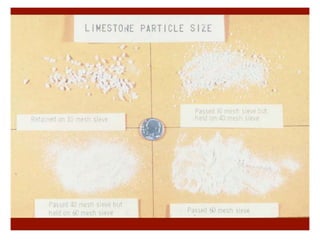
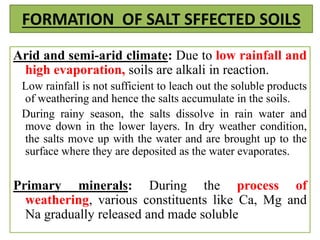
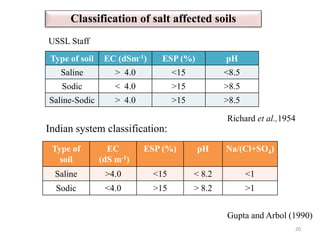
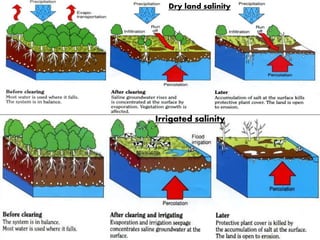
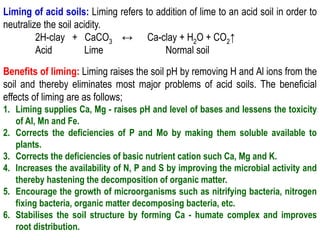
Soil fertility refers to a soil's ability to sustain plant growth through adequate nutrient supply and lack of toxins. Soil fertility comes from inherent nutrients in parent material and acquired fertility from inputs like manure and fertilizers. Factors affecting soil fertility include climate, topography, and microorganisms. Soil pH impacts nutrient availability, with acidic soils having issues like aluminum/manganese toxicity and phosphorus deficiency. Saline soils form in arid areas due to low rainfall, poor drainage, and accumulation of salts from irrigation water, fertilizers, or sea spray. Liming can remedy acidic soil problems by raising pH and supplying calcium and magnesium.













![Liming materials: defined as the substance whose Ca and Mg
compounds are capable of neutralizing the soil acidity.
1. Quick lime (CaO) / Burnt lime / oxide of lime / simply lime.
2. Slacked lime [Ca(OH)2] or hydrated lime/ hydroxide of lime
3. Calcitic lime stone (CaCO3) / Agricultural lime or carbonate
of lime which is ground lime stone.
4. Dolomite lime stone (CaCO3. MgCO3) - high in Mg
5. Industrial wastes rich in Ca, Basic slag-Ca silicate
Lime recommendations: Soil pH is a measure of the degree of
soil acidity /basicity. pH is otherwise is an indicator of whether lime
should be applied to the soil. But it is not a measure of how much
lime is needed to obtain a desired change in pH.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soilfertility-220903140635-d0048530/85/SOIL-FERTILITY-pptx-15-320.jpg)