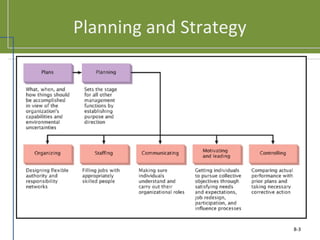
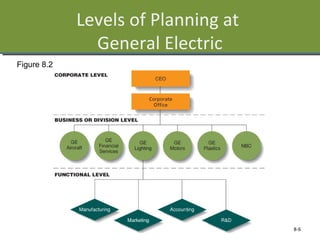
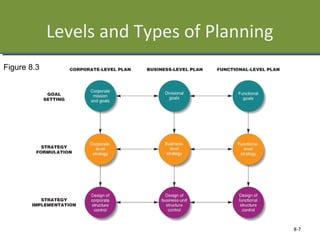
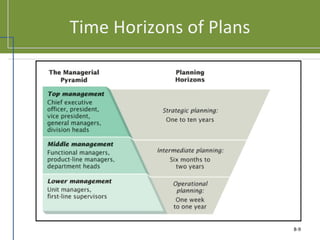
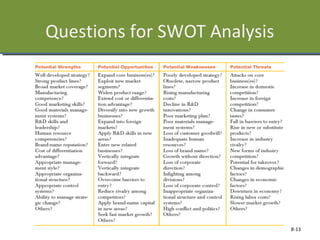
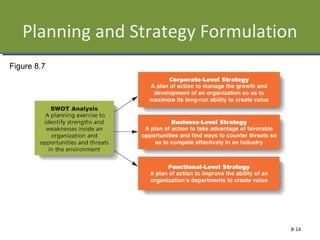
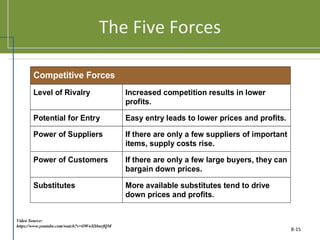
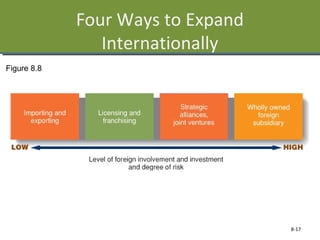
This document discusses planning and strategy for organizations. It defines planning as identifying goals and courses of action, while strategy is deciding on goals, actions, and resource allocation. There are different levels and time horizons for plans, from short-term operational plans to long-term strategic plans. Scenario planning involves generating forecasts of future conditions and responses. Strategies are formulated through analyzing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats via SWOT analysis. Porter's five competitive forces model also informs strategy by assessing rivalry, potential entry, supplier and customer power, and substitutes.