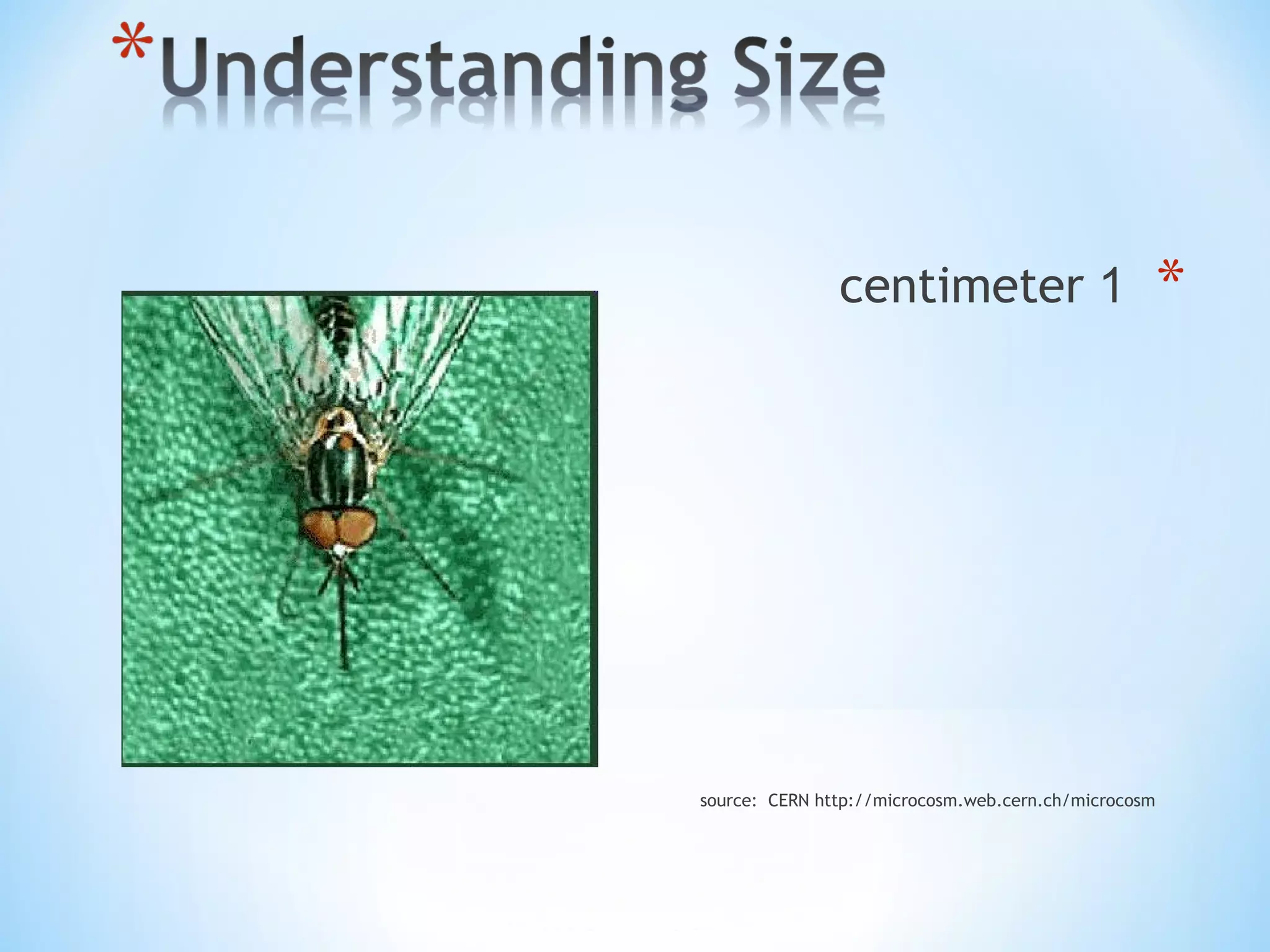
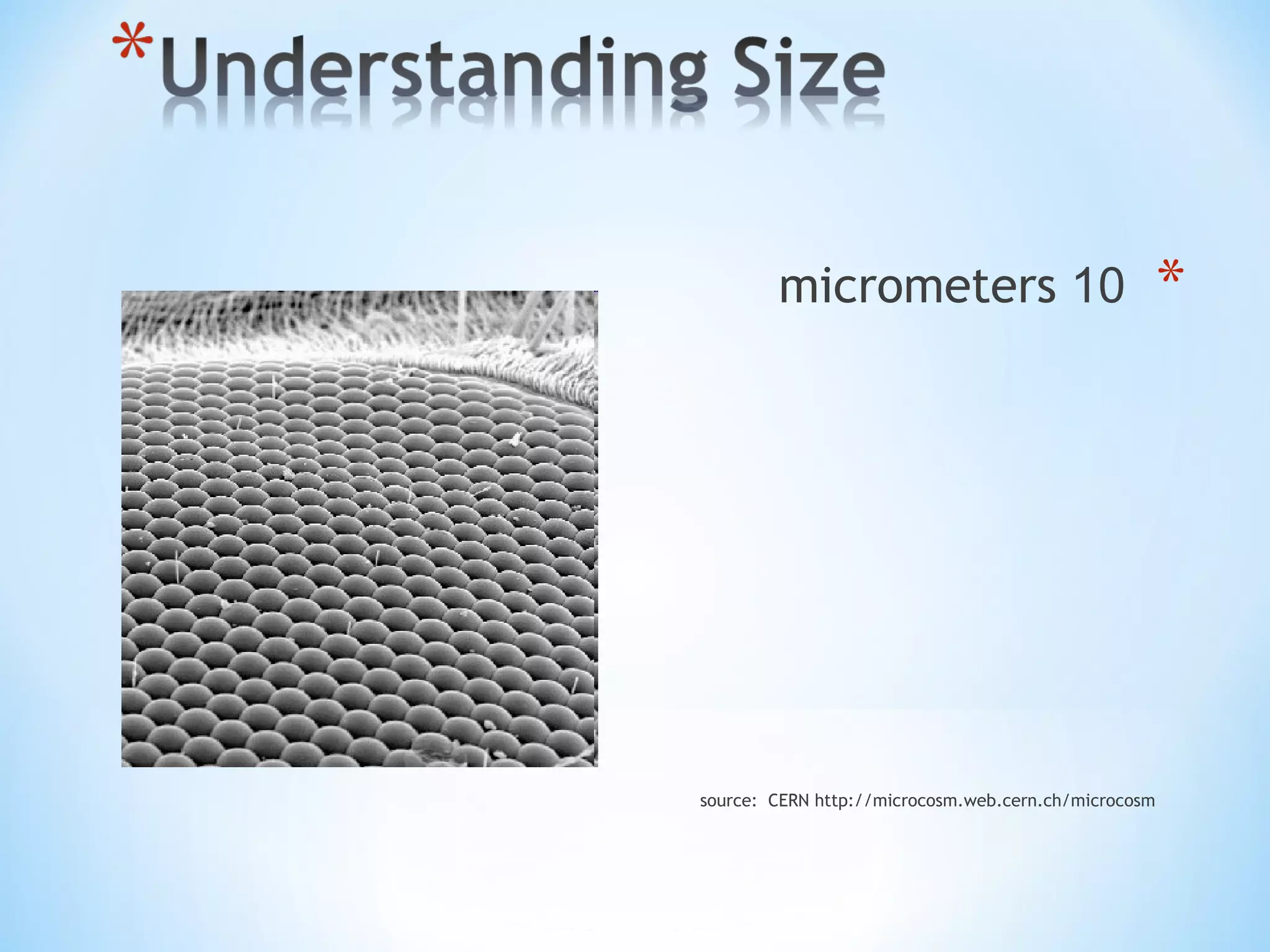
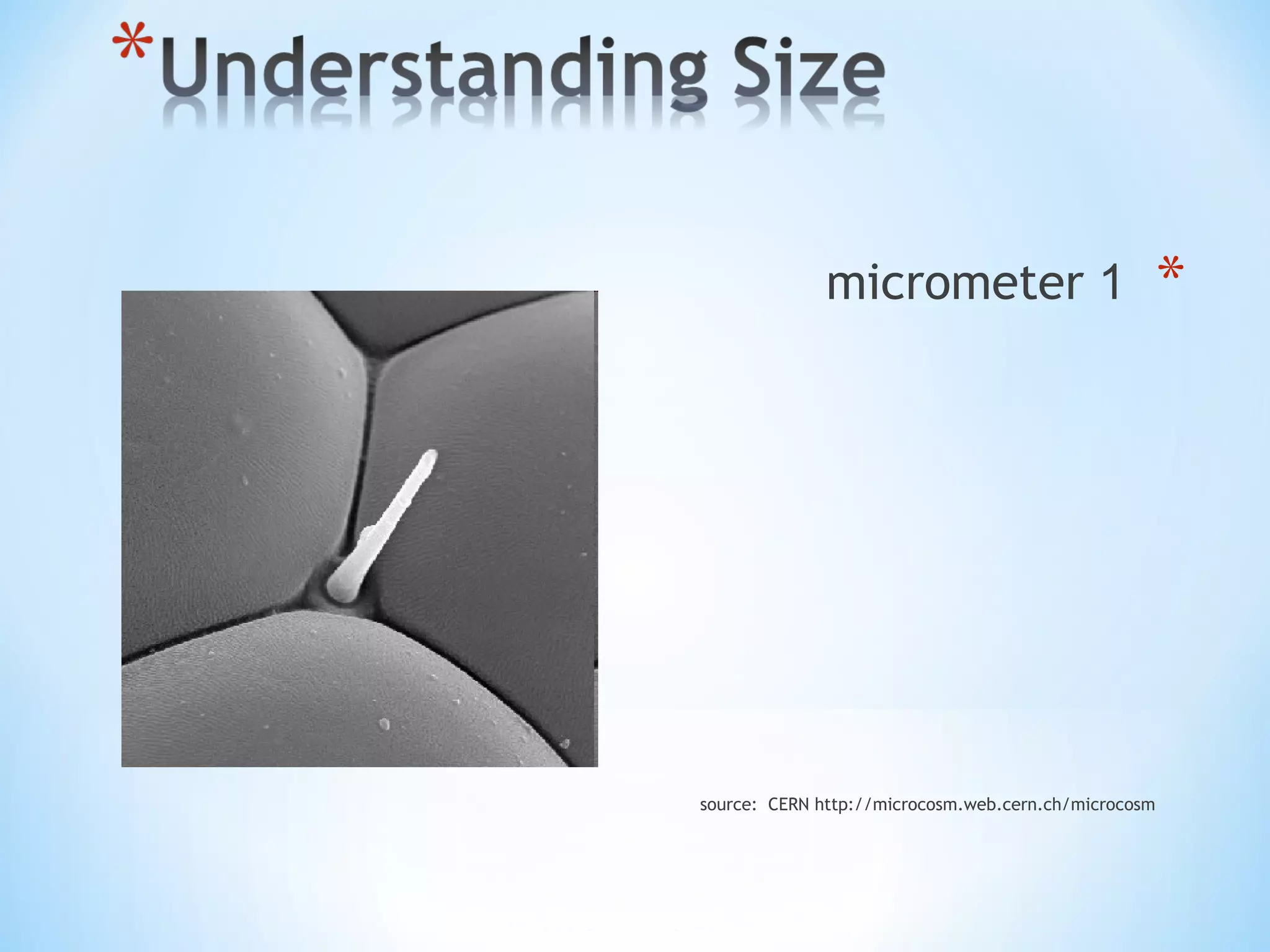
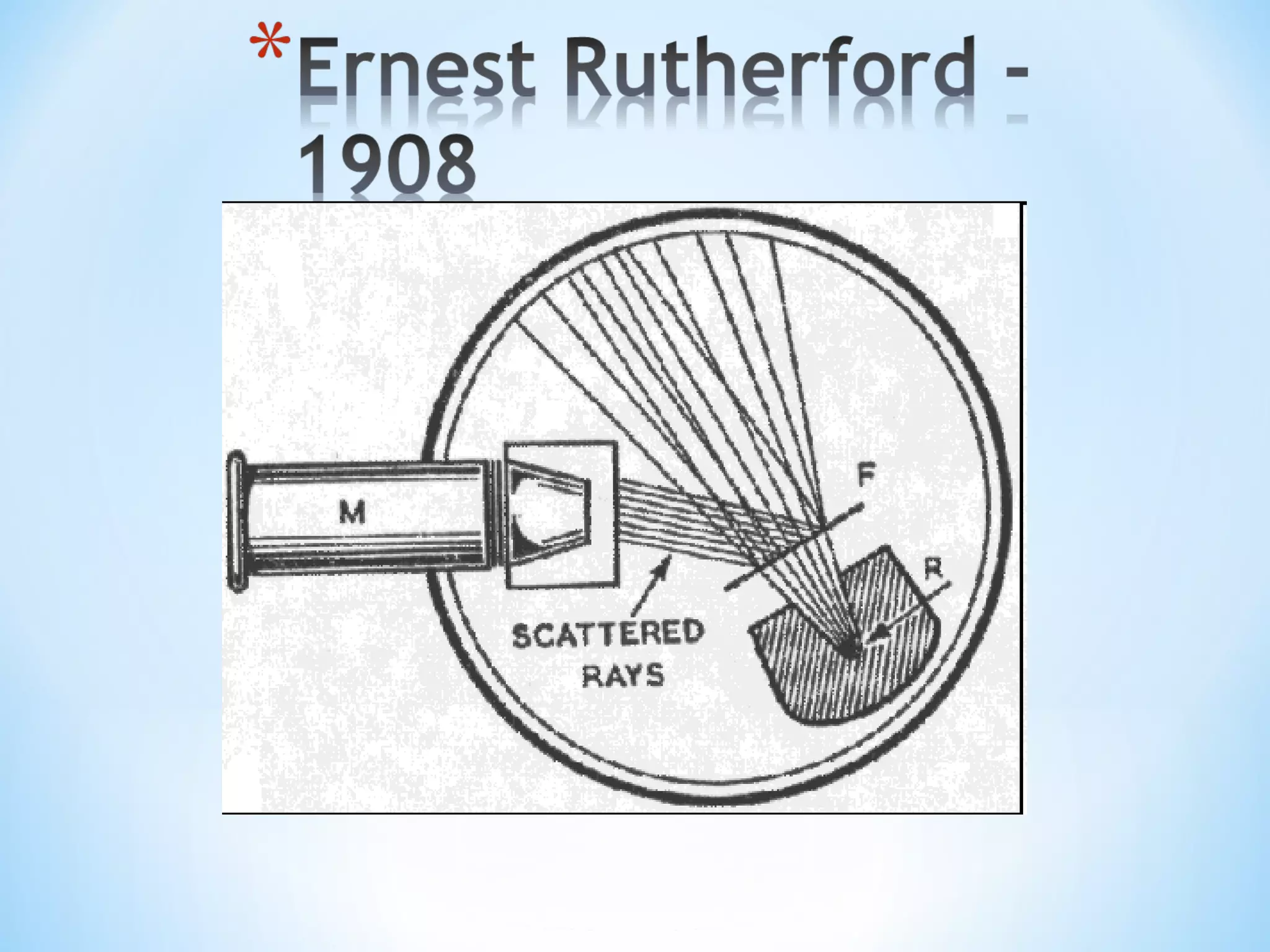
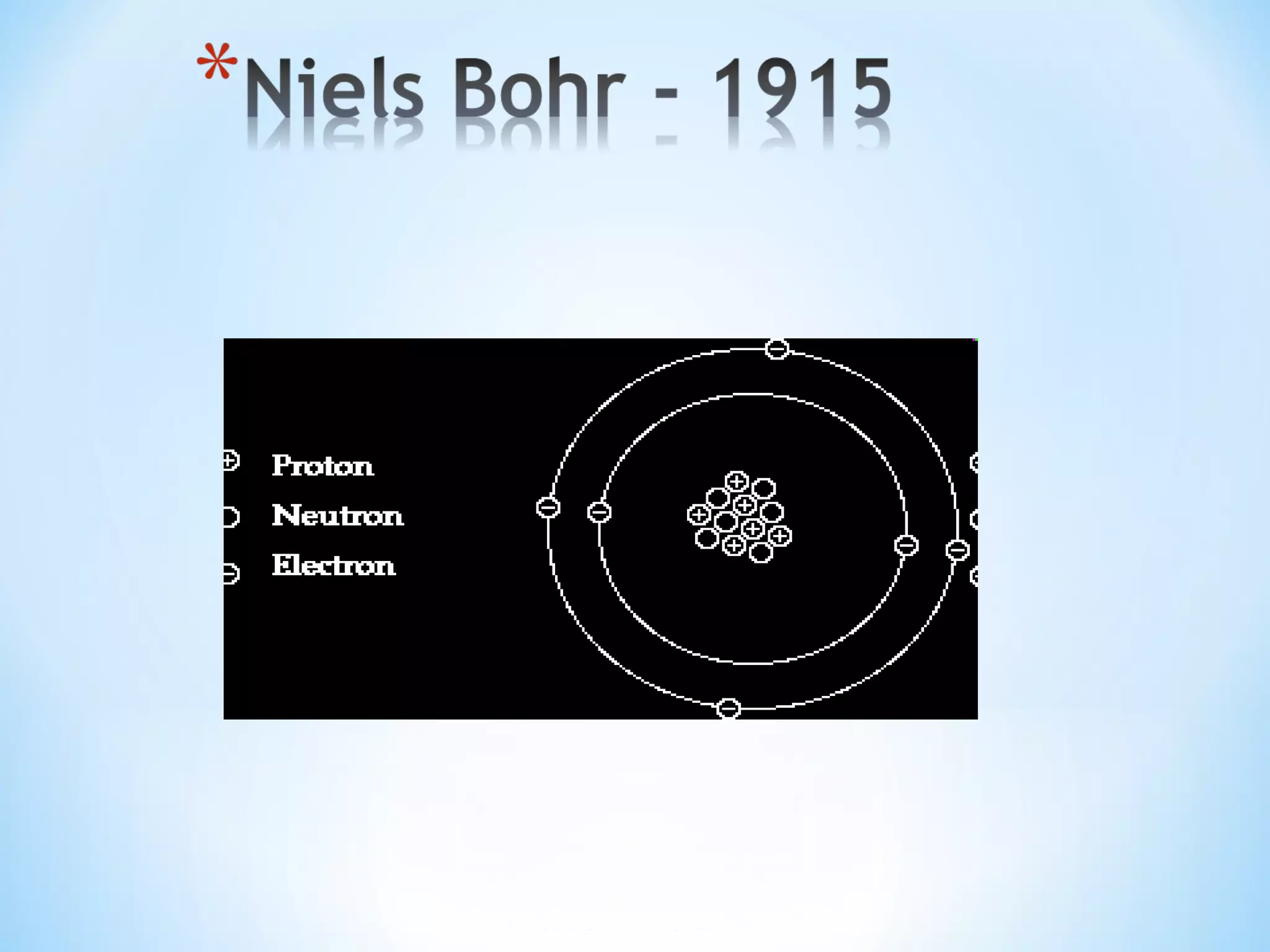
Nanotechnology involves science and engineering at the nanoscale of approximately 1 to 100 nanometers. It allows materials to be studied and manipulated at the atomic and molecular level. Common nanotechnology applications include making products stronger, lighter, and smarter through techniques like pyrolysis and attrition that break down materials into nanoparticles. Both advantages like increased performance and disadvantages like high costs and potential health risks exist for nanotechnology.