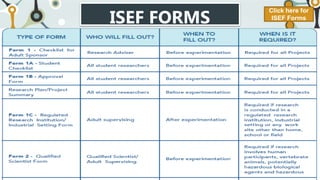
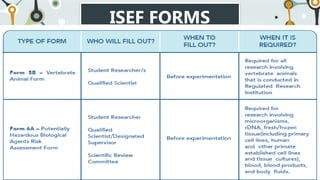
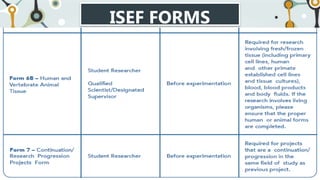
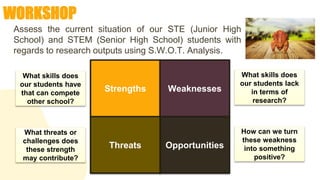
This document provides information about the National Science and Technology Fair (NSTF) Guidebook, including its objectives, fair features, roles and responsibilities of those involved, required International Science and Engineering Fair (ISEF) forms, and Gelacio's School-based Research Agenda. The guidebook is used for science fairs from the school to national level. It aims to develop STEM skills through research projects addressing real-world issues. The fair features different categories of competition and exhibitions. Key roles include students, advisors, qualified scientists, and committees that ensure safety and ethics.