Embed presentation
Downloaded 345 times





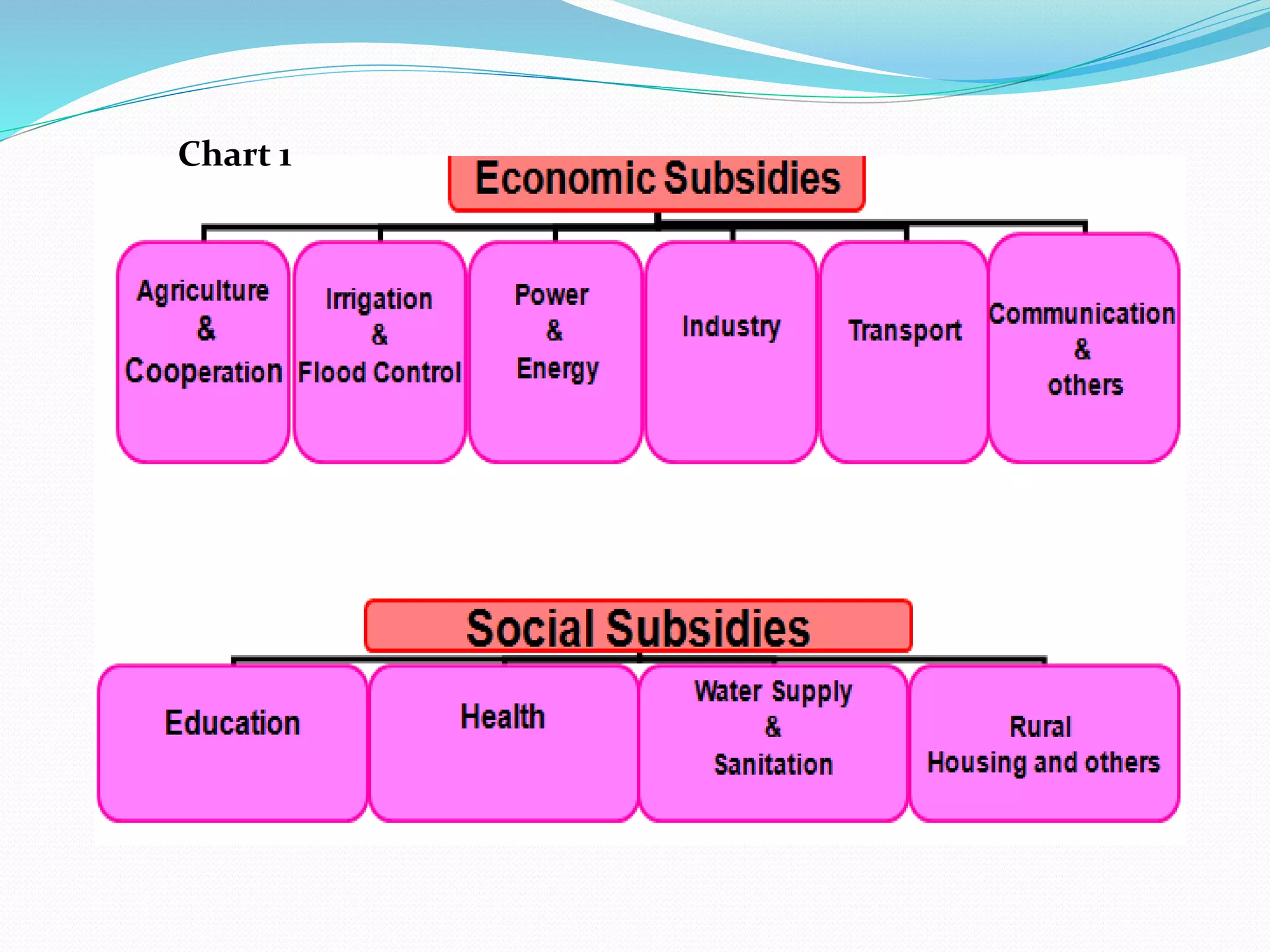
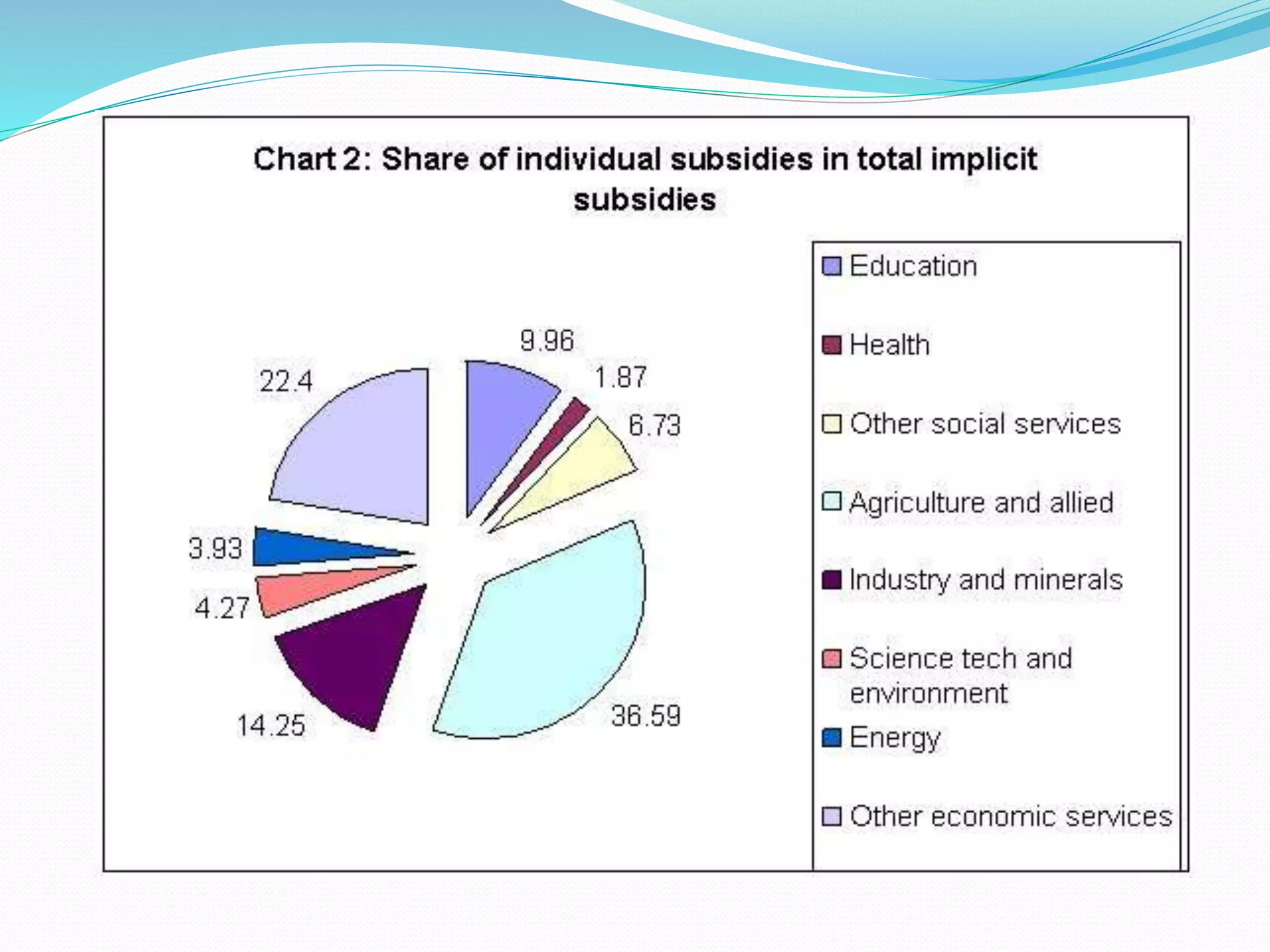


This document discusses the phases and types of subsidies in India. It describes subsidies as incentives that play an important role in economic development by optimizing resource allocation, stabilizing prices of essential goods and services, and redistributing income to help the poor. The document then outlines three phases of subsidy reform in India from 1996-2002, which gradually reduced and deregulated subsidies on petroleum products, fertilizers, and LPG. Finally, it lists six main types of subsidies used in India, including cash subsidies that provide goods at lower prices, interest subsidies, tax subsidies, in-kind subsidies, procurement subsidies, and regulatory subsidies.








