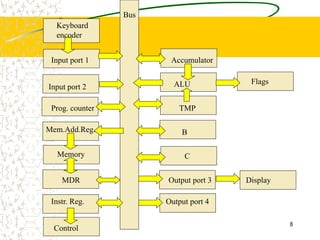
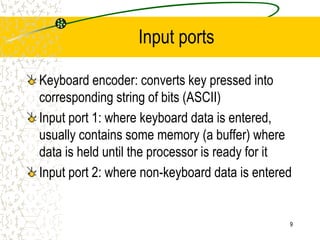
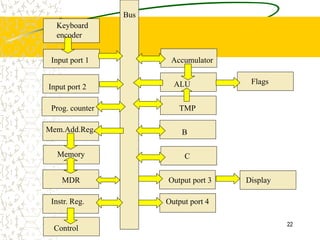
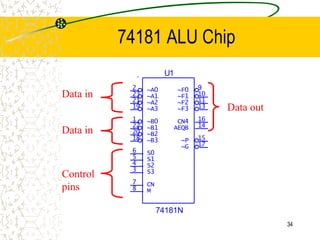
The document discusses microcode, which represents low-level instructions in digital computers, and is essential for converting higher-level commands into machine language. It explains the architecture of computers, including components such as the program counter, memory registers, input/output ports, and the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), detailing how data and instructions are processed. Additionally, it addresses microprogramming, control pins, and the importance of bus architecture in data movement and electrical signal management within computer systems.