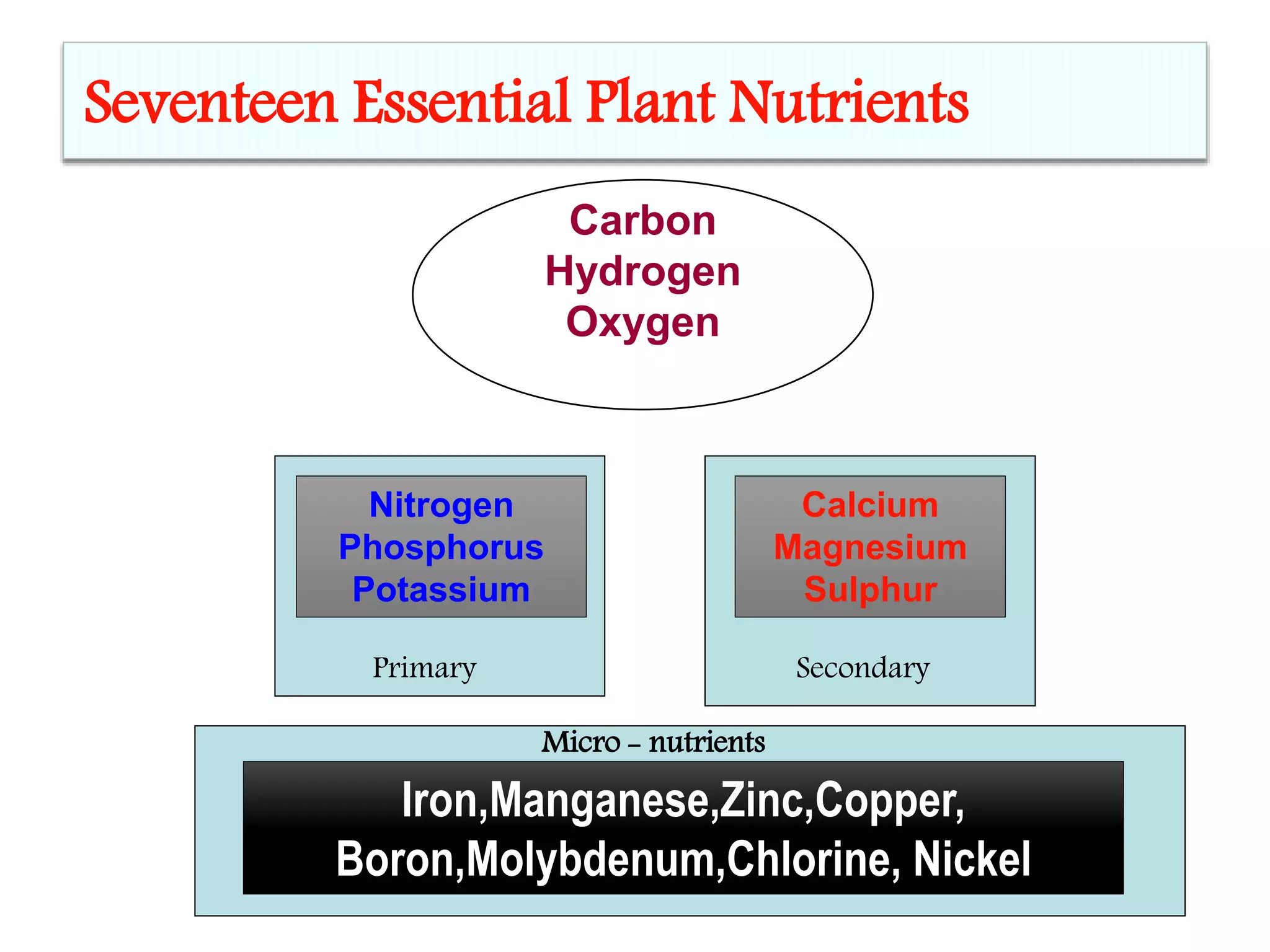
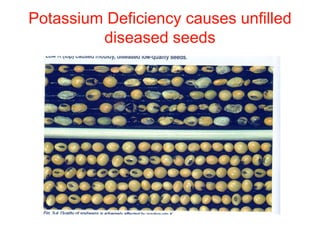
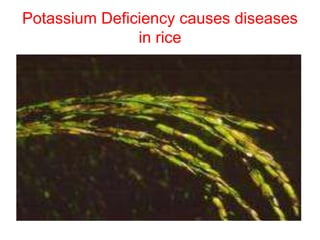
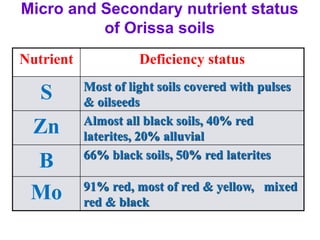
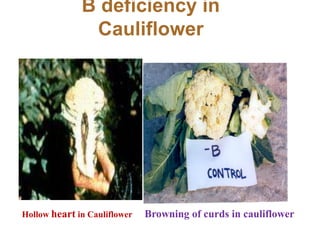
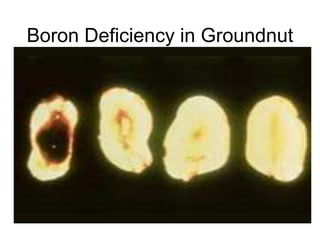
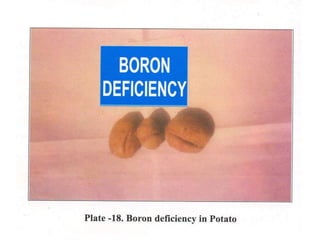
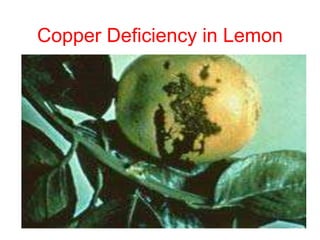
This document discusses 17 essential plant nutrients and their functions, as well as deficiencies that can occur from insufficient nutrients in soil. It covers primary, secondary, and micro nutrients - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur, iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, molybdenum, chlorine, and nickel. The document also notes that imbalanced fertilizer use has depleted soil fertility and reduced agricultural productivity and production, posing a threat to national food security.