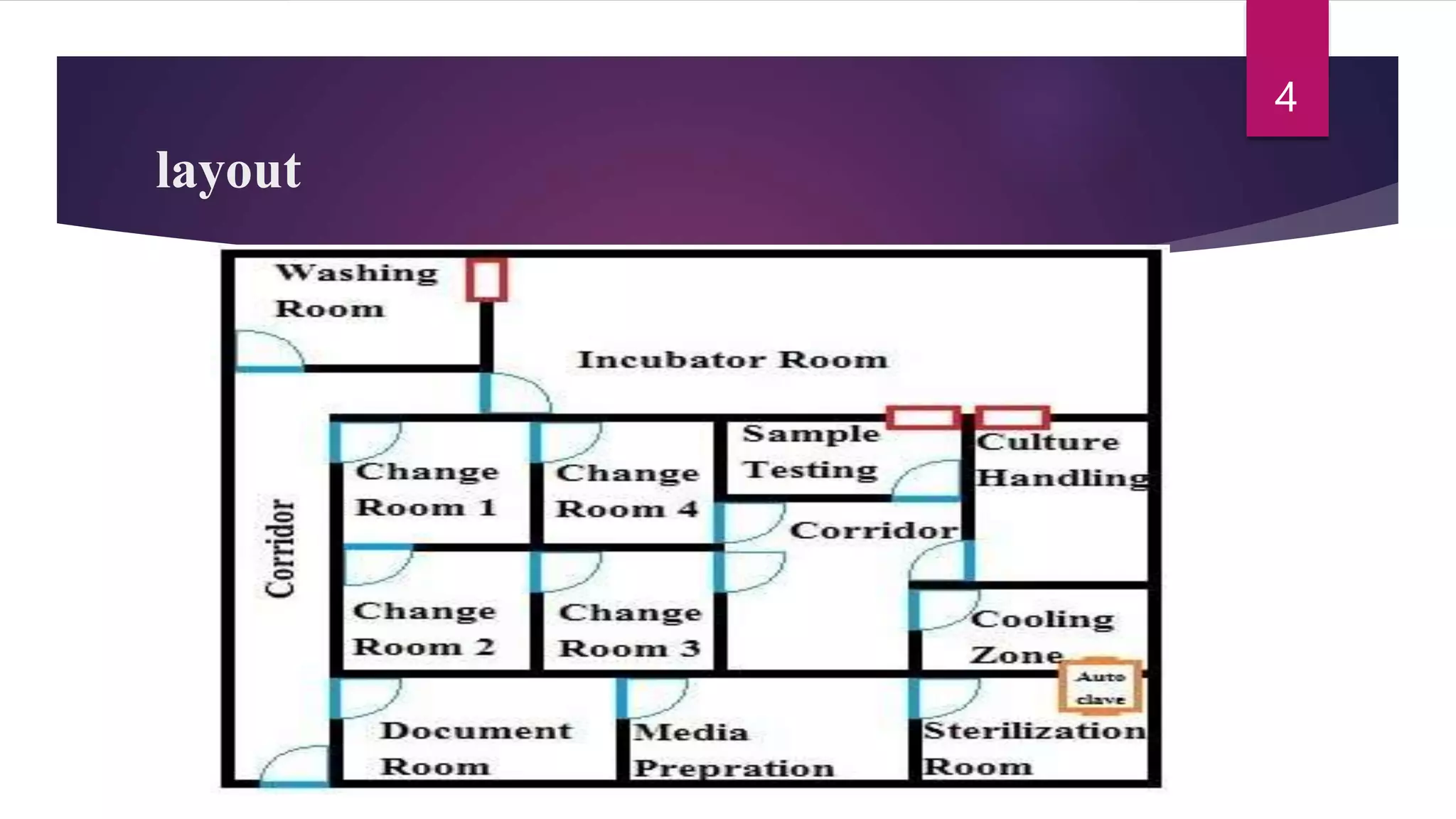
The document discusses auditing of microbiology laboratories. It provides definitions of auditing and outlines areas that should be assessed such as laboratory layout, equipment and facilities, documentation practices, and manufacturing processes. Key areas that are important for auditors to evaluate include laboratory organization, sampling procedures, media preparation, equipment maintenance, method validation, documentation, biosafety, and proficiency testing. The role of the microbiology laboratory in auditing sterile product facilities is also described.