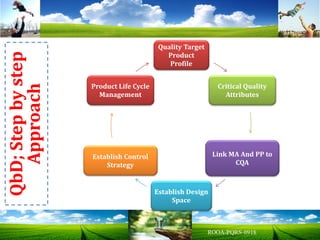
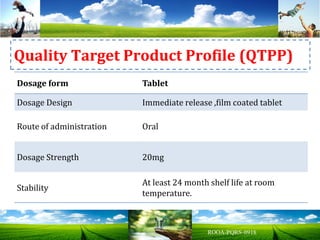
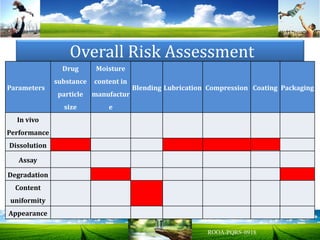
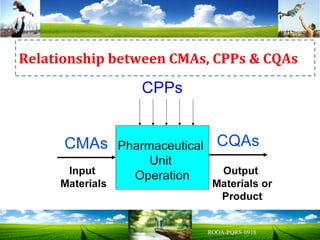
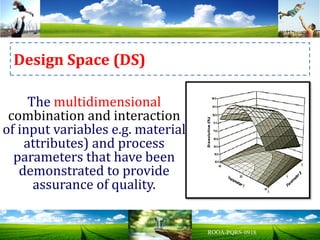
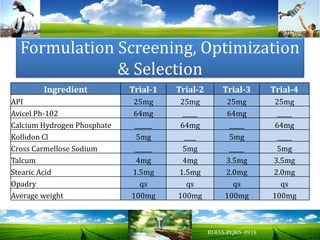
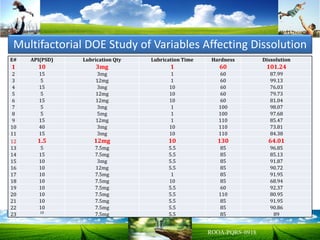
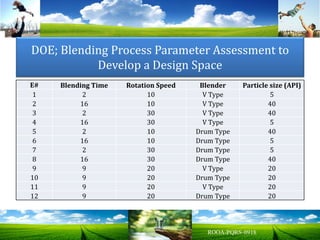
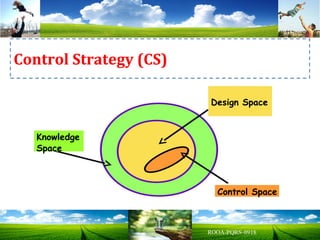
The document discusses key concepts in Quality by Design (QbD) for pharmaceutical product development including establishing a Quality Target Product Profile, identifying Critical Quality Attributes and linking them to Critical Material Attributes and Critical Process Parameters through Design of Experiments. It provides examples of establishing a design space for a tablet formulation through a multifactorial study of variables affecting dissolution and for a blending process through assessment of process parameters. The importance of developing a control strategy based on the design space to ensure final product quality is also highlighted.