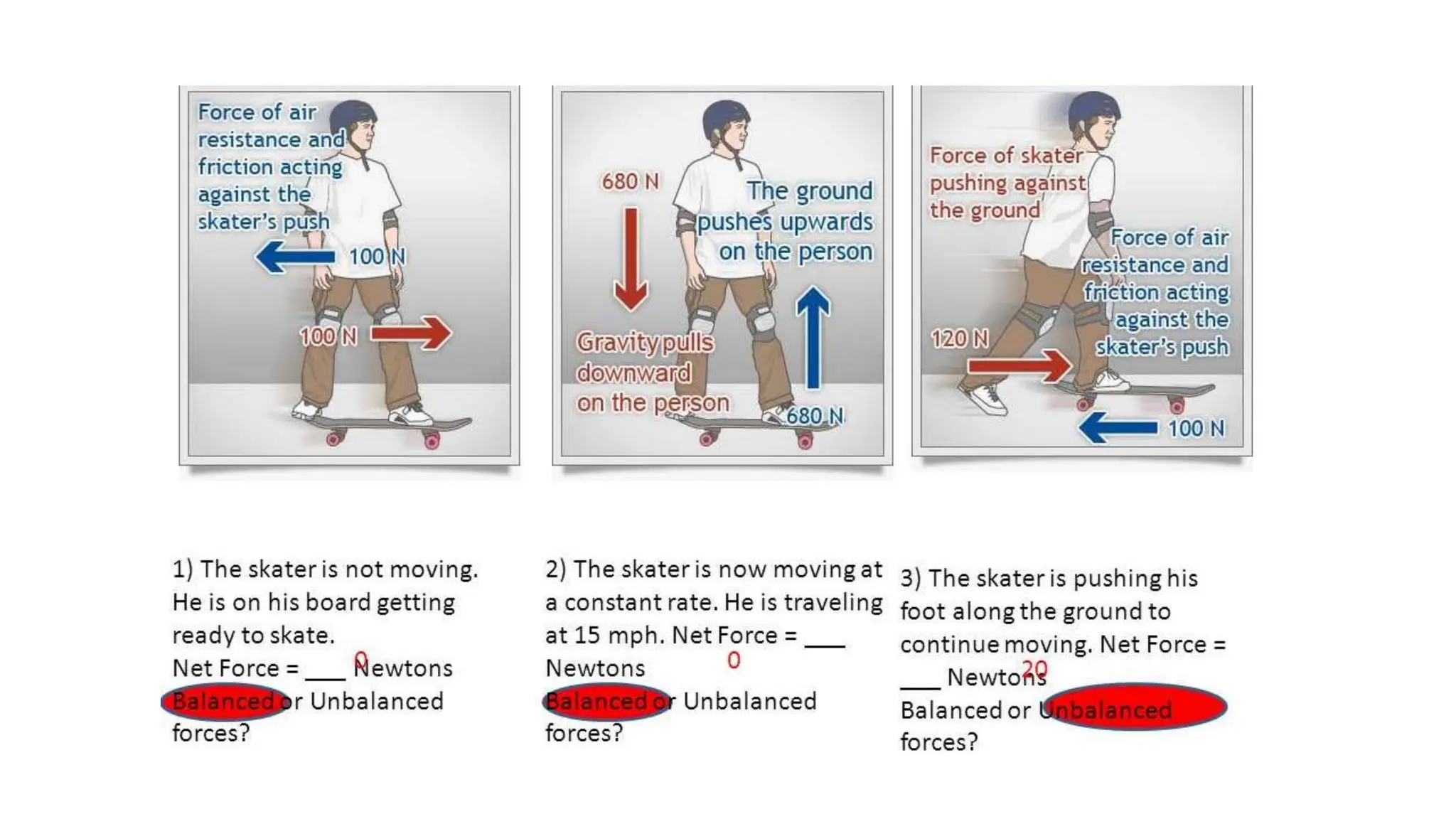
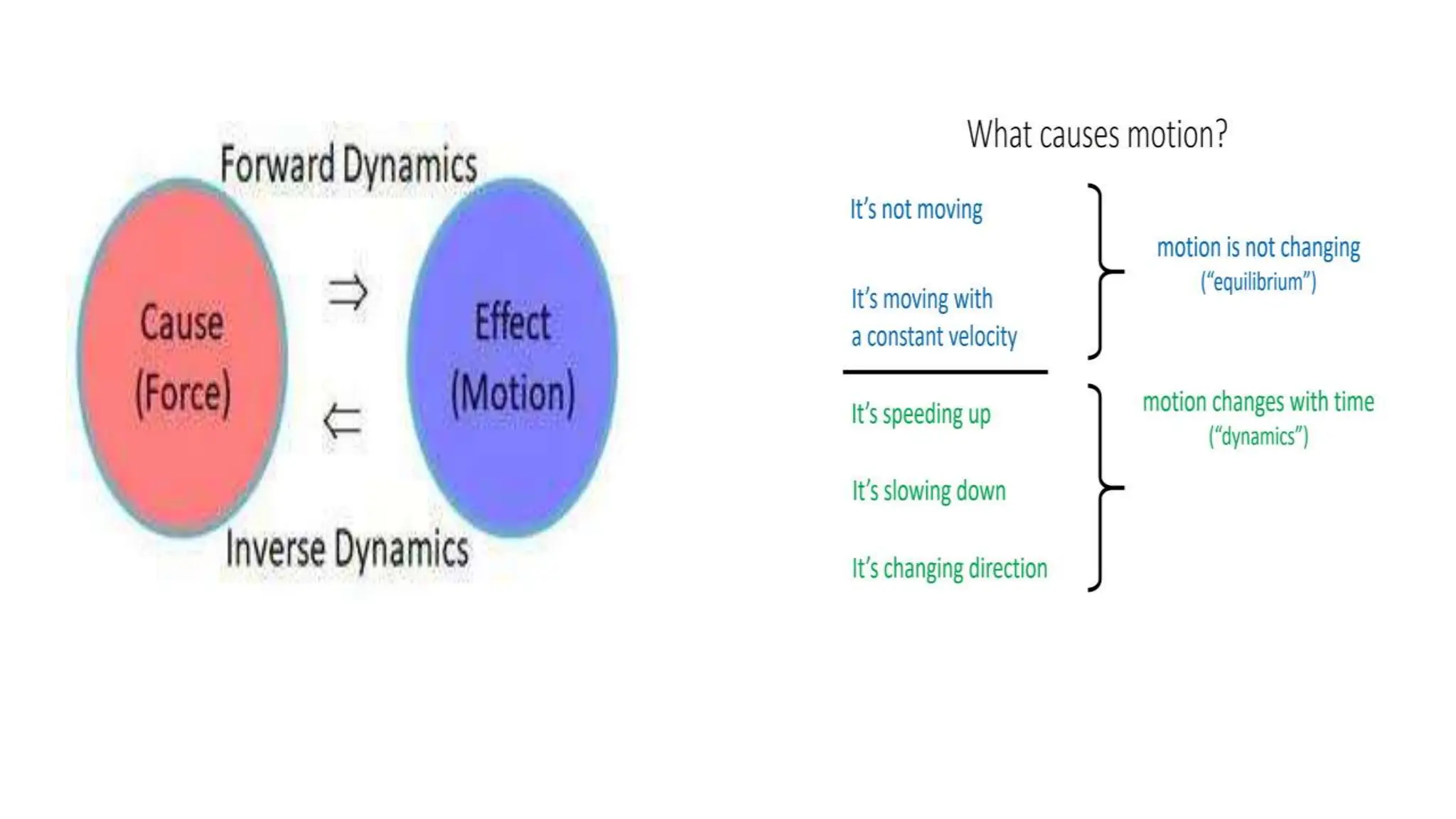
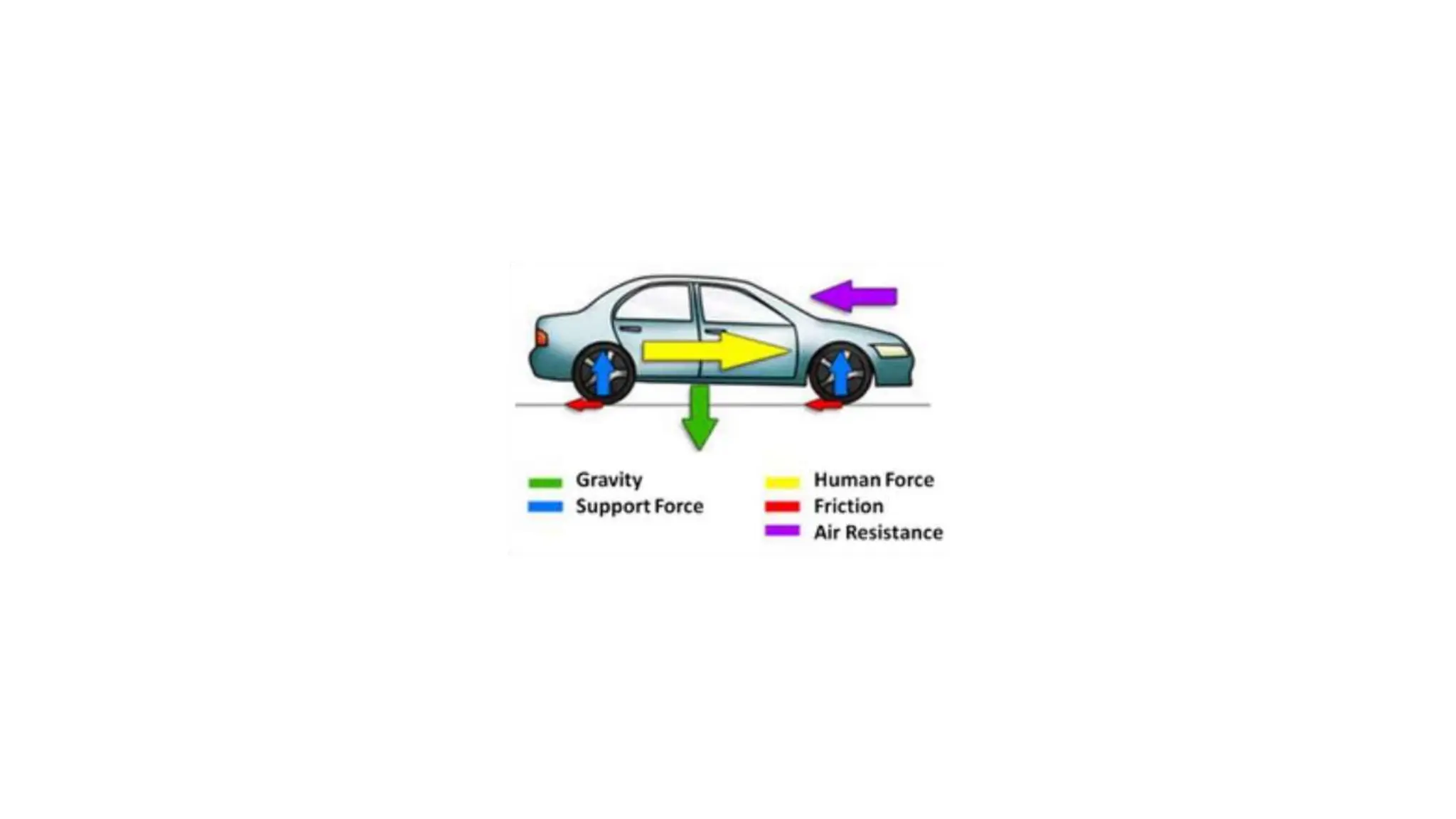
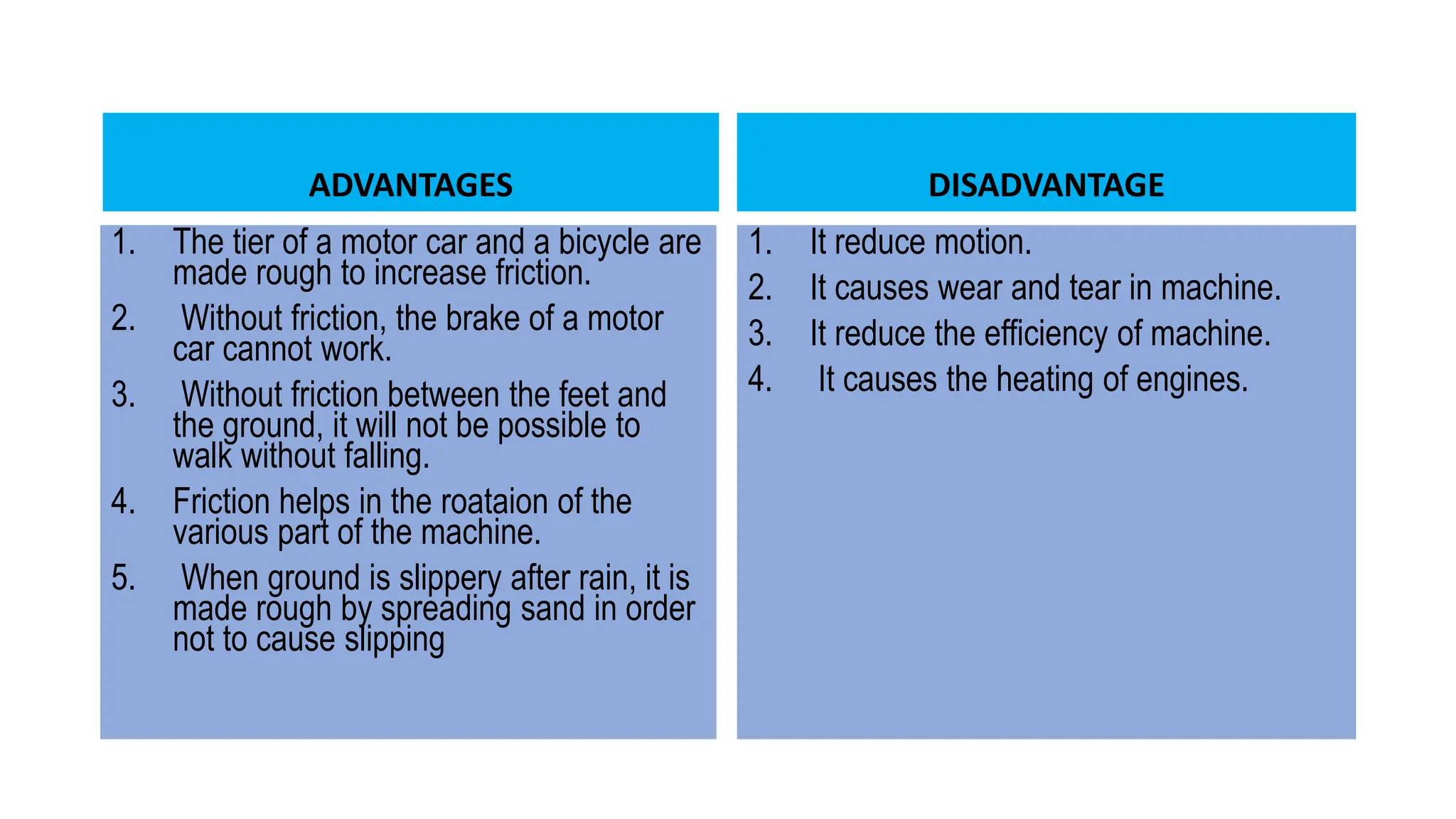
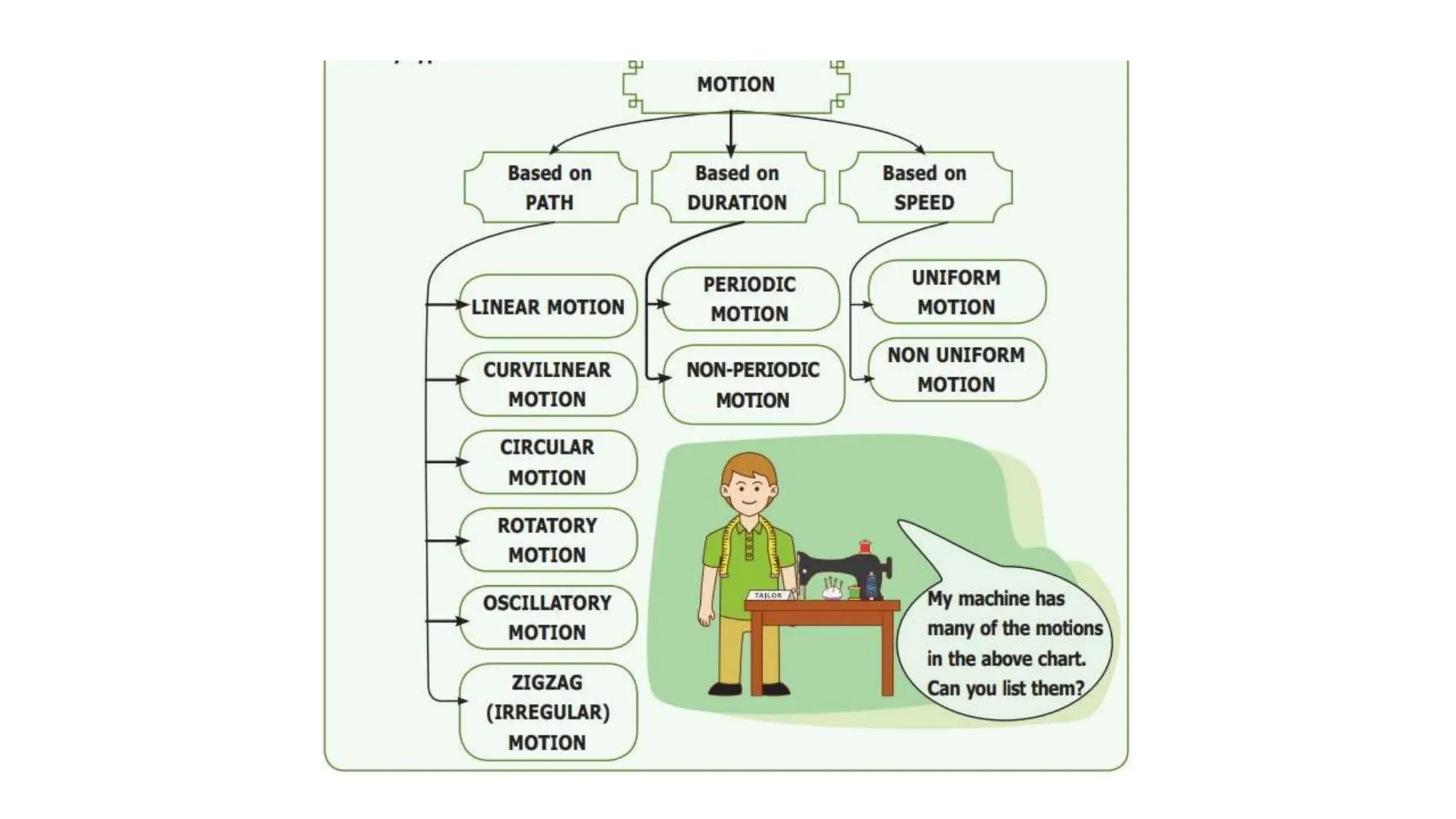
