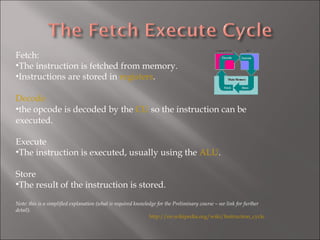
The CPU controls data transfer and operations, directing data to the ALU for calculations and ensuring correct data paths. It works with the system clock for synchronization. The ALU performs calculations and logic functions and determines relationships between values. Registers like the accumulator and address register store instruction and results. Buses transport signals between components, and the fetch-execute cycle fetches instructions from memory, decodes and executes them, then stores results.