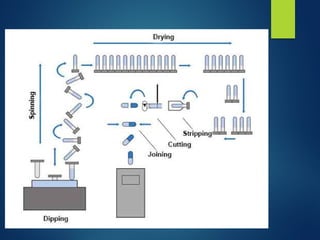
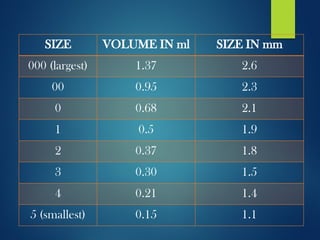
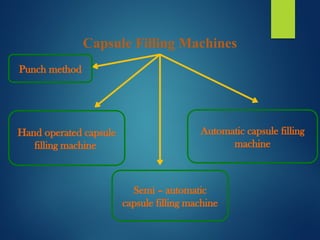
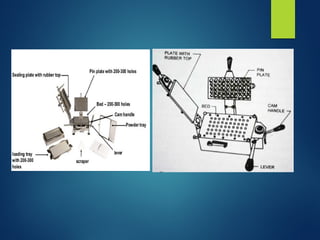
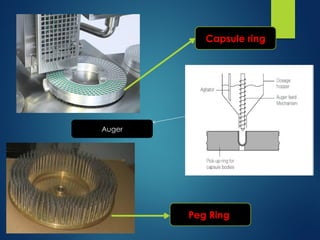
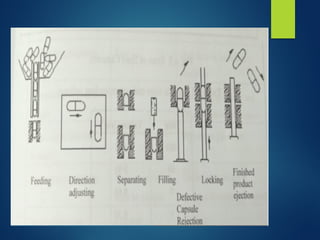
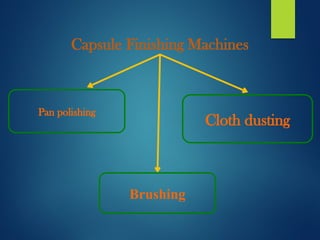
The document discusses the production, filling, and quality control of hard gelatin capsules, outlining the process from the formation of the capsule shells to their final inspection and labeling. It details the materials and methods used in capsule filling, including various machines and techniques employed for achieving precise dosages. Additionally, the document covers special formulation techniques and quality control tests necessary to ensure capsule efficacy and safety.