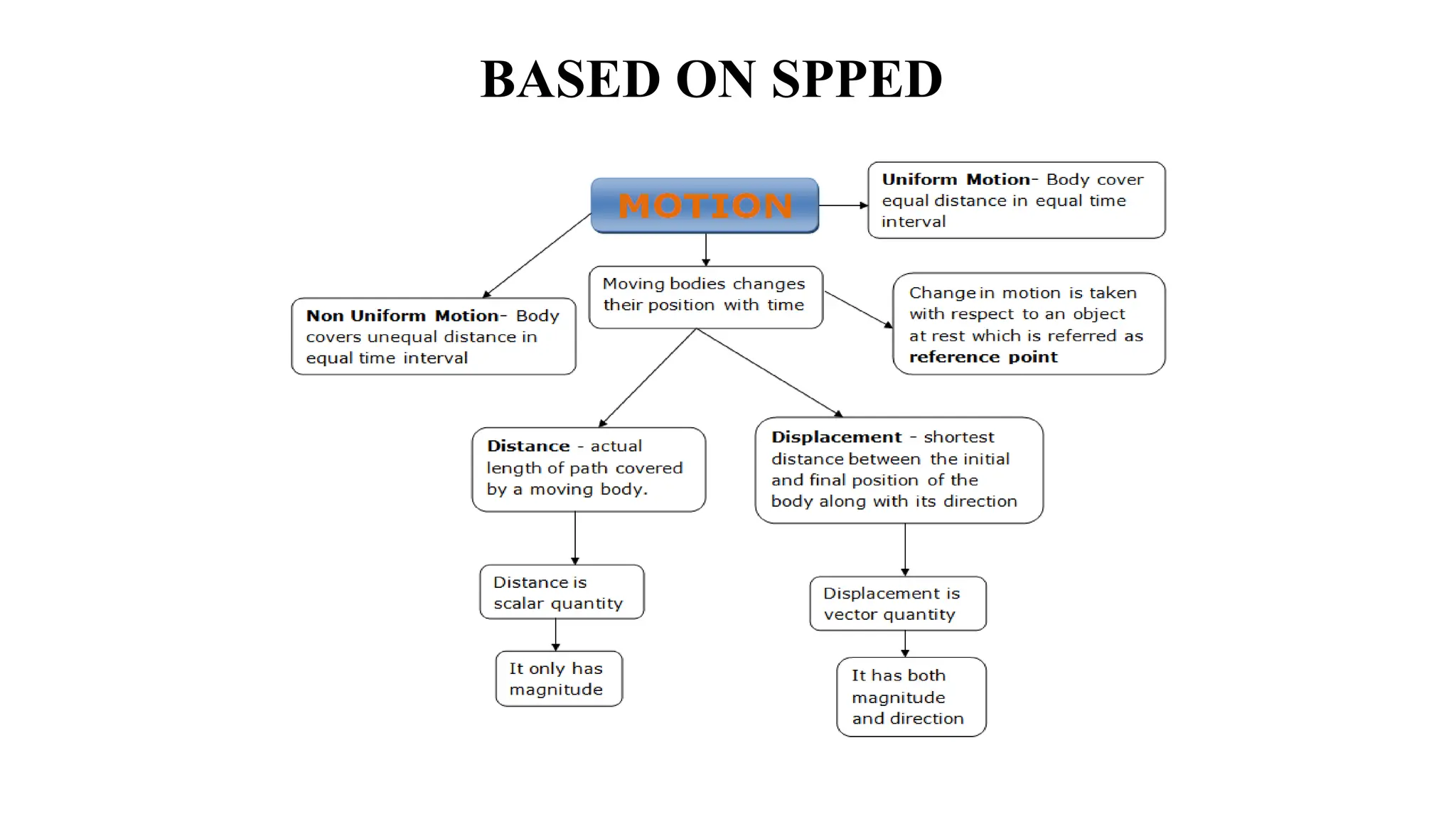
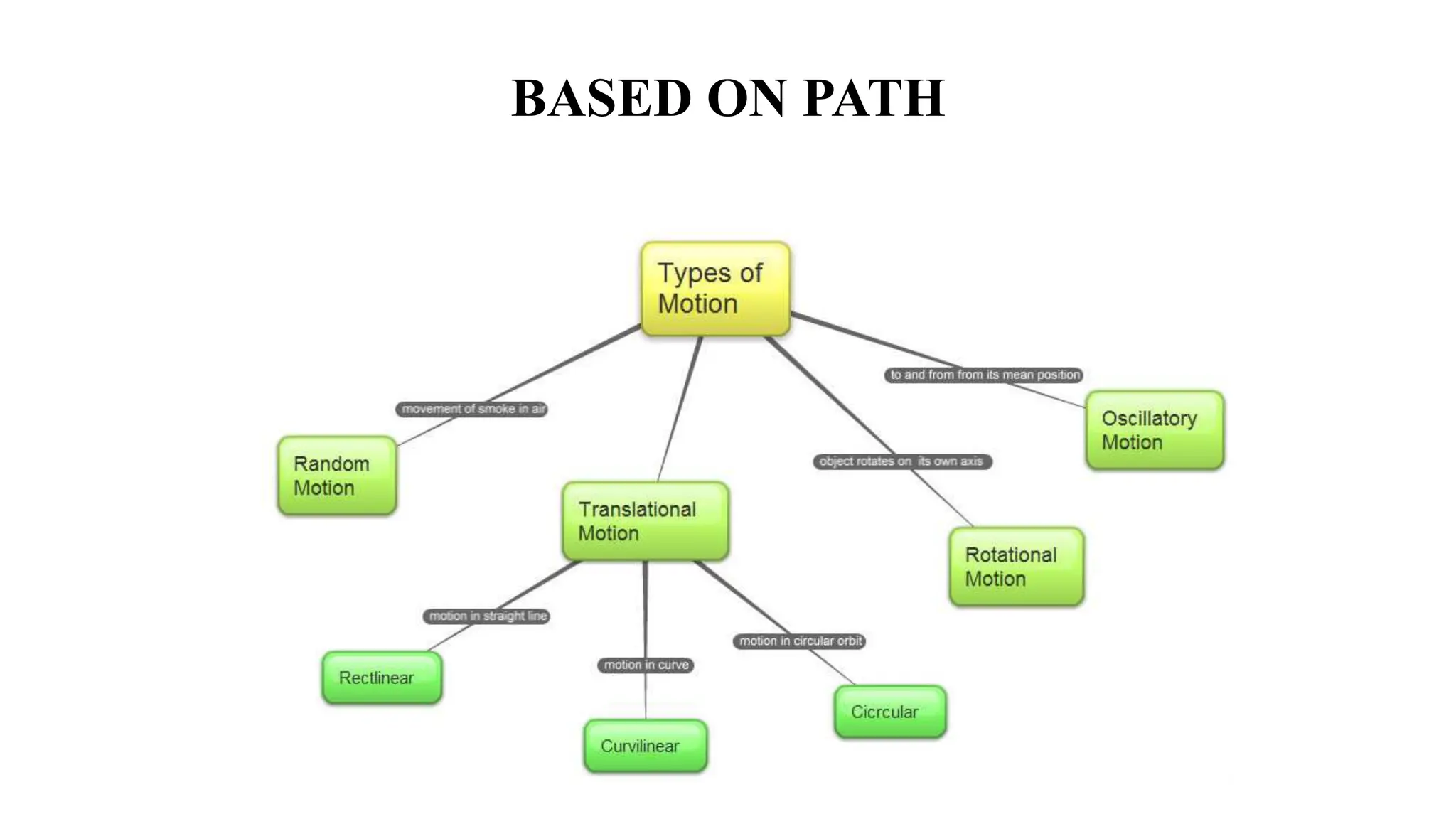
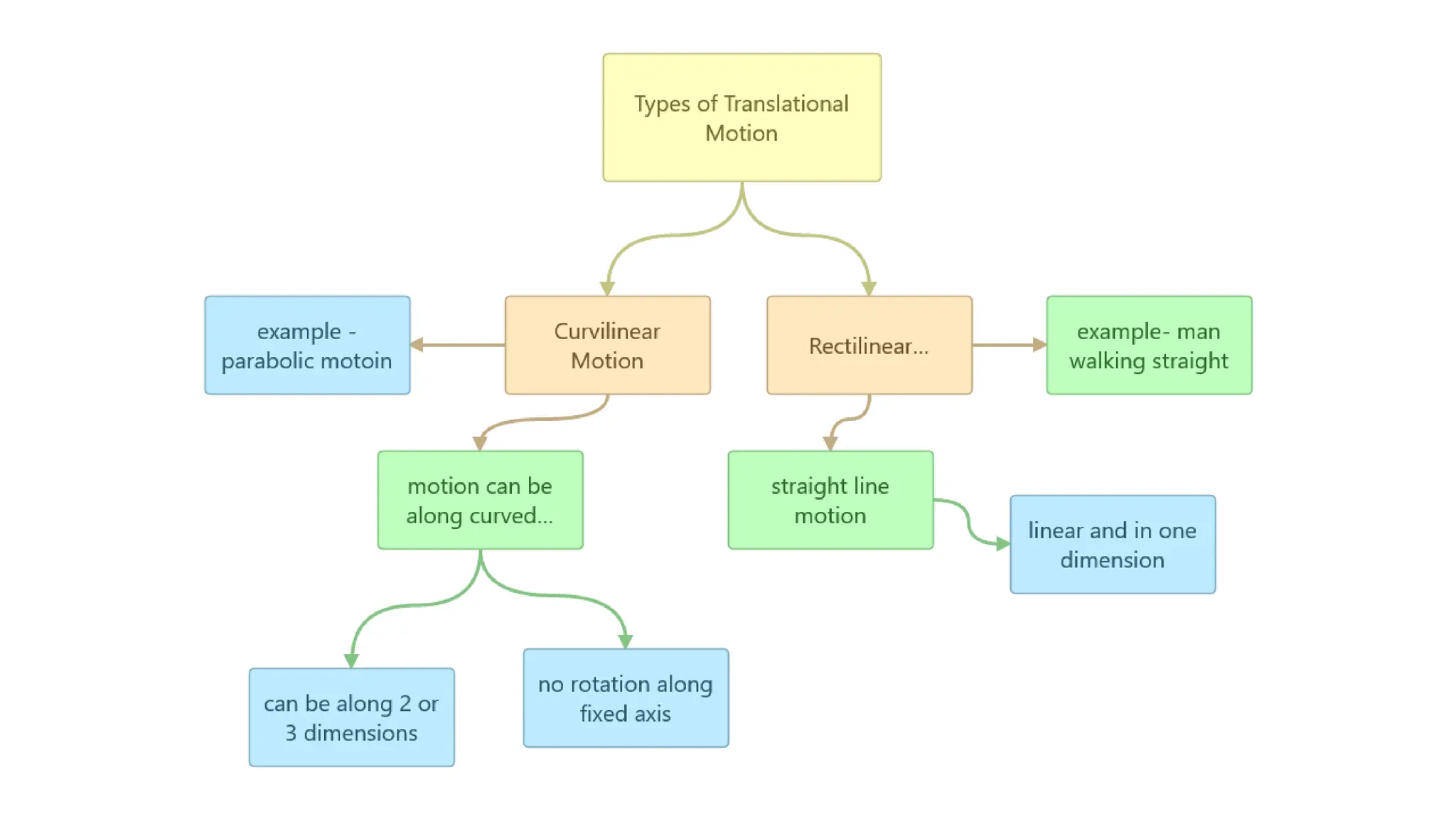
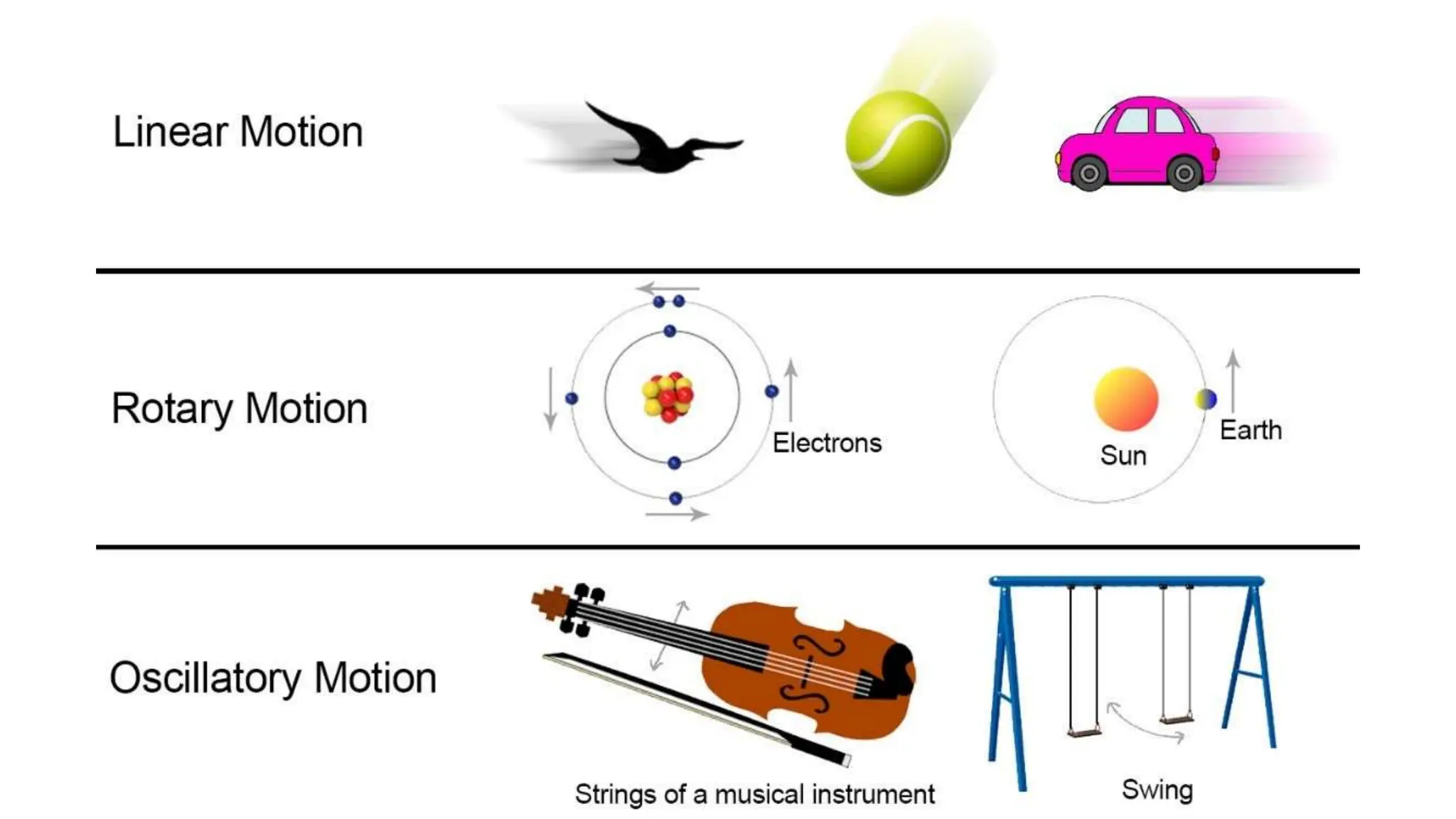
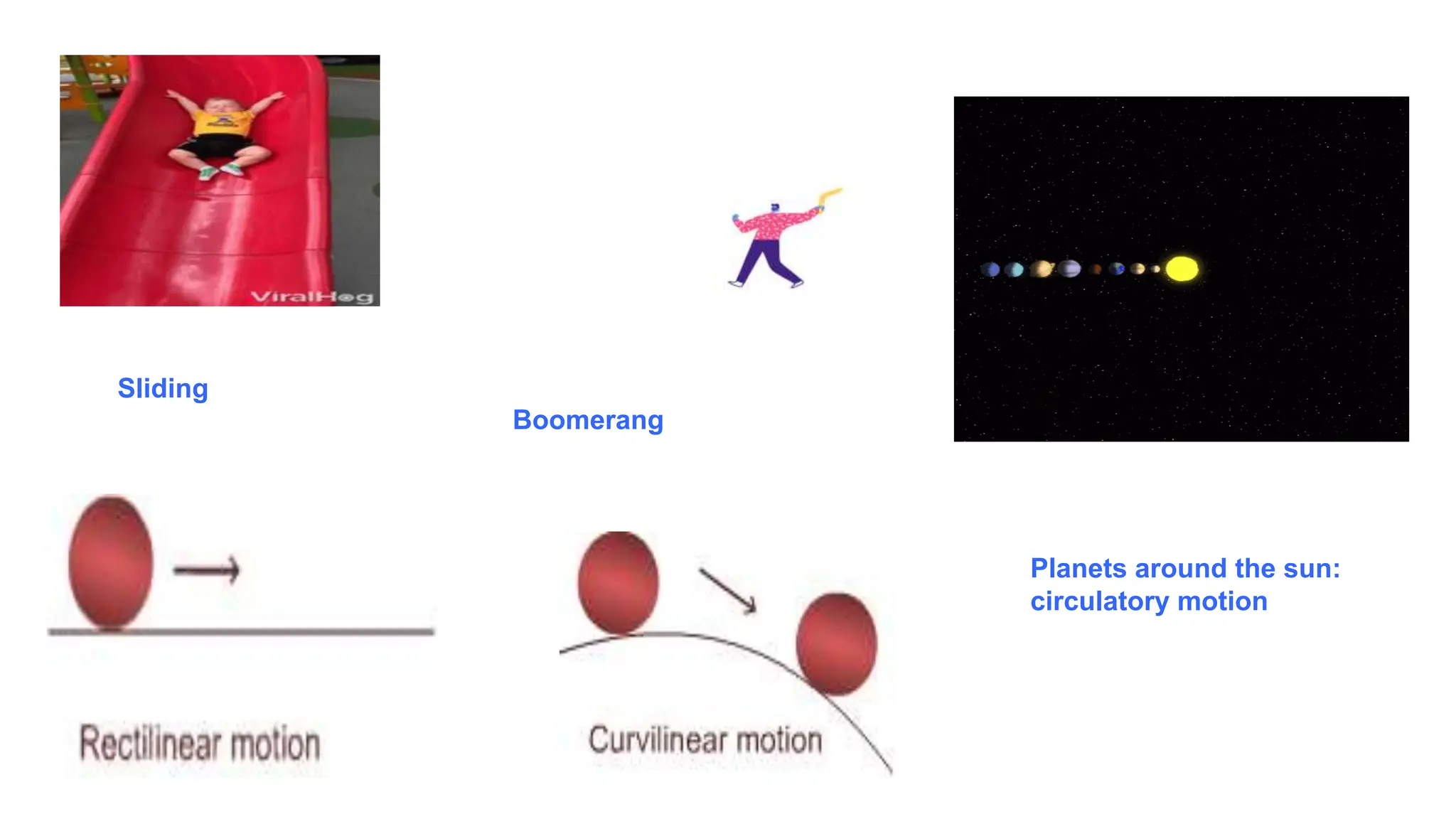
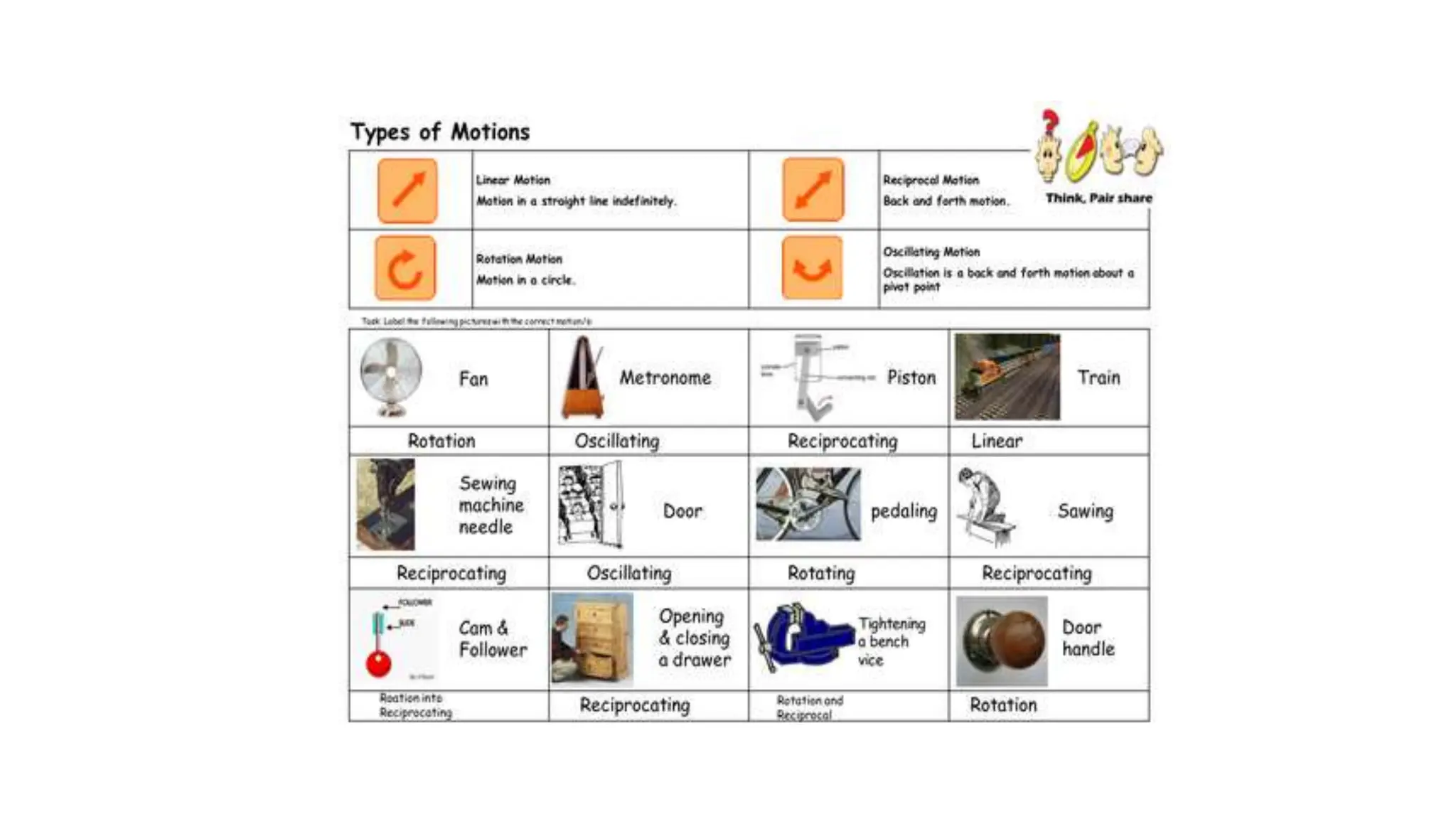
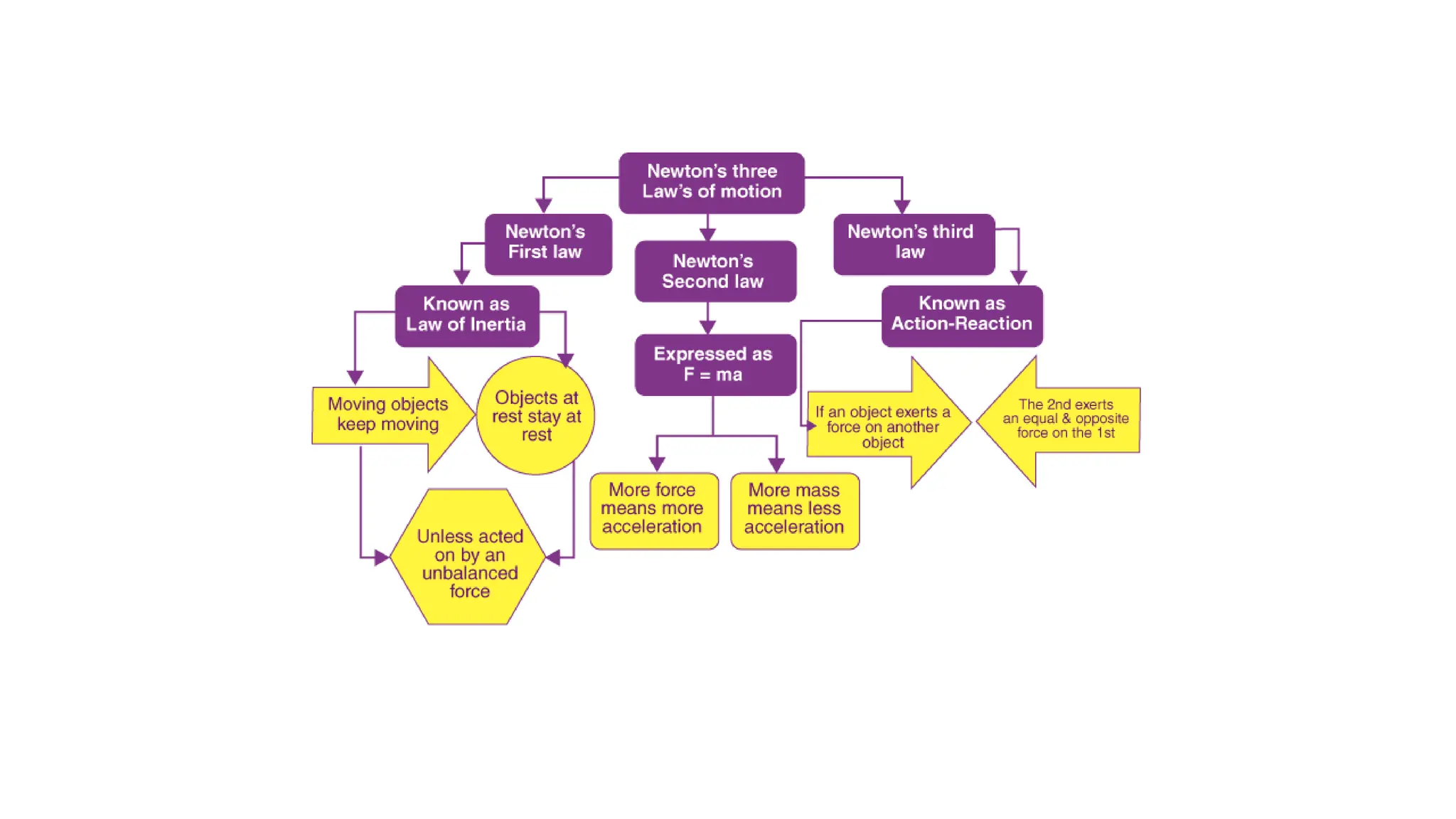
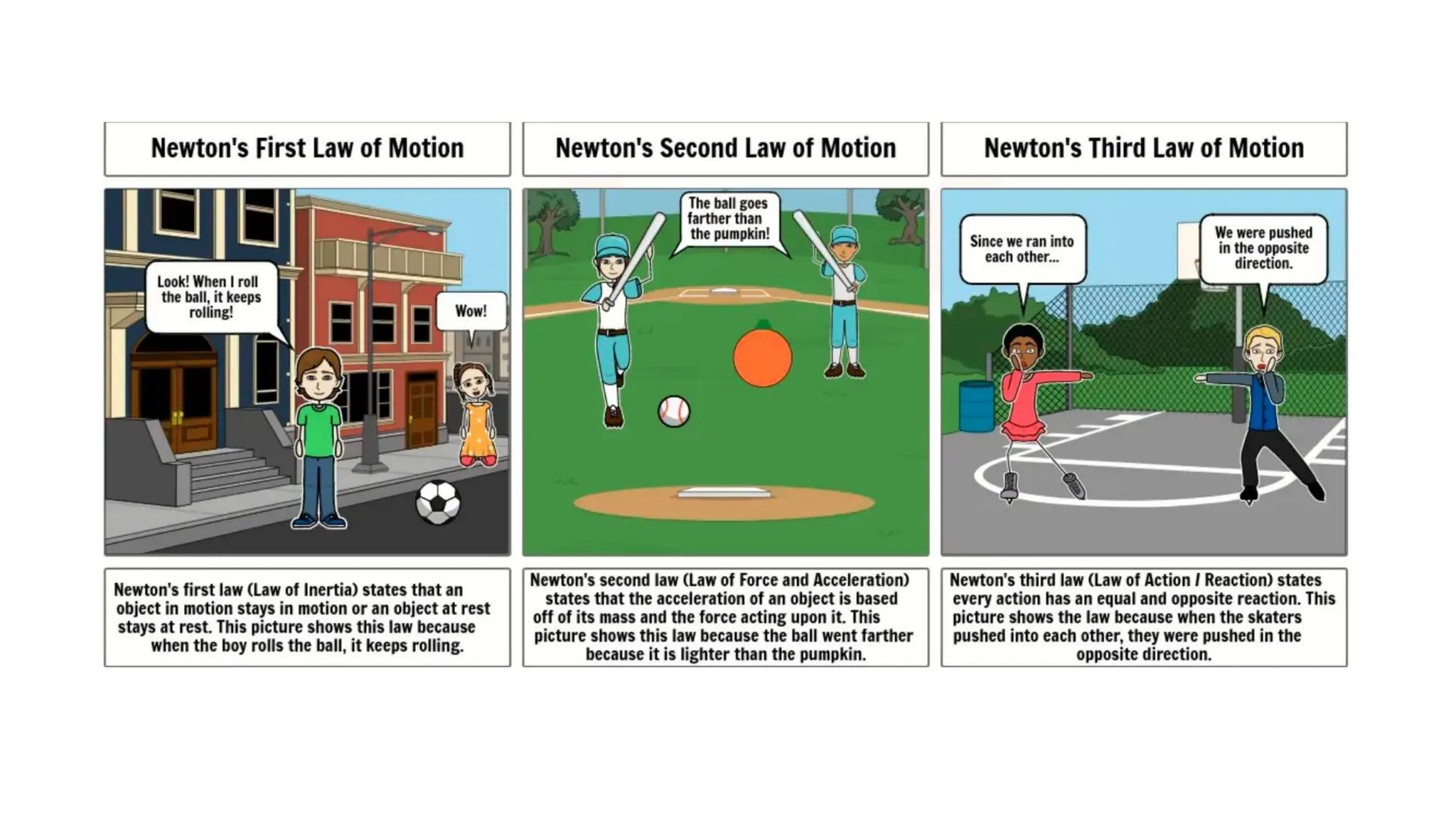
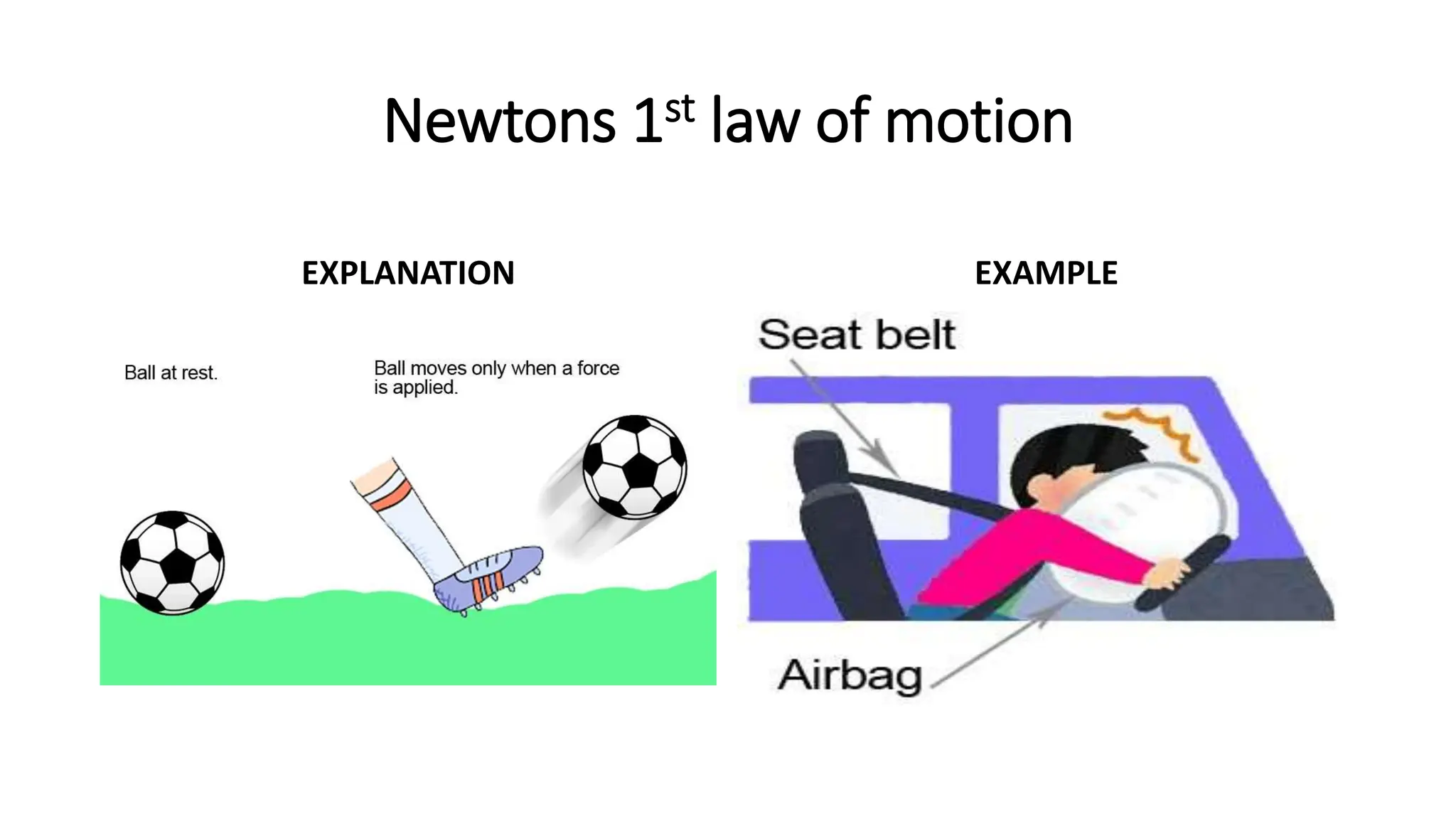
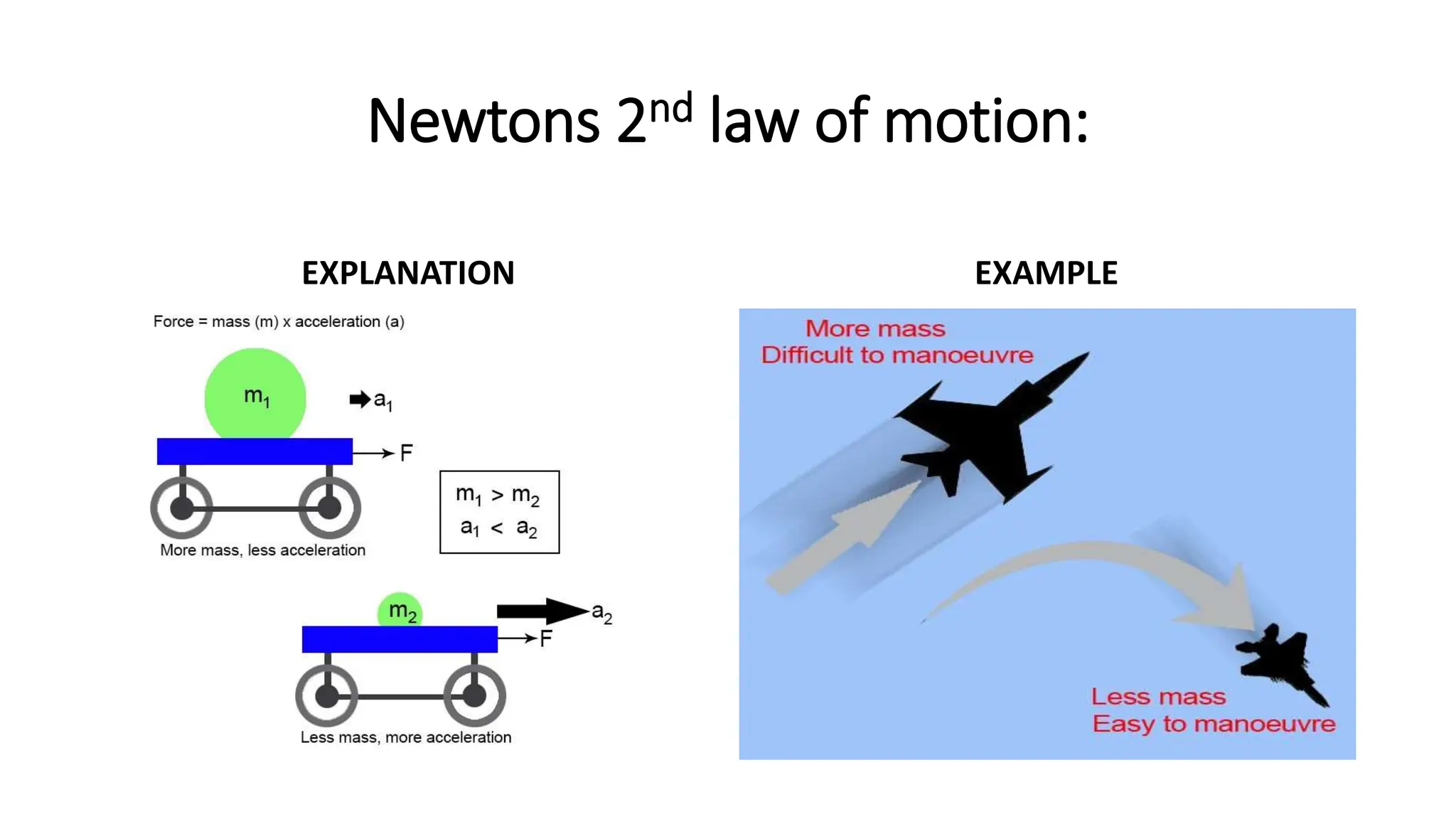
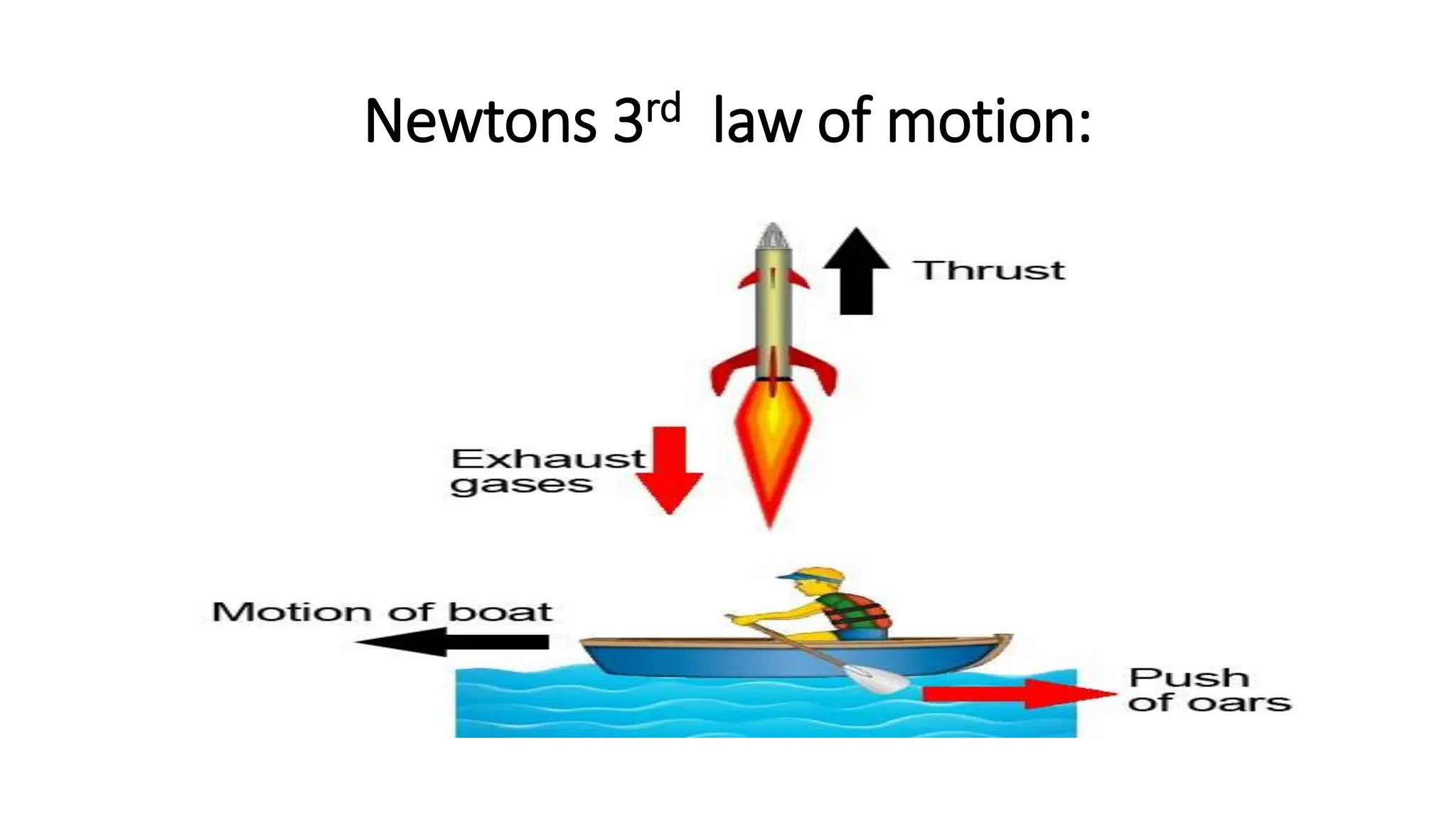
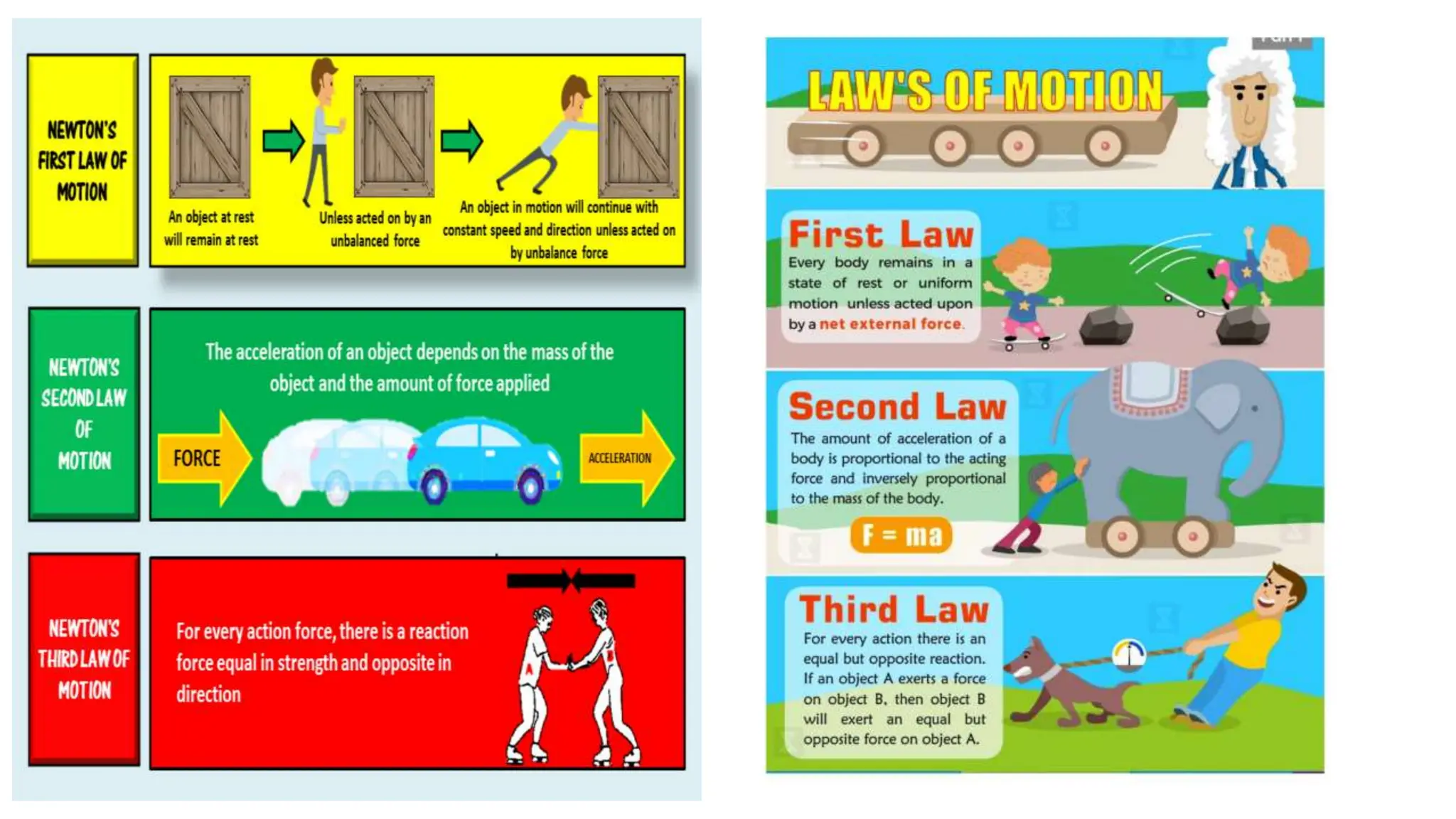
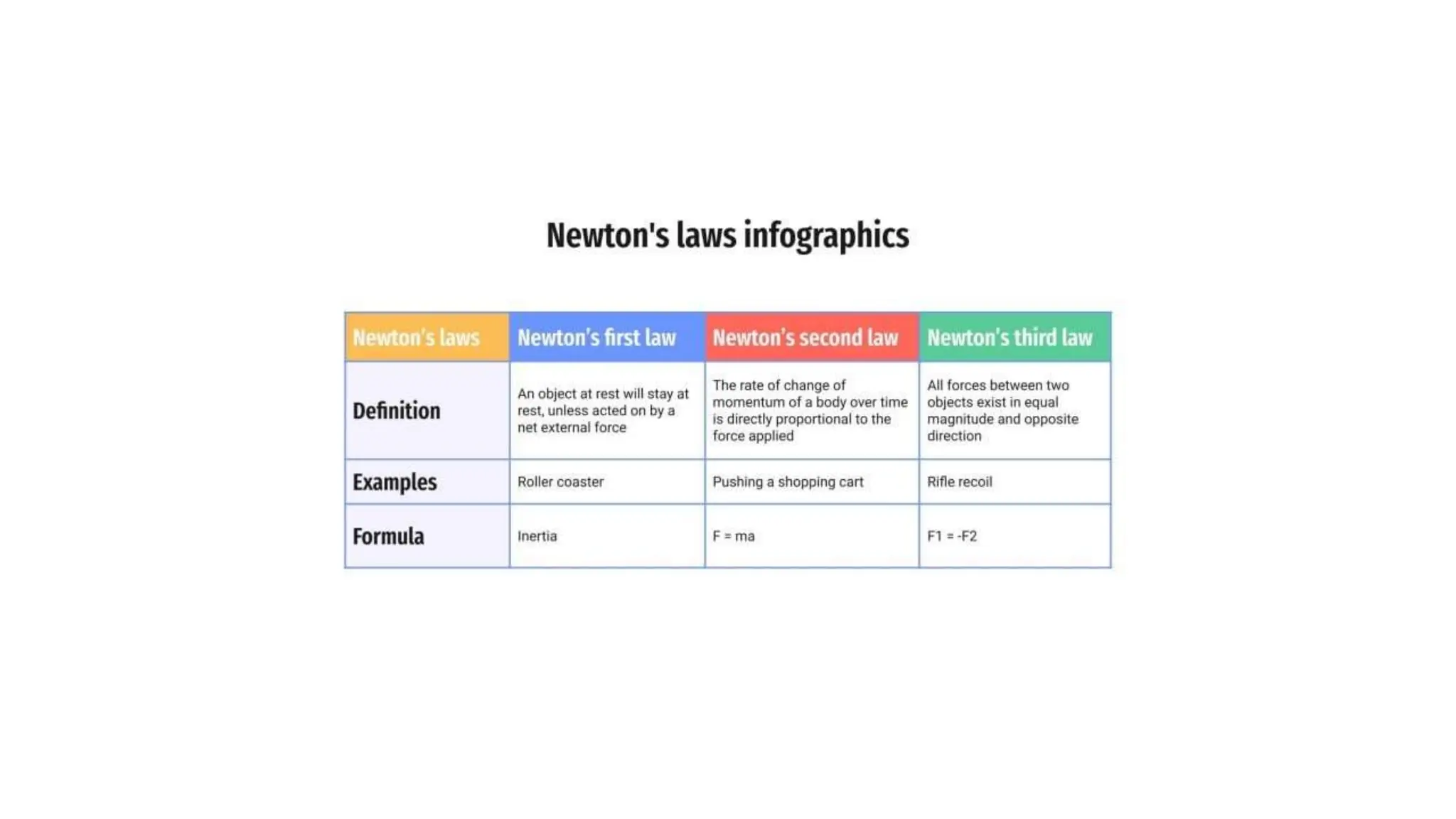
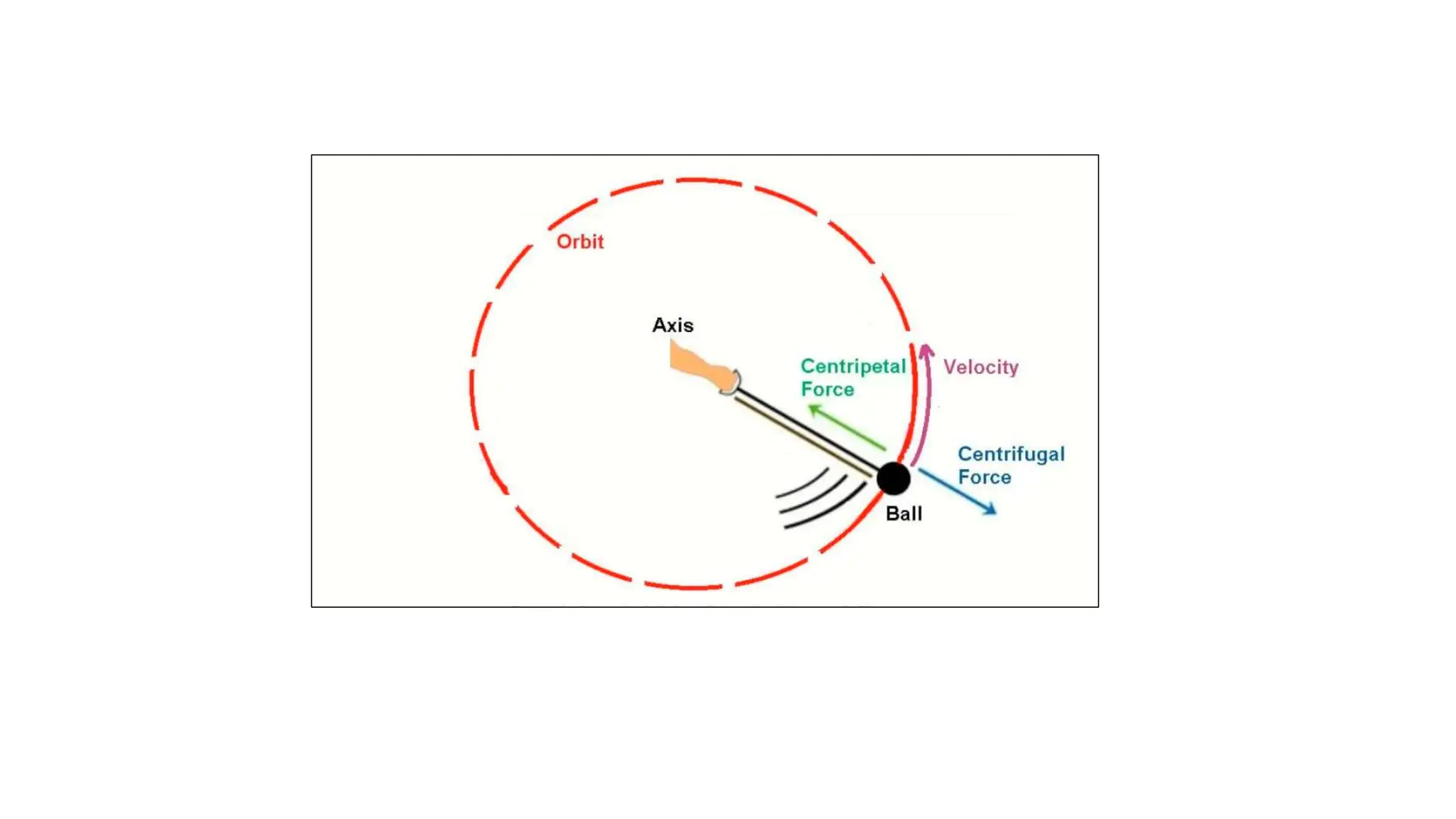
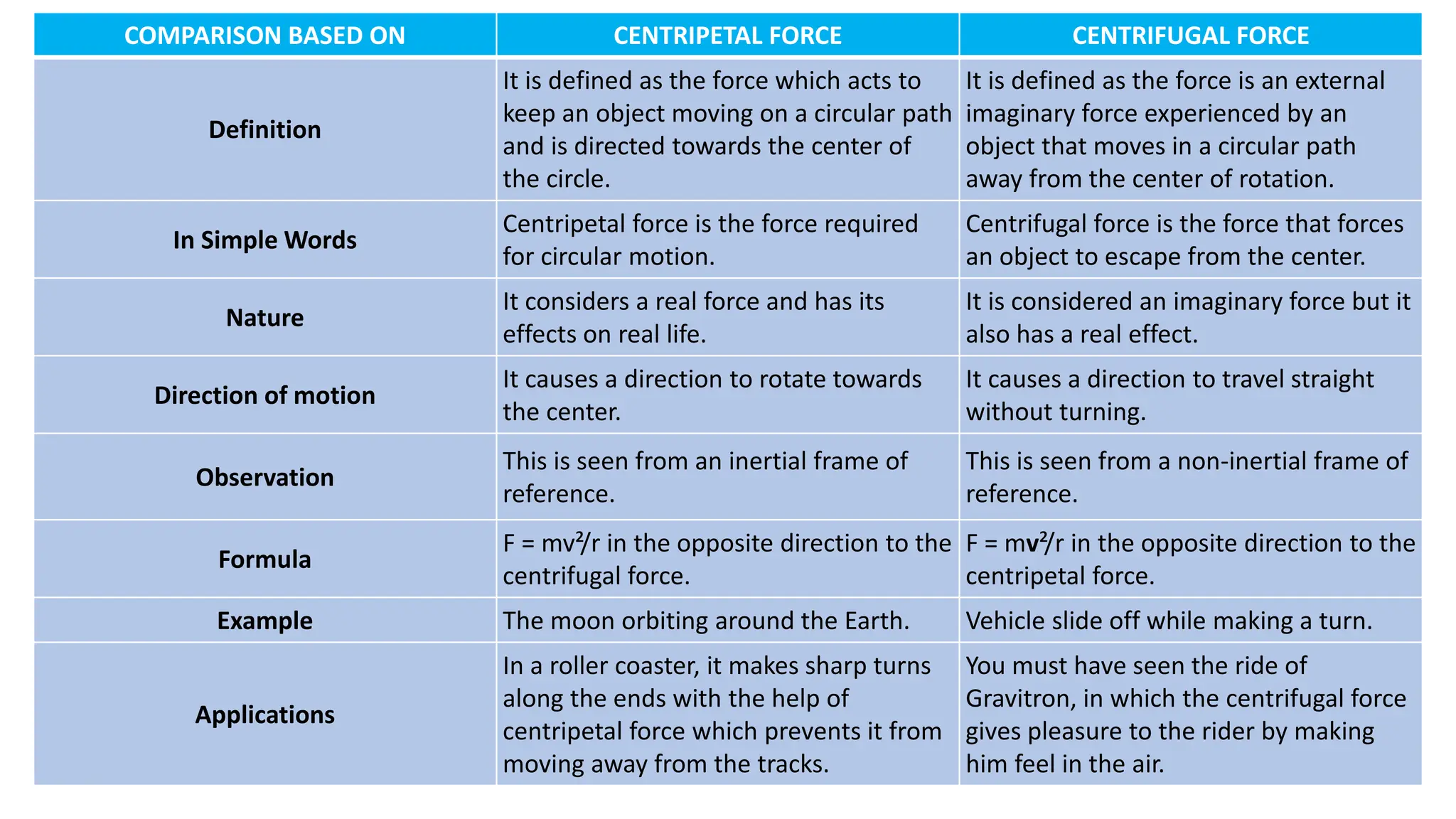
The document discusses the principles and laws of motion, including types of motion, causes of motion, and the importance of friction in various applications. It explains methods to reduce friction and outlines advantages and disadvantages associated with friction. Additionally, it covers Newton's laws of motion, differentiating between centripetal and centrifugal forces, with examples of each and their real-life applications.




![TYPE OF FORCE
.
FORCE
Contact Force
Like force [push
Unlike force
[pull]
Fractional
force.
Field Force
Magnet force
Gravitational
force
Electric force](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/principlesofmotion-231212043116-ed10be9a/75/PRINCIPLES-LAWS-OF-MOTION-with-its-types-examples-5-2048.jpg)