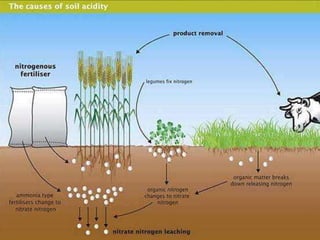
This document discusses problems in forest soils and their management. It identifies physical problems such as slow permeability, excessive permeability, subsurface hardening, surface crusting, shallow soils, and waterlogging. It also identifies chemical problems including salt-affected soils, alkaline soils, saline soils, and acid soils. Management strategies are provided for each problem, such as drainage, adding organic matter or sand to change texture, liming, and selecting suitable tree species. The challenges of managing problematic forest soils are utilizing degraded lands for plantation, providing adequate nutrients, and balancing inputs with plant needs. Soil conservation is important as soil is fundamental to terrestrial ecology.