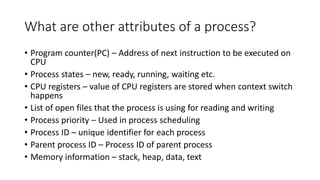
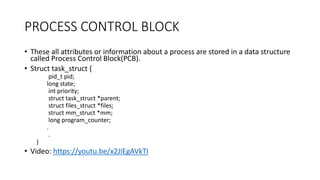
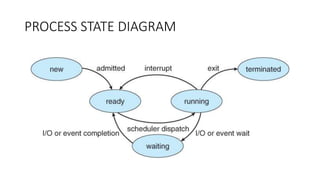
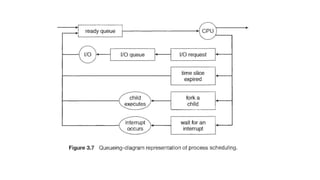
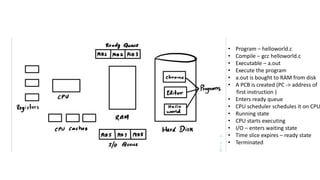
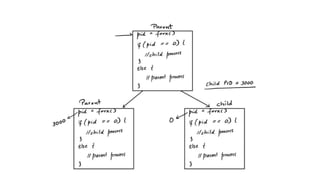
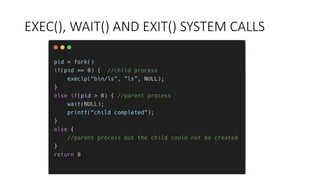
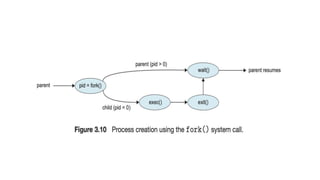
The document covers key concepts of process management in operating systems, explaining the differences between programs and processes, process control blocks, and various system calls such as fork(), exec(), wait(), and exit(). It also discusses process states, and the phenomena of zombie and orphan processes, providing formal definitions along with notable interview questions related to these topics. Additionally, it includes links to educational videos and examples to enhance understanding of process creation and management in Linux systems.