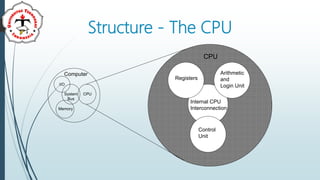
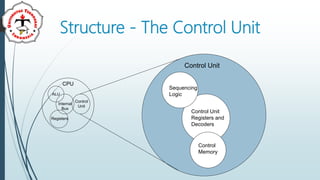
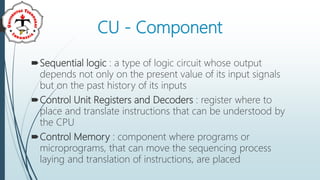
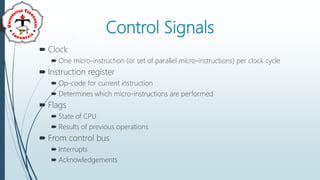
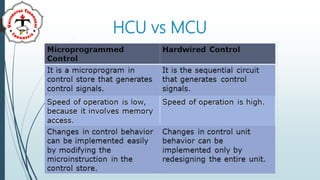
The document discusses the control unit (CU) of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). It explains that the CU controls instruction execution sequence, interprets instructions, guides data flow, regulates timing, and handles tasks like fetching, decoding, and storing results. The CU has three main components: sequential logic, control unit registers and decoders, and control memory where microprograms are stored. The document also compares hardwired control units, which have fixed circuitry, to microprogram control units, which use replaceable microprograms stored in control memory.