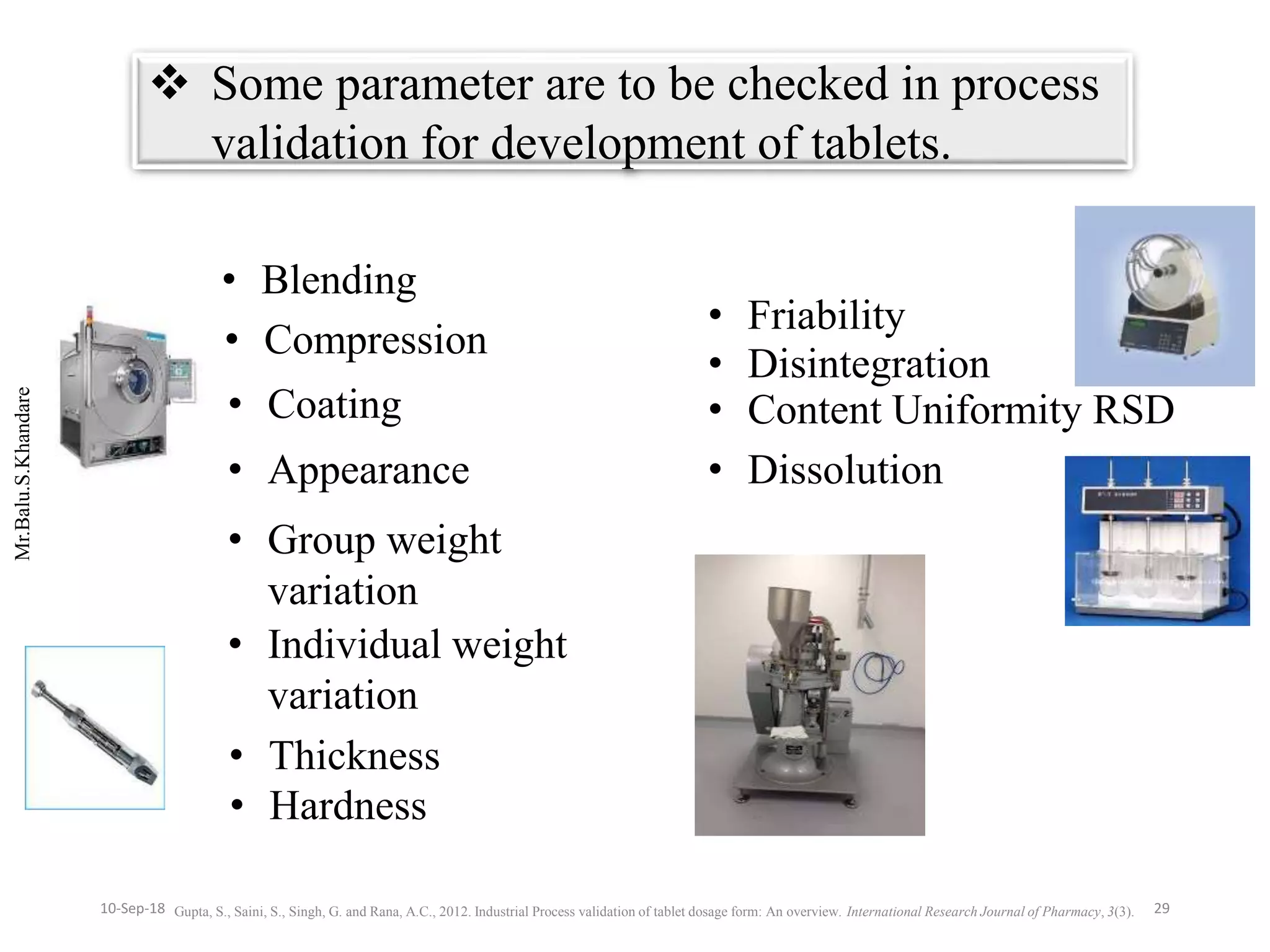
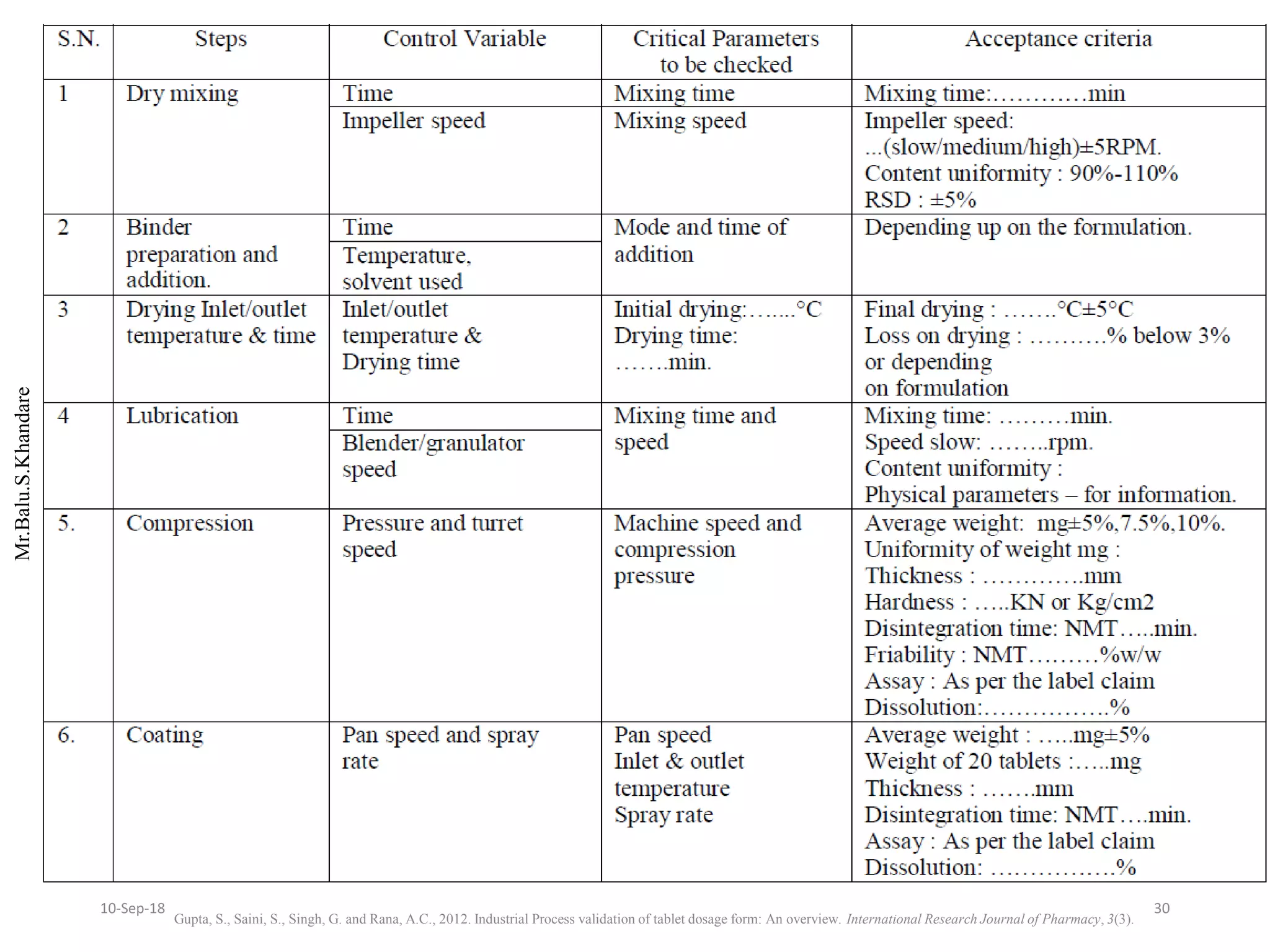
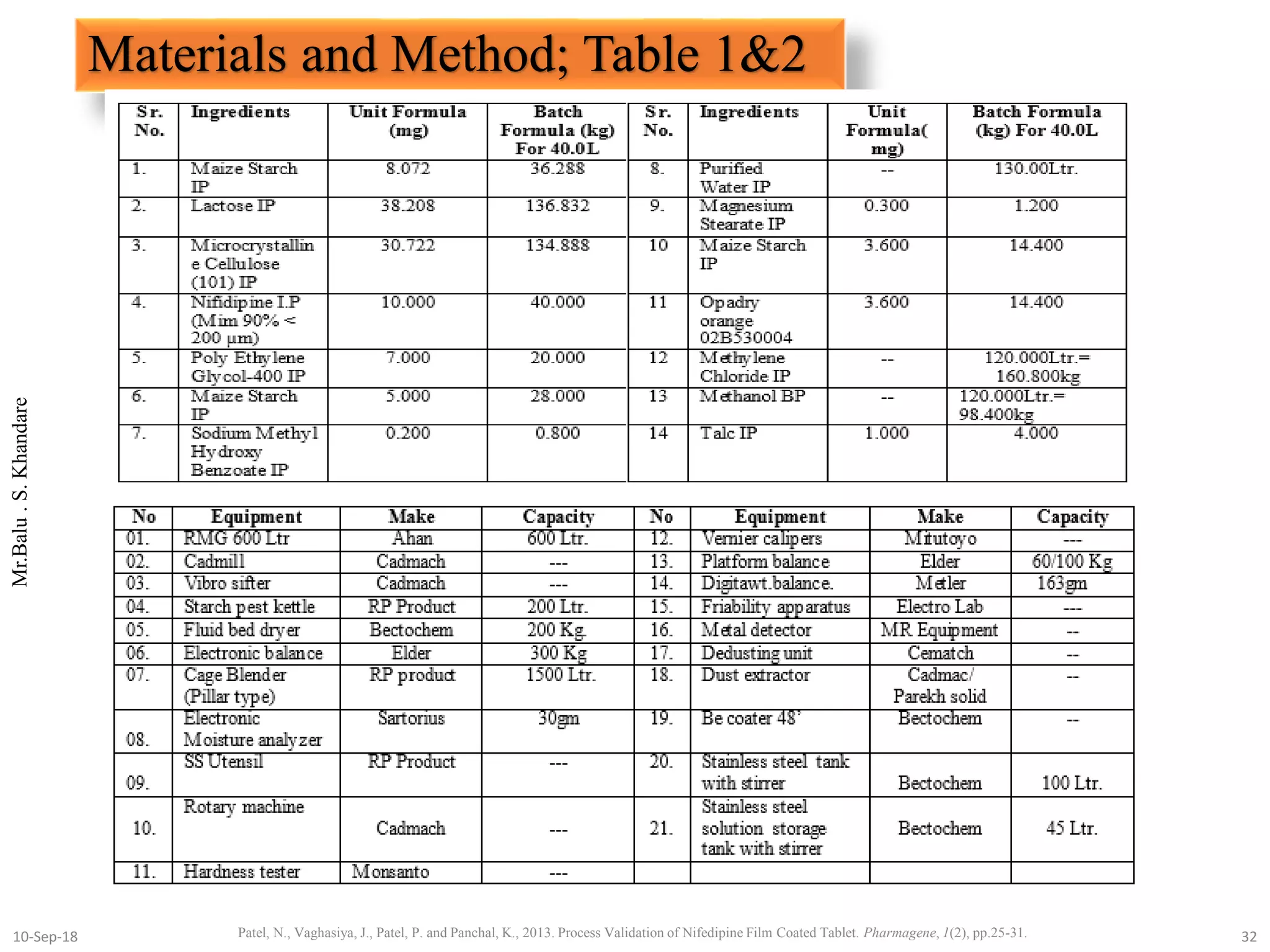
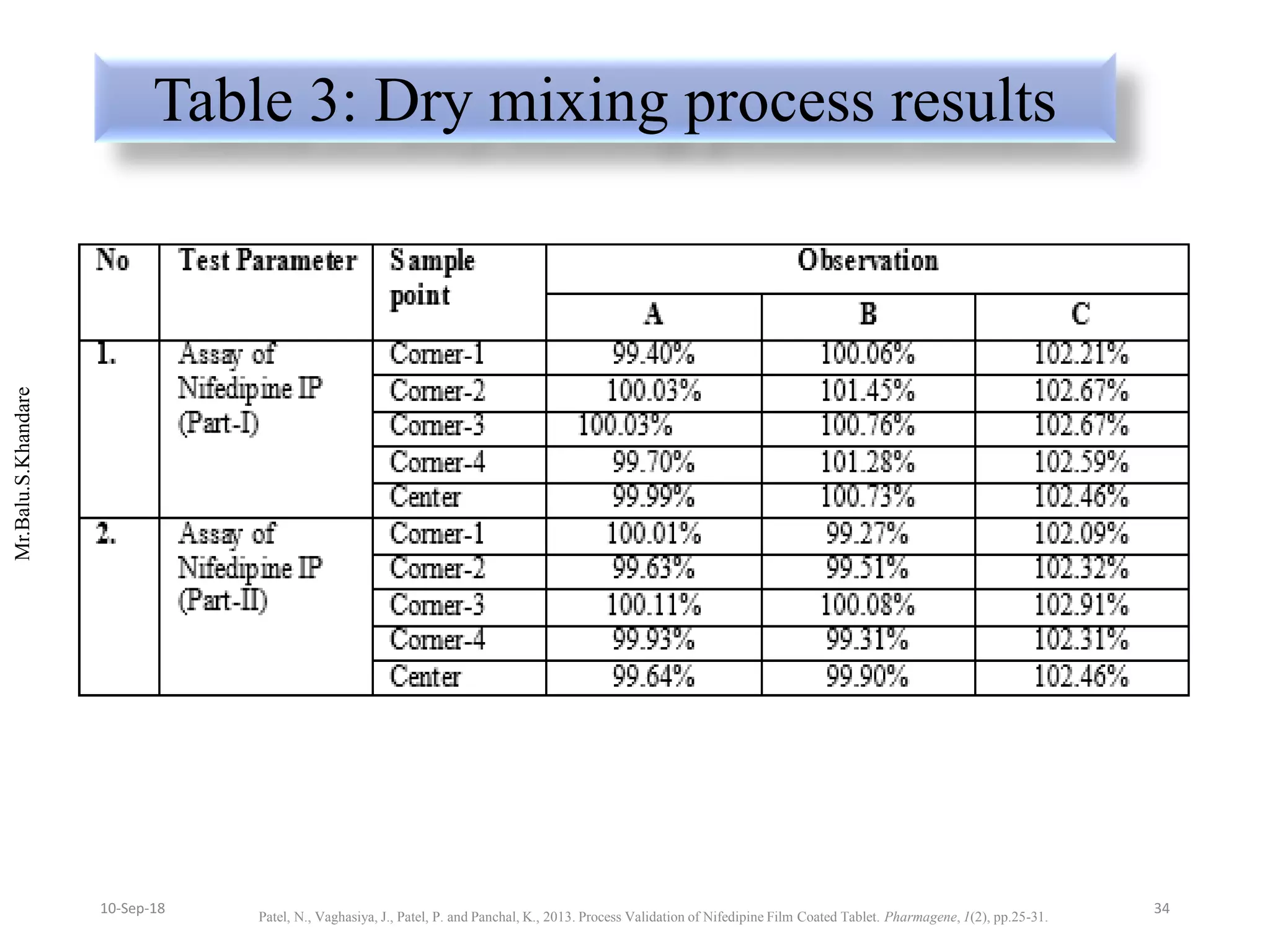
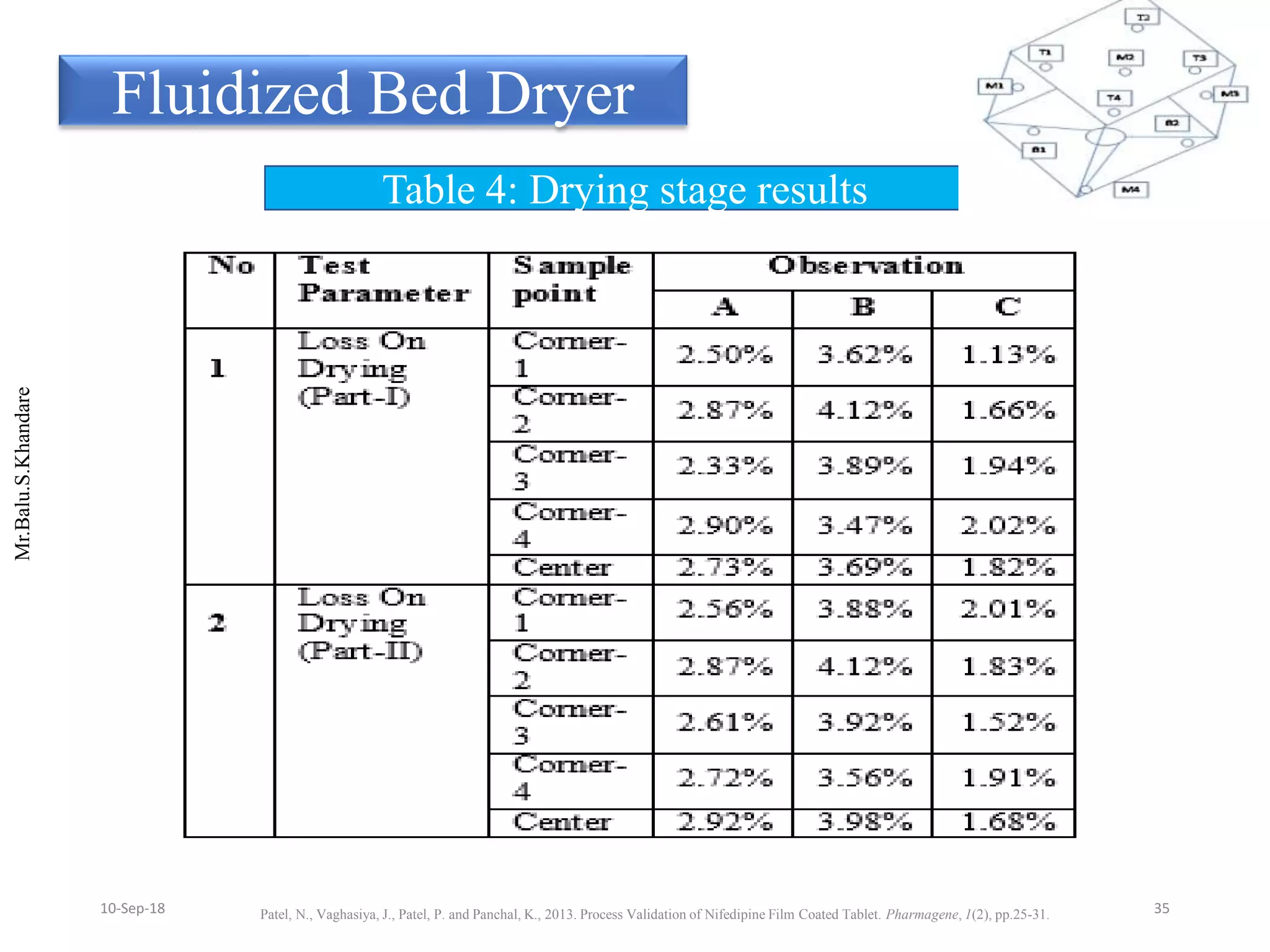
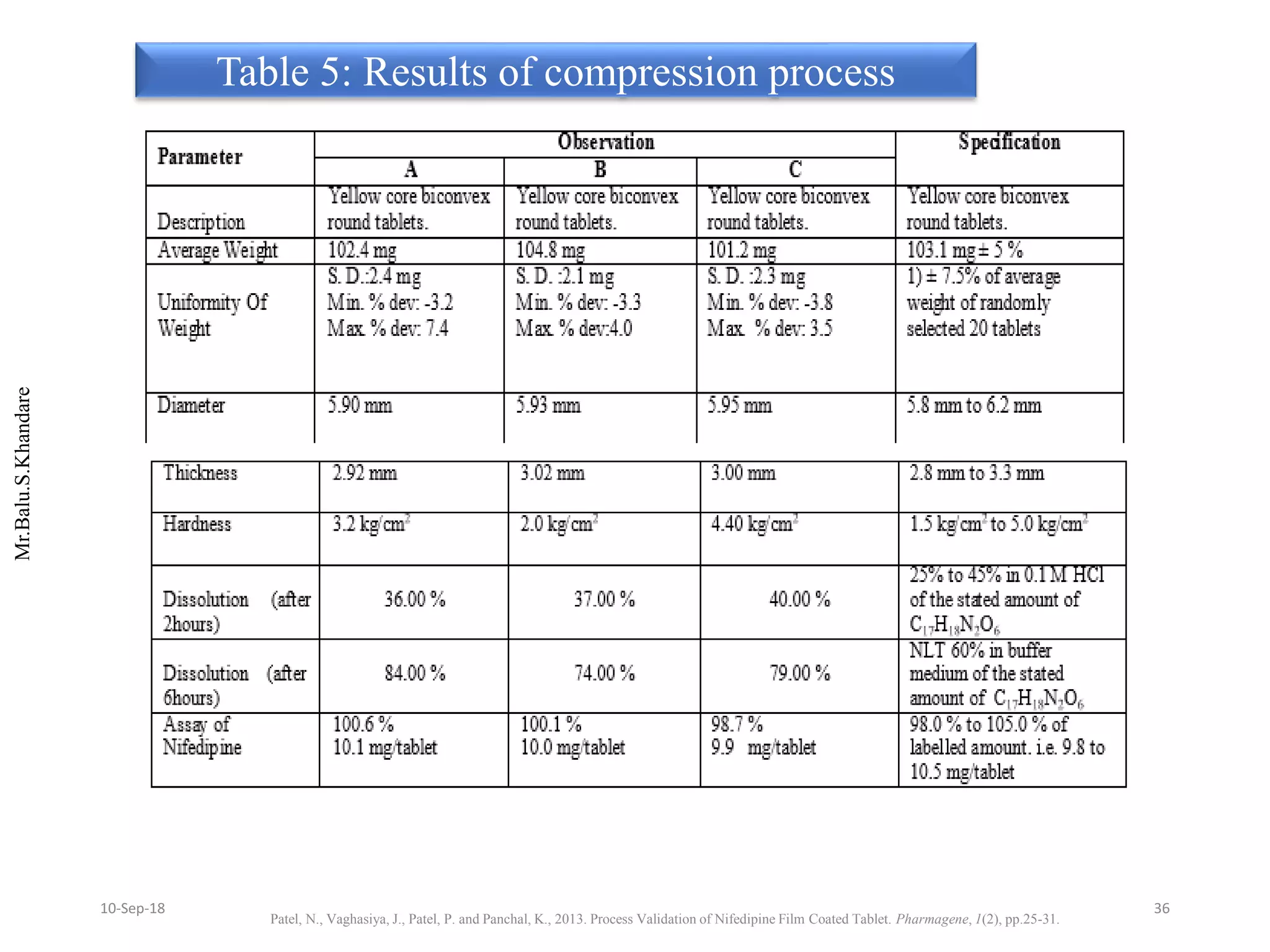
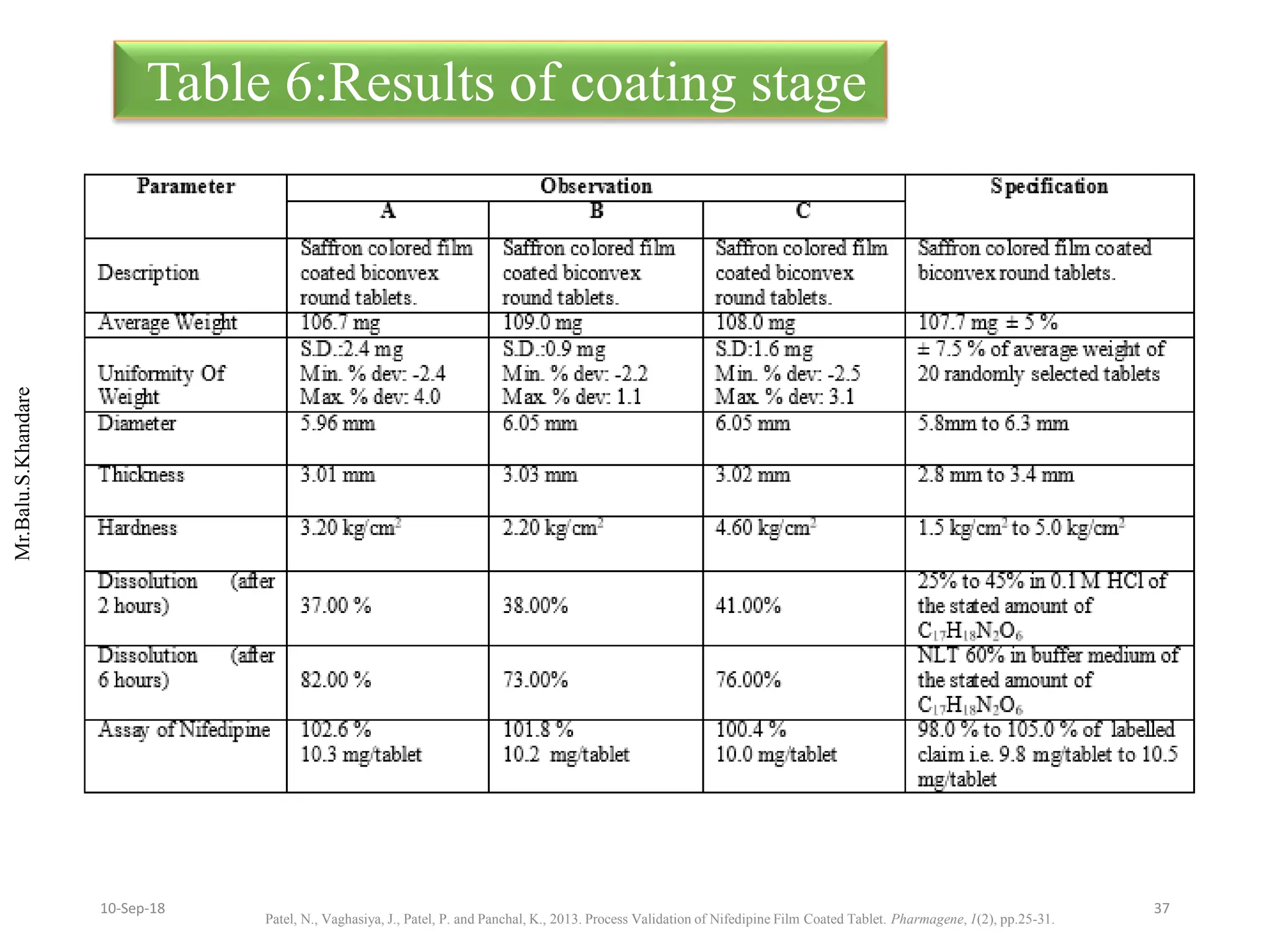
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on process validation for tablet development. It begins with an introduction to process validation, defining it as collecting and evaluating data from the design stage through commercial production to establish that the process is capable of consistently producing quality product. It then covers the types of process validation including prospective, retrospective, concurrent, and revalidation. The key steps in validation involve developing a protocol, conducting installation, operational, and performance qualifications, analyzing results, and reaching a conclusion. Parameters to be checked for tablet validation include blending, compression, coating, appearance, weight variation, thickness, hardness, friability, disintegration, content uniformity, and dissolution. A case study on validation of a nifedipine